Abstract
Background
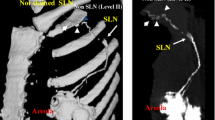
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) became a standard procedure for patients with early breast cancer, however, an indication of SLN navigation to metastatic disease may lead to misdiagnosis for staging. Preoperative CTLG with a water-soluble iodinated contrast medium visualizes the correct primary SLNs and its afferent lymphatic channels surrounding detailed anatomy, therefore it can predict LN metastasis by visualizing the lymph vessel obstruction or stain defect of the SLN by tumor. The current study presents the value of CTLG for preoperative prediction for SLN status.
Methods
A total of 228 patients with Tis-T2 breast cancer who did not receive primary chemotherapy were studied. SLN metastasis was diagnosed according to the following staining patterns of SLNs and afferent lymphatic vessels: stain defect of SLN, obstruction, stagnation, dilation, and detour of the lymphatic vessels by tumor occupation. The diagnosis was compared with the pathological results to evaluate the accuracy of prediction for SLN metastasis using CTLG.
Results
Twenty-seven of 228 patients had metastatic SLN pathologically. Twenty-five of these were diagnosed as metastatic preoperatively. The accuracy for metastatic diagnosis using CTLG was 89.0 %, sensitivity was 92.6 %, and specificity was 88.6 %. The positive predictive value was 52.1 % and negative predictive value was 98.8 %.
Conclusion
CTLG can select the candidate with truly node negative cases in early breast cancer patients, because it predicts lymph node metastasis preoperatively from natural status of the lymphographic image. It also might omit the SLN biopsy itself.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, Luini A, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy as a staging procedure in breast cancer: update of a randomised controlled study. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:983–90.
Motomura K, Egawa C, Komoike Y, Kataoka T, Nagumo S, Koyama H, et al. Sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer: technical aspects and controversies. Breast Cancer. 2007;14:25–30.
Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006;106:4–16.
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Ashikaga T, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:881–8.
Giuliano AE, Jones RC, Brennan M, Statman R. Sentinel lymphadenectomy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2345–50.
Suga K, Ogasawara N, Okada M, Matsunaga N. Interstitial CT lymphography-guided localization of breast sentinel lymph node: preliminary results. Surgery. 2003;133:170–9.
Suga K, Ogasawara N, Yuan Y, Okada M, Matsunaga N, Tangoku A. Visualization of breast lymphatic pathways with an indirect computed tomography lymphography using a nonionic monometric contrast medium iopamidol: preliminary results. Invest Radiol. 2003;38:73–84.
Cox CE, Pendas S, Cox JM, Joseph E, Shons AR, Yeatman T, et al. Guidelines for sentinel node biopsy and lymphatic mapping of patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1998;227:645–51.
Motomura K, Inaji H, Komoike Y, Hasegawa Y, Kasugai T, Noguchi S, et al. Combination technique is superior to dye alone in identification of the sentinel node in breast cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2001;76:95–9.
Radovanovic Z, Golubovic A, Plzak A, Stojiljkovic B. Radova- novic D. Blue dye versus combined blue dye-radioactive tracer technique in detection of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;30:913–7.
Tangoku A, Yamamoto S, Suga K, Ueda K, Nagashima Y, Hida M, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy using computed tomography-lymphography in patients with breast cancer. Surgery. 2004;135:258–65.
Mokhtar M, Tadokoro Y, Nakagawa M, Morimoto M, Takechi H, Kondo K, Tangoku A. Triple assessment of sentinel lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer using preoperative CTLG, intraoperative fluorescence navigation and OSNA. Breast Cancer 29 Jul 2014. (Epub ahead of print).
Lubach D, Ludemann W, Berens V, von Rautenfield D. Recent findings on the angioarchitecture of the lymph vessel system of human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:733–7.
Schmid-Schonbein GW. Microlymphatics and lymph flow. Physiol Rev. 1990;70:987–1028.
Casley-Smith J. The structure and functioning of the blood vessels, interstitial tissues and lymphatics. In: Foeldi M, Casley-Smith J, editors. Lymphangiology. Stuttgart: Schayyauer Verlag; 1983. p. 27–143.
Weissleder R, Heautot JF, Schaffer BK, Nossiff N, Papisov MI, Bogdanov A Jr, et al. MR lymphography: study of a high- efficiency lymphotrophic agent. Radiology. 1994;191:225–30.
Suga K, Yamamoto S, Tangoku A, Oka M, Kawakami Y, Matsunaga N. Breast sentinel lymph node navigation with three-dimensional interstitial multidetector-row computed tomographic lymphography. Invest Radiol. 2005;40(6):336–42.
Veronesi U, De Cicco C, Galimberti VE, Fernandez JR, Rotmensz N, Viale G, et al. A comparative study on the value of FDG-PET and sentinel node biopsy to identify occult axillary metastases. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:473–8.
Jung J, Park H, Park J, Kim H. Accuracy of preoperative ultrasound and ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology for axillary staging in breast cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2010;80:271–5.
Sever A, Jones S, Cox K, Weeks J, Mills P, Jones P. Preoperative localization of sentinel lymph nodes using intradermal microbubbles and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2009;96:1295–9.
Alvarez S, Añorbe E, Alcorta P, López F, Alonso I, Cortés J. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: a systematic review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:1342–8.
Giuliano AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, Beitsch PD, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz PW, et al. Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Med. Assoc. 2011;305:569–75.
Conflict of interest
There was no funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, M., Morimoto, M., Takechi, H. et al. Preoperative diagnosis of sentinel lymph node (SLN) metastasis using 3D CT lymphography (CTLG). Breast Cancer 23, 519–524 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-015-0597-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-015-0597-8