Abstract
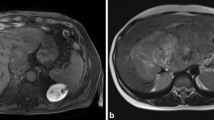
Recently, the caudate lobe has seemed to be the final target for aggresive cancer surgery of the liver. This lobe has five surfaces: the dorsal, left and hilar-free surfaces and the right and ventral-border planes. Surgeons have divided the caudate lobe into three parts: Spiegel’s lobe, which is called the ‘caudate lobe and papillary process’ by anatomists, the caudate process, viewed as almost the same entity by anatomists, and the paracaval portion corresponding to the dorsally located parenchyma in front of the inferior vena cava. All three parts are supplied by primary branches originating from the left and right portal veins, including the hilar bifurcation area. The hilar bifurcation branch often (50%) supplies the paracaval portion and it sometimes (29%) extends its territory to Spiegel’s lobe. It was postulated by Couinaud that the paracaval portion or the S9 is not defined by its supplying portal vein branch but by its ‘dorsal location’ in the liver. Couinaud’s caudate lobe or dorsal-liver concept caused, and still now causes, great logical confusion for surgeons. We attempt here to describe the margins of the lobe, border branches of the portal vein, the left/ right territorial border of the portal vein or Cantlie’s line and other topics closely relating to the surgery within these contexts. Finally, the caudate lobe as a liver segment will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belghiti J, Guevara OA, Noun R, Saldinger PF, Kianmanesh R (2001) Liver hanging maneuver: a safe approch to right hepatectomy without liver mobilization. J Am Coll Surg 193, 109–11.
Cheng YF, Huang TL, Chen CL et al. (1997) Anatomic dissociation between the intrahepatic bile duct and portal vein. World J Surg 21, 297–300.
Cho A, Okazumi S, Takayama W et al. (2000) Anatomy of the right anterosuperior area (segment 8) of the liver: Evaluation with helical CT during arterial portography. Radiology 214, 491–5.
Couinaud C (1989) Surgical Anatomy of the Liver Revisited. Couinaud, Paris.
Couinaud C (1994) The paracaval segments of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2, 145–51.
Elias D, Lasser PH, Desruennes E, Mankarios H, Jiang Y (1992) Surgical approach to segment 1 for malignat tumors of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 175, 17–24.
Gadziev EM, Ravnik D, Stanisavljevic D, Trotovsek B (1997) Venous drainage of the dorsal sector of the liver: differences between segments I and IX. Surg Radiol Anat 19, 79–83.
Hata F, Murakami G, Hirata K, Kitagawa S, Mukaiya M (1999b) Configuration of hepatic veins in the right surgical lobe of the human liver with special reference to their complementary territorial relationships: morphometrical analysis of controlled specimens with clearly defined portal segmentation. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 76, 1–16.
Hata F, Murakami G, Mukaiya M, Hirata K (1999a) Identification of segments VI and VII of the liver based on the ramification patterns of the intrahepatic portal and hepatic veins. Clin Anat 12, 229–44.
Heloury Y, Leborgne J, Rogez JM, Robert R, Barbin JY, Hureau J (1988) The caudate lobe of the liver. Surg Radiol Anat 10, 83–91.
Hirai I, Kimura W, Murakami G, Suto K, Fuse A (2003) Surgical anatomy of the inferior vena cava ligament. Hepato gastroenterology 49, 355–62.
Hirai I, Murakami G, Kimura W, Kanamura T, Sato I (2002) Anatomical consideration of a reliable approach to the caudate lobe using the hanging maneuver without mobilization of the liver with special reference to its application to prepare an extended left liver graft in living-related transplantation. Clin Anat 15, 389–401.
Inoue T, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K, Sakai K, Uozumi A (1986) Ramification of the intrahepatic portal vein identified by percutaneous transhepatic portography. World J Surg 10, 287–93.
Ishibashi Y, Sato TJ, Hirai I, Murakami G, Hata F, Hirata K (2001) Ramification pattern and topographical relationship between the portal and hepatic veins in the left anatomical lobe of the human liver. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 78, 75–82.
