Abstract
The main cytokines regulating bone remodeling are the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) and its decoy receptor, osteoprotegerin (OPG). Recent data have linked RANKL and OPG to cardiovascular disease as well. NT-pro-BNP and adiponectin are well-established biomarkers of heart failure reflecting neuroendocrine activation in this multi-complex disorder. The objective of this article was to investigate whether RANKL is associated with neuroendocrine activation in 75 elderly males with mild to moderate congestive heart failure (CHF) and left ventricular ejection fraction <40%. The control group consisted of 20 healthy male volunteers with matching age and body mass index (BMI). Serum RANKL (sRANKL), OPG, NT-pro-BNP, adiponectin, leptin, clinical, and echocardiography parameters were evaluated. In comparison to the control group, the CHF patients showed significantly increased sRANKL levels [126.8 (122.6) vs. 47.8 (44.4) pg/ml, P < 0.0001]. There was a significant relative risk of systolic CHF in elderly males associated with increased sRANKL above the calculated cut-off of 83 pg/ml [OR = 10.286 (95%CI 3.079–34.356), P < 0.0001; RR = 3.600 (95%CI = 1.482–8.747)]. In the CHF patients, the log-transformed values of sRANKL levels correlated positively with the log-transformed values of the serum NT-pro-BNP and adiponectin levels (P = 0.004, r = 0.326 and P = 0.037, r = 0. 241, respectively), while inversely correlated with the BMI and creatinine clearance (P = 0.015, r = −0.281 and P = 0.042, r = −0.236, respectively). In multivariate regression model, sRANKL was a significant determinant of NT-pro-BNP independent of age, BMI and creatinine clearance (P = 0.002, R 2 = 0.546). In conclusion, our study suggests that in elderly males with systolic heart failure sRANKL was significantly associated with parameters of neuroendocrine activation such as NT-pro-BNP and adiponectin. Further studies are needed to elucidate the potential role of sRANKL in the complex pathogenesis of heart failure.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CHF:
-
Congestive heart failure
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- LVEDD:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter
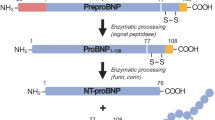
- NT-pro-BNP:
-
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
- NYHA:
-
New York Heart Association
- sRANKL:
-
Serum RANKL levels
References
V.L. Roger, S.A. Weston, M.M. Redfield, J.P. Hellermann-Homan, J. Killian, B.P. Yawn, S.J. Jacobsen, Trends in heart failure incidence and survival in a community-based population. JAMA 292, 344–350 (2004)
E. Braunwald, Biomarkers in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 2148–2159 (2008)
W.H. Tang, G.S. Francis, D.A. Morrow, L.K. Newby, C.P. Cannon, R.L. Jesse, A.B. Storrow, R.H. Christenson, F.S. Apple, J. Ravkilde, A.H. Wu, National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine, National academy of clinical biochemistry laboratory medicine practice guidelines: clinical utilisation of cardiac biomarker testing in heart failure. Circulation 116(5), e99–e109 (2007)
B.F. Boyce, L. Xing, Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 473, 139–146 (2008)
D.L. Lacey, E. Timms, H.L. Tan, M.J. Kelley, C.R. Dunstan, T. Burgess, R. Elliott, A. Colombero, G. Elliott, S. Scully, H. Hsu, J. Sullivan, N. Hawkins, E. Davy, C. Capparelli, A. Eli, Y.X. Qian, S. Kaufman, I. Sarosi, V. Shalhoub, G. Senaldi, J. Guo, J. Delaney, W.J. Boyle, Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93, 165–176 (1998)
