Abstract
Background
Belimumab (Benlysta) is currently approved for the treatment of active Lupus despite standard therapy. Few data are available on the efficacy of this drug in lupus nephritis (LN).
Methods
17 LN female followed in two Nephrology Italian Unit received belimumab for a median period of 36 months (range 6–42 months). The indications were: arthralgia in 3 patients, cutaneous manifestations in 2, residual proteinuria in 8, and the need to reduce steroids for severe side effects in 4. Of interest, 1 patient started therapy during Peritoneal Dialysis and continued after kidney transplantation due to non-responsive arthralgias.
Results
Arthralgia and skin manifestations resolved in all patients. Proteinuria normalized in three patients and stabilized in all but one of the others. Steroids were indefinitely stopped in six patients (35%) and reduced to around 40% of the basal dosage in the other patients. During belimumab therapy, three extrarenal and one renal SLE flares were diagnosed accounting for a rate of renal flares of 0.02/patient/year. No major adverse events leading to therapy withdrawal occurred.
Clinical case
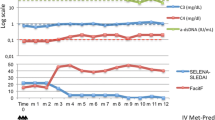
Arthralgia resolved, immunological parameters improved and prednisone could be reduced within few months in the patient who started belimumab during peritoneal dialysis. After kidney transplantation belimumab was stopped but due to arthralgias unresponsive to standard immunosuppressive therapy it was restarted with success.
Conclusions
Belimumab allows the achievement of complete response together with the withdrawal or the reduction of corticosteroids in almost all our patients. Of interest its satisfactory use in a patient in peritoneal dialysis and after kidney transplantation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman A, Isenberg DA (2008) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 358(9):929–939
Yurkovich M, Vostretsova K, Chen W, Avina-Zubieta JA (2014) Overall and cause-specific mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Care Res 66:608–616
Zonana-Nacach A, Barr SG, Magder LS, Petri M (2000) Damage in systemic lupus erythematosus and its association with corticosteroids. Arthritis Rheum 43(8):1801–1808
Carreira PL, Isenberg DA (2019) Recent developments in biologic therapies for the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 58(3):382–387
Oon S, Huq M, Godfrey T, Nikpour M (2018) Systematic review, and meta-analysis of steroid-sparing effect, of biologic agents in randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials for systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 48(2):221–239
Beckwith H, Lightstone L (2014) Rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nephron Clin Pract 128(3–4):250–254
Navarra SV, Guzmán RM, Gallacher AE, BLISS-52 Study Group et al (2011) Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 377(9767):721–731
Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, BLISS-76 Study Group et al (2011) A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 63(12):3918–3930
Vincent FB, Morand EF, Schneider P, Mackay F (2014) The BAFF/APRIL system in SLE pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10(6):365–373
van Vollenhoven RF, Petri MA, Cervera R et al (2012) Belimumab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: high disease activity predictors of response. Ann Rheum Dis 71(8):1343–1349
Trentin F, Gatto M, Zen M et al (2018) Effectiveness, tolerability, a review of observational clinical-practice-based studies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 54(2):331–343
Zhang F, Bae SC, Bass D et al (2018) A pivotal phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus located in China, Japan and South Korea. Ann Rheum Dis 77(3):355–363
Bruce IN, Urowitz M, van Vollenhoven R et al (2016) Long-term organ damage accrual and safety in patients with SLE treated with belimumab plus standard of care. Lupus 25(7):699–709
Iaccarino L, Bettio S, Reggia R et al (2017) Effects of belimumab on flare rate and expected damage progression in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 69(1):115–123
Iaccarino L, Andreoli L, Bocci EB et al (2018) Clinical predictors of response and discontinuation of belimumab in patients with systemic systemic lupus erythematosus in real life setting. Results of a large, multicentric, nationwide study. J Autoimmun 86:1–8
Urowitz MB, Ohsfeldt RL, Wielage RC, Kelton KA, Asukai Y, Ramachandran S (2019) Organ damage in patients treated with belimumab versus standard of care: a propensity score-matched comparative analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 78(3):372–379
Dooley MA, Houssiau F, Aranow C, BLISS-52, and -76 Study Groups et al (2013) Effect of belimumab treatment on renal outcomes: results from the phase 3 belimumab clinical trials in patients with SLE. Lupus 22(1):63–72
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277
Mosca M, van Vollenhoven R (2013) New drugs in systemic lupus erythematosus: when to start and when to stop. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(4 Suppl 78):S82–S85
Doria A, Stohl W, Schwarting A et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in anti-double-stranded DNA-positive, hypocomplementemic patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 70(8):1256–1264
Cheigh JS, Stenzel KH (1993) End-stage renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Kidney Dis 21(1):2–8
Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A et al (2019) 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 78(6):736–745
Mok CC, Ho CT, Chan KW, Lau CS, Wong RW (2002) Outcome and prognostic indicators of diffuse proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis treated with sequential oral cyclophosphamide and azathioprine. Arthritis Rheum 46(4):1003–1013
Korbet SM, Lewis EJ, Collaborative Study Group (2013) Severe lupus nephritis: the predictive value of a ≥ 50% reduction in proteinuria at 6 months. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(9):2313–2318
Petri M, Purvey S, Fang H, Magder LS (2012) Predictors of organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: the hopkins lupus cohort. Arthritis Rheum 64(12):4021–4028
Parker B, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD et al (2015) Impact of early disease factors on metabolic syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: data from an international inception cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 74(8):1530–1536
Collins CE, Dall'Era M, Kan H, Macahilig C, Molta C, Koscielny V, Chang DJ (2016) Response to belimumab among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in clinical practice settings: 24-month results from the observe study in the USA. Lupus Sci Med 3(1):e000118
Sciascia S, Radin M, Yazdany J, Levy RA, Roccatello D, Dall'Era M, Cuadrado MJ (2017) Efficacy of belimumab on renal outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 16(3):287–293
Moroni G, Longhi S, Giglio E, Messa P, Ponticelli C (2013) What happens after complete withdrawal of therapy in patients with lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(4 Suppl 78):S75–S81 (Epub 2013 Oct 4)
Doria A, Bass D, Schwarting A et al (2018) A 6-month open-label extension study of the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 27(9):1489–1498
Banham GD, Flint SM, Torpey N et al (2018) Belimumab in kidney transplantation: an experimental medicine, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 391(10140):2619–2630
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Research idea and study design: GM and RAS. Data acquisition: VB, BT, GF, GP and PF. Data analysis/interpretation: GM, NDP, LB and MRP. Supervision or mentorship: GM, RAS, PM. Each author contributed important intellectual content during manuscript drafting or revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fondazione Ca’ Granda IRCCS Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico di Milano, Italy (protocol number 504_2019bis).
Research involving human participants and/or animals and informed consent
The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and informed consent was given to all patients that participated in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binda, V., Trezzi, B., Del Papa, N. et al. Belimumab may decrease flare rate and allow glucocorticoid withdrawal in lupus nephritis (including dialysis and transplanted patient). J Nephrol 33, 1019–1025 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00706-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00706-3