Ishiyama S, Fuse A, Kuzu H, Kawaguchi K, Tsukamoto M (1997) Rational resection of the right dorsal liver for hepatic hilar bile duct carcinoma. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg 30, 2253–6.
(In Japanese with English abstract.) Ishiyama S, Yamada Y, Narishima Y, Yamaki T, Kunii Y, Yamauchi H (1999) Surgical anatomy of the hilar bile duct. Bil Tract Panc 20, 811–20. (In Japanese.)
Ishiyama S, Yamauchi H (2000) Anatomy of the caudate lobe using corrosion liver casts. Geka 62, 426–33. (In Japanese.)
Ito H (1988) Anatomy of the daughter bronchus and its clinical relevance. Kikanshi-Gaku 9, 312–23. (In Japanese.)
Kamiya J, Nimura Y, Hayakawa N, Kondo S, Nagino M, Kanai M (1994) Preoperative cholangiography of the caudate lobe: surgical anatomy and staging for biliary carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 4, 385–9.
Kanamura T, Murakami G, Hirai I et al. (2001) High dorsal drainage routes of Spiegel’s lobe: venous plexus at the upper terminal of the ligamentum venosum and non-typical but thick caudate vein emptying into the terminal portions of the major hepatic veins. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 8, 549–56.
Kanamura T, Murakami G, Ko S et al. (2003) Evaluation of the hilar bifurcation territory in the human liver caudate lobe provides critical informations to design reliable margins for various caudate lobe surgery: an anatomical study using livers with or without the external caudate notch. World J Surg 26, 222–28.
Kawarada Y, Isaji S, Taoka H, Tabata M, Das BC, Yokoi H (1999) S4a + S5 with caudate lobe (S1) resection using the Taj Mahal liver parenchymal resection for carcinoma of the biliary tract. J Gastrointest Surg 3, 369–73.
Kitagawa S, Murakami G, Hata F, Hirata K (2000) Configuration of the right portion of the caudate lobe with special reference to the identification of its right margin. Clin Anat 13, 321–40.
Kogure K, Kuwano H, Fujimaki N, Makuuchi M (2000) Relation among portal segmentation, proper hepatic vein, and external notch of the caudate lobe in the human liver. Ann Surg 231, 223–8.
Koshino T, Murakami G, Sato TJ et al. (2002) Configurations of the segmental and subsegmental bronchi and arteries in the right upper lobe of the human lung with special reference to their concomitant relations and double subsegmental supply. Anat Sci Int 77, 56–65.
Kumon M (1985) Anatomy of the caudate lobe with special reference to the portal vein and bile duct. Kanzo 26, 1193–9. (In Japanese.)
Kumon M, Araki K, Ogata T et al. (1984) Vascular cast of the liver and its observation in view of liver surgery: Ramification patterns of the segmental portal vein in the right ventral segment (S5 + S8). Kan-Tan-Sui 8, 265–70. (In Japanese.)
Kumon M, Matushima M, Matubara T et al. (1989) Anatomy of the porta hepatis and caudate lobe using vascular cast of the liver. Tan-to-Sui 10, 1417–22. (In Japanese.)
Kwon DH, Murakami G, Wang HJ, Chung MS, Hata F, Hirata K (2001) Ventral margin of the paracaval portion of the human caudate lobe. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 8, 148–53.
Kwon DH, Murakami G, Wang HJ, Chung MS, Hata F, Hirata K (2002) Configuration along the ventral margin of the paracaval portion of the human caudate lobe. Clin Anat 15, 325–36.
Makuuchi M, Hasegawa H, Yamasaki S (1984) Significace of division of the vena cava ligament for extrahepatic dissection of the right hepatic vein. Nihon Rinsho Geka Gattskai-Shi 45, 1041–5. (In Japanese.)
Makuuchi M, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki S, Takayasu K (1987) Four new hepatectomy procedures for resection of the right hepatic vein and preservation of the inferior right hepatic vein. Surg Gynecol Obstet 164, 69–72.