Y.Y. Kong, H. Yoshida, I. Sarosi, H.L. Tan, E. Timms, C. Capparelli, S. Morony, A.J. Oliveira-dos-Santos, G. Van, A. Itie, W. Khoo, A. Wakeham, C.R. Dunstan, D.L. Lacey, T.W. Mak, W.J. Boyle, J.M. Penninger, OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 397(6717), 315–323 (1999)
Y.Y. Kong, W.J. Boyle, J.M. Penninger, Osteoprotegerin ligand: a regulator of immune responses and bone physiology. Immunol. Today 21(10), 495–502 (2000)
D.M. Anderson, E. Maraskovsky, W.L. Billingsley, W.C. Dougall, M.E. Tometsko, E.R. Roux, M.C. Teepe, R.F. DuBose, D. Cosman, L. Galibert, A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature 390, 175–179 (1997)
A. Rogers, R.E. Eastell, Circulating osteoprotegerin and receptor activator for nuclear factor kappaB ligand: clinical utility in metabolic bone disease assessment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90(11), 6323–6331 (2005)
H. Yasuda, N. Shima, N. Nakagawa, K. Yamaguchi, M. Kinosaki, S. Mochizuki, A. Tomoyasu, K. Yano, M. Goto, A. Murakami, E. Tsuda, T. Morinaga, K. Higashio, N. Udagawa, N. Takahashi, T. Suda, Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3597–3602 (1998)
M. Schoppet, A.M. Sattler, J.R. Schaefer, M. Herzum, B. Maisch, L.C. Hofbauer, Increased osteoprotegerin serum levels in men with coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88(3), 1024–1028 (2003)
S. Jono, Y. Ikari, A. Shioi, K. Mori, T. Miki, K. Hara, Y. Nishizawa, Serum osteoprotegerin levels are associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. Circulation 106(10), 1192–1194 (2002)
S. Kiechl, G. Schett, G. Wenning, K. Redlich, M. Oberhollenzer, A. Mayr, P. Santer, J. Smolen, W. Poewe, J. Willeit, Osteoprotegerin is a risk factor for progressive atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 109(18), 2175–2180 (2004)
T. Ueland, R. Jemtland, K. Godang, J. Kjekshus, A. Hognestad, T. Omland, I.B. Squire, L. Gullestad, J. Bollerslev, K. Dickstein, P. Aukrust, Prognostic value of osteoprotegerin in heart failure after acute myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 44(10), 1970–1976 (2004)
T. Ueland, A. Yndestad, E. Øie, G. Florholmen, B. Halvorsen, S.S. Frøland, S. Simonsen, G. Christensen, L. Gullestad, P. Aukrust, Dysregulated osteoprotegerin/RANK ligand/RANK axis in clinical and experimental heart failure. Circulation 111(19), 2461–2468 (2005)
S. Helske, P.T. Kovanen, K.A. Lindstedt, K. Salmela, J. Lommi, H. Turto, K. Werkkala, M. Kupari, Increased circulating concentrations and augmented myocardial extraction of osteoprotegerin in heart failure due to left ventricular pressure overload. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 9(4), 357–363 (2007)
N. Ouchi, R. Shibata, K. Walsh, Cardioprotection by adiponectin. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 16, 141–146 (2006)
Y. Okamoto, S. Kihara, N. Ouchi, M. Nishida, Y. Arita, M. Kumada, K. Ohashi, N. Sakai, I. Shimomura, H. Kobayashi, N. Terasaka, T. Inaba, T. Funahashi, Y. Matsuzawa, Adiponectin reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 106(22), 2767–2770 (2002)
C. Kistorp, J. Faber, S. Galatius, F. Gustafsson, J. Frystyk, A. Flyvbjerg, P. Hildebrandt, Plasma adiponectin, body mass index, and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 112(12), 1756–1762 (2005)
S.D. Anker, R. Sharma, The syndrome of cardiac cachexia. Int. J. Cardiol. 85(1), 51–66 (2002)
The Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association. (1994). Criteria for diagnosis and treatment of heart failure. Little, Brown and Company
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories, ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 166(l), 111–117 (2002)
