Abstract
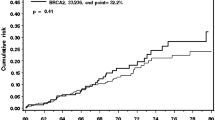
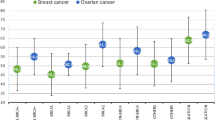
Accurate estimations of lifetime risks of breast and ovarian cancer are crucial for counselling women from BRCA1/