Masselot R, Leborgne J (1978) Anatomical study of the hepatic veins. Anat Clin 1, 109–25.
Miyagawa S, Hashikura Y, Miwa S et al. (1998) Concomitant caudate lobe resection as option for donor hepatectomy in adult living related liver transplantation. Transplant 15, 661–3.
Miyazaki M, Ito H, Nakagawa K et al. (1998) Aggressive surgical approaches to hilar cholangiocarcinoma: Hepatic or local resection? Surgery 123, 131–6.
Mizumoto R, Suzuki H (1988) Surgical anatomy of the hepatic hilum with special reference to the caudate lobe. World J Surg 12, 2–10.
Nagaoka Y, Miyamoto S, Murakami G, Hata F, Hirata K (2001) Configuration of the liver segment observed in the frontal section including the origin of the left portal trunk at the hepatic hilum. Acta Anat Nippon 76, 223–32. (In Japanese with English abstract.)
Nagino M, Kamiya J, Kanai M et al. (2000) Right trisegment portal vein embolization for biliary tract carcinoma: Technique and clinical utility. Surgery 127, 155–60.
Nagino M, Nimura Y, Kamiya J et al.(1998) Segmental liver resections for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Hepato-Gastroenterology 45, 7–13.
Nakamura S, Tsuzuki T (1981) Surgical anatomy of the hepatic veins and the inferior vena cava. Surg Gynecol Obstet 152, 43–50.
Nimura Y, Kamiya J, Nagino M et al. (1998) Aggressive surgical treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 5, 52–61.
Onishi H, Kawarada Y, Das BC et al. (2000) Surgical anatomy of the medial segment (S4) of the liver with special reference to bile ducts and vessels. Hepato-Gastroenterology 47, 143–50.
Ono ML, Murakami G, Sato TJ, Sawada K (2000) Hepatic grooves and portal segmentation. Acta Anat Nippon 75, 517–23.
Ortale JR, de Freitas Azevedo CHN, de Castro CM (2000) Anatomy of the intrahepatic ramification of the portal vein in the right hemiliver. Cell Tissue Organ 166, 378–87.
Ryu M (2002) Three-dimensional Surgical Anatomy of the Liver. Igaku-Tosho-Shuttsupan, Tokyo. (In Japanese.)
Sato TJ, Hirai I, Murakami G, Kanamura T, Hata F, Hirata K (2002) An anatomical study of the short hepatic vein with special reference to deliniation of the caudate lobe if it conducted during liver hanging maneuver without usual mobilization. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 9, 55–60.
Seto M, Kudo M, Murakami G (1998) Morphometrical study of the human liver with special reference to the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt technique. Sapporo Med J 67, 99–104.
Takayama T, Makuuchi M, Kubota K, Sano K, Harihara Y, Kawarasaki H (2000) Living-related transplantation of left liver plus caudate lobe. J Am Coll Surg 190, 635–8.
Takayama T, Tanaka T, Higaki T, Katou K, Teshima Y, Makuuchi M (1994) High dorsal resection of the liver. J Am Coll Surg 179, 73–5.
Takayasu K, Moriyama N, Muramatsu Y, Shima Y, Goto H, Yamada T (1985) Intrahepatic portal vein branches studied by percutaneous transhepatic portography. Radiology 154, 31–6.
Wakiguchi S, Yamaguchi H, Nagaoka Y et al. (2001) Liver segment S2 is consistently located dorsal to S3 but sometimes medial and/or inferior to S3. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 78, 17–22.
Williams PL (1995) Gray’s Anatomy, 38th edn, Churchill livingstone, London.
Yamane T, Mori K, Sakamoto K, Ikei S, Akagi M (1988) Intrahepatic ramification of the portal vein in the right and caudate lobes of the liver. Acta Anat 133, 162–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, G., Hata, F. Human liver caudate lobe and liver segment. Anato Sci Int 77, 211–224 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-7722.2002.00033.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-7722.2002.00033.x