F.E. Silvestry, R.E. Kerber, M.M. Brook, J.D. Carroll, K.M. Eberman, S.A. Goldstein, H.C. Herrmann, S. Homma, R. Mehran, D.L. Packer, A.F. Parisi, T. Pulerwitz, J.B. Seward, T.S. Tsang, M.A. Wood, Echocardiography-guided interventions. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 22(3), 213–231 (2009)
N. Massy-Westropp, W. Rankin, M. Ahern, J. Krishnan, T.C. Hearn, Measuring grip strength in normal adults: reference ranges and a comparison of electronic and hydraulic instruments. J. Hand Surg. 29(3), 514–519 (2004)
D.W. Cockroft, M.H. Gault, Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16, 31–41 (1976)
E.M. Wilson, H.R. Gunasinghe, M.L. Coker, P. Sprunger, D. Lee-Jackson, B. Bozkurt, A. Deswal, D.L. Mann, F.G. Spinale, Plasma matrix metalloproteinase and inhibitor profiles in patients with heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 8(6), 390–398 (2002)
J. George, S. Patal, D. Wexler, Y. Sharabi, E. Peleg, Y. Kamari, E. Grossman, D. Sheps, G. Keren, Circulating adiponectin concentrations in patients with congestive heart failure. Heart 92(10), 1420–1424 (2006)
T. Tamura, Y. Furukawa, R. Taniguchi, Y. Sato, K. Ono, H. Horiuchi, Y. Nakagawa, T. Kita, T. Kimura, Serum adiponectin level as an independent predictor of mortality in patients with congestive heart failure. Circ. J. 71(5), 623–630 (2007)
O. Tsukamoto, M. Fujita, M. Kato, S. Yamazaki, Y. Asano, A. Ogai, H. Okazaki, M. Asai, Y. Nagamachi, N. Maeda, Y. Shintani, T. Minamino, M. Asakura, I. Kishimoto, T. Funahashi, H. Tomoike, M. Kitakaze, Natriuretic peptides enhance the production of adiponectin in human adipocytes and in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53(22), 2070–2077 (2009)
M.H. Gannagé-Yared, F. Fares, M. Semaan, S. Khalife, S. Jambart, Circulating osteoprotegerin is correlated with lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, adiponectin and sex steroids in an ageing male population. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 64(6), 652–658 (2006)
M.B. McEntegart, B. Awede, M.C. Petrie, N. Sattar, F.G. Dunn, N.G. MacFarlane, J.J. McMurray, Increase in serum adiponectin concentration in patients with heart failure and cachexia: relationship with leptin, other cytokines, and B-type natriuretic peptide. Eur. Heart J. 28(7), 829–835 (2007)
J.V. Patel, M. Sosin, H.S. Lim, I. Chung, N. Panja, R.C. Davis, E.A. Hughes, G.Y. Lip, Raised leptin concentrations among South Asian patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 122(1), 34–40 (2007)
G.S. Filippatos, K. Tsilias, K. Venetsanou, E. Karambinos, D. Manolatos, A. Kranidis, J. Antonellis, F. Kardaras, L. Anthopoulos, G. Baltopoulos, Leptin serum levels in cachectic heart failure patients. Relationship with tumor necrosis factor-alpha system. Int. J. Cardiol. 76(2–3), 117–122 (2000)
K.K. Koh, M.J. Quon, S.H. Han, W.J. Chung, J.Y. Ahn, Y.H. Seo, I.S. Choi, E.K. Shin, Additive beneficial effects of fenofibrate combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45(10), 1649–1653 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Serbian Ministry of Science (grant 145019). We thank Merck Sharp and Dohme for their unrestricted educational grant. We also thank Mrs M. Argirovic from MSD for support during application procedure for educational grant. This work was also supported by biochemical laboratory “Zavod za laboratorijsku dijagnostiku Konzilijum’’—Belgrade, Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loncar, G., Bozic, B., Cvorovic, V. et al. Relationship between RANKL and neuroendocrine activation in elderly males with heart failure. Endocr 37, 148–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9282-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9282-z