Abstract
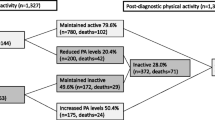
Published data have shown that physical activity (PA) has a positive role on the primary prevention of breast cancer risk. However, the role of PA on breast cancer outcome has been controversial with inconsistent data. The lack of a meta-analysis that addresses that issue prompted the current report. A comprehensive literature search identified eight studies, of which two studies were excluded. The remaining six studies (12,108 patients with breast cancer) were included in this meta-analysis. Pre-diagnosis PA reduced all causes mortality by 18% but had no effect on breast cancer deaths. Post-diagnosis PA reduced breast cancer deaths by 34% (HR = 0.66, 95% CI, 0.57–0.77, P < 0.00001), all causes mortality by 41% (HR = 0.59, 95% CI, 0.53–0.65, P < 0.00001), and disease recurrence by 24% (HR = 0.76, 95% CI, 0.66–0.87, P = 0.00001). Breast cancer mortality was reduced by pre-diagnosis PA in women with body mass index (BMI) < 25 kg/m2, while post-diagnosis PA reduced that risk among those with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2. On the other hand, post-diagnosis PA reduced all causes mortality regardless of the BMI. The analysis showed that post-diagnosis PA reduced breast cancer deaths (HR = 0.50, 95% CI, 0.34–0.74, P = 0.0005), and all causes mortality (HR = 0.36, 95% CI, 0.12–1.03, P = 0.06) among patients with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumor, while women with ER-negative disease showed no gain. The current meta-analysis provides evidence for an inverse relationship between PA and mortality in patients with breast cancer and supports the notion that appropriate PA should be embraced by breast cancer survivors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisch RE, Wyshak G, Albright NL, Albright TE, Schiff I, Jones KP, Witschi J, Shiang E, Koff E, Marguglio M. Lower prevalence of breast cancer and cancers of the reproductive system among former college athletes compared to non-athletes. Br J Cancer. 1985;52:885–91.
Friedenreich CM, Rohan TE. A review of physical activity and breast cancer. Epidemiology. 1995;6:311–7.
Thune I, Furberg AS. Physical activity and cancer risk: dose-response and cancer, all sites and site-specific. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33:S530–50. discussion S609-510.
Vainio H, Kaaks R, Bianchini F. Weight control and physical activity in cancer prevention: international evaluation of the evidence. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2002;11(Suppl 2):S94–100.
Lee IM. Physical activity in women: how much is good enough? JAMA. 2003;290:1377–9.
Bianchini F, Kaaks R, Vainio H. Weight control and physical activity in cancer prevention. Obes Rev. 2002;3:5–8.
Monninkhof EM, Elias SG, Vlems FA, van der Tweel I, Schuit AJ, Voskuil DW, van Leeuwen FE. Physical activity and breast cancer: a systematic review. Epidemiology. 2007;18:137–57.
Abrahamson PE, Gammon MD, Lund MJ, Britton JA, Marshall SW, Flagg EW, Porter PL, Brinton LA, Eley JW, Coates RJ. Recreational physical activity and survival among young women with breast cancer. Cancer. 2006;107:1777–85.
Holick CN, Newcomb PA, Trentham-Dietz A, Titus-Ernstoff L, Bersch AJ, Stampfer MJ, Baron JA, Egan KM, Willett WC. Physical activity and survival after diagnosis of invasive breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:379–86.
Holmes MD, Chen WY, Feskanich D, Kroenke CH, Colditz GA. Physical activity and survival after breast cancer diagnosis. JAMA. 2005;293:2479–86.
Irwin ML, Smith AW, McTiernan A, Ballard-Barbash R, Cronin K, Gilliland FD, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L. Influence of pre- and postdiagnosis physical activity on mortality in breast cancer survivors: the health, eating, activity, and lifestyle study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3958–64.
Pierce JP, Stefanick ML, Flatt SW, Natarajan L, Sternfeld B, Madlensky L, Al-Delaimy WK, Thomson CA, Kealey S, Hajek R, Parker BA, Newman VA, Caan B, Rock CL. Greater survival after breast cancer in physically active women with high vegetable-fruit intake regardless of obesity. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2345–51.
Enger SM, Bernstein L. Exercise activity, body size and premenopausal breast cancer survival. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:2138–41.
Sternfeld B, Weltzien E, Quesenberry CP Jr, Castillo AL, Kwan M, Slattery ML, Caan BJ. Physical activity and risk of recurrence and mortality in breast cancer survivors: findings from the lace study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:87–95.
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17:2815–34.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH. Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:820–6.
Borugian MJ, Sheps SB, Kim-Sing C, Van Patten C, Potter JD, Dunn B, Gallagher RP, Hislop TG. Insulin, macronutrient intake, and physical activity: are potential indicators of insulin resistance associated with mortality from breast cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:1163–72.
Irwin ML, Crumley D, McTiernan A, Bernstein L, Baumgartner R, Gilliland FD, Kriska A, Ballard-Barbash R. Physical activity levels before and after a diagnosis of breast carcinoma: the health, eating, activity, and lifestyle (heal) study. Cancer. 2003;97:1746–57.
Goodwin PJ, Boyd NF. Body size and breast cancer prognosis: a critical review of the evidence. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1990;16:205–14.
McTiernan A, Tworoger SS, Ulrich CM, Yasui Y, Irwin ML, Rajan KB, Sorensen B, Rudolph RE, Bowen D, Stanczyk FZ, Potter JD, Schwartz RS. Effect of exercise on serum estrogens in postmenopausal women: a 12-month randomized clinical trial. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2923–8.
Hoffman-Goetz L, Apter D, Demark-Wahnefried W, Goran MI, McTiernan A, Reichman ME. Possible mechanisms mediating an association between physical activity and breast cancer. Cancer. 1998;83:621–8.
Friedenreich CM, Cust AE. Physical activity and breast cancer risk: impact of timing, type and dose of activity and population subgroup effects. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42:636–47.
Wilson DB, Porter JS, Parker G, Kilpatrick J. Anthropometric changes using a walking intervention in African American breast cancer survivors: a pilot study. Prev Chronic Dis. 2005;2:A16.
Fairey AS, Courneya KS, Field CJ, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Mackey JR. Effects of exercise training on fasting insulin, insulin resistance, insulin-like growth factors, and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003;12:721–7.
Kaaks R. Nutrition, hormones, and breast cancer: is insulin the missing link? Cancer Causes Control. 1996;7:605–25.
Jernstrom H, Barrett-Connor E. Obesity, weight change, fasting insulin, proinsulin, c-peptide, and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in women with and without breast cancer: the rancho bernardo study. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 1999;8:1265–72.
Stoll BA. Diet and exercise regimens to improve breast carcinoma prognosis. Cancer. 1996;78:2465–70.
Torjesen PA, Birkeland KI, Anderssen SA, Hjermann I, Holme I, Urdal P. Lifestyle changes may reverse development of the insulin resistance syndrome. The oslo diet and exercise study: a randomized trial. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:26–31.
Lyman GH, Kuderer NM. The strengths and limitations of meta-analyses based on aggregate data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5:14.
LaPorte RE, Montoye HJ, Caspersen CJ. Assessment of physical activity in epidemiologic research: problems and prospects. Public Health Rep. 1985;100:131–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, E.M., Al-Homaidh, A. Physical activity and survival after breast cancer diagnosis: meta-analysis of published studies. Med Oncol 28, 753–765 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9536-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9536-x