Abstract
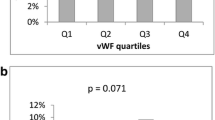
The von Willebrand factor (vWF) levels increase in acute-phase ischemic stroke because of endothelial dysfunction and thrombus formation and may reduce acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) efficiency in hemostatic cascade. The aim of the study is to investigate the relationship between vWF levels and ASA resistance in ischemic stroke patients. Fifty acute ischemic stroke patients (mean age 66.3 ± 13 years, 34 males) were given 300 mg/day aspirin for at least 10 days, and 25 healthy volunteers as a control group were compared using platelet function analyzer-100 test. All risk factors were investigated for a correlation to ASA resistance. ASA resistance was apparent in 32 % of the study group and in 20 % of the control group (p = 0.140). vWF levels were elevated in only ASA nonresponders and the ischemic stroke group that showed a statistically significant association with aspirin resistance (p ≤ 0.05). vWF levels increase in ASA nonresponders and ischemic stroke group in acute phase. High vWF levels may relate to ASA resistance and recurrent strokes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooney M-T, Dudina AL, O'Callaghan P, von Graham MI. Willebrand factor in CHD and stroke: relationships and therapeutic implications. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2007;9:180–90.
Van Schiem C, Van Loon JE, De Maat MF, Leebeek WG. Genetic determinants of von Willebrand factor levels and activity in relation to the risk of cardiovascular disease: a review. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:899–908.
Sato M, Suzuki A, Nagata K, Uchiyama S. Increased von Willebrand factor in acute stroke patients with atrial fibrillation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006;15:1–7.
Ruggeri Z.M, Ware J. von Willebrand factor. FASEB J. 1993; 7:308.
De Meyer SF, Stoll G, Wagner DD, von Kleinschnitz C. Willebrand factor: an emerging target in stroke therapy. Stroke. 2012;43:599–606.
Jastrzebska M, Torbus-Lisiecka B, Honczarenko K, Foltynska AK, Chelstowski K, Naruszewicz M. Von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen and other risk factors of thrombosis in patients with a history of cerebrovascular ischemic stroke and their children. Nutr Metab Cardiavasc Dis. 2002;12:132–40.
van Schie MC, de Maat MP, Isaacs A, van Duijn CM, Deckers JW, Dippel DW, et al. Variation in the von Willebrand factor gene is associated with von Willebrand factor levels and with the risk for cardiovascular disease. Blood. 2011;117:1393–9.
Bugnicourt JM, Roussel B, Garcia PY, Canaple S, Lamy C, Godefroy O. Aspirin non-responder status and early neurological deterioration: a prospective study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011;113:196–201.
Dawson J, Quinn T, Rafferty M, Higgins P, Ray G, Lees KR, et al. Aspirin resistance and compliance with therapy. Cardiovasc Ther. 2011;29:301–7.
Markus HS, McCollum C, Imray C, Goulder MA, Gilbert J, King A. The von Willebrand inhibitor ARC1779 reduces cerebral embolization after carotid endarterectomy: a randomized trial. Stroke. 2011;42:2149–53.
Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B. The role of glycoprotein Ib-alpha and von Willebrand factor interaction in stroke development. Hämostaseologie. 2010;30:136–8.
Chakroun T, Gerotziafas G, Robert F, Lecrubier C, Samama MM, Hatmi M, et al. In vitro aspirin resistance detected by PFA-100TM closure time: pivotal role of plasma von Willebrand factor. Br J Haematol. 2004;124:80–5.
Bongers TN, de Maat MP, van Goor ML, Bhagwanbali V, van Vliet HH, Gómez García EB et al. ‘High von Willebrand factor levels increase the risk of first ischemic stroke: influence of ADAMTS13, inflammation, and genetic variability.’ Stroke. 2006;37(11):2672–7.
Conway DS, Pearce LA, Chin BS, Hart RG, Lip GY. ‘Prognostic value of plasma von Willebrand factor and soluble P-selectin as indices of endothelial damage and platelet activation in 994 patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.’ Circulation. 2003 1;107(25):3141–5.
Hanson E, Jood K, Karlsson S, Nilsson S, Bloomstrand C, Jern C. Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor in the etiologic subtypes of ischemic stroke. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:275–81.
Wieberdink RG, van Schie MC, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman ACM, Witteman JPM, de Maat M, et al. High von Willebrand factor levels increase the risk of stroke: the Rotterdam Study. Stroke. 2010;41:2151–6.
Mannucci PM. Platelet/von Willebrand factor inhibitors to the rescue of ischemic stroke. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30:1882–4.
Acknowledgments
The PFA-100 test financial support was provided by government hospital funding. None of the authors have any conflict of interest to disclose. Experiments were undertaken with the understanding and written consent of each subject. This study conducted in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arslan, Y., Yoldaş, T.K. & Zorlu, Y. Interaction Between vWF Levels and Aspirin Resistance in Ischemic Stroke Patients. Transl. Stroke Res. 4, 484–487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0259-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0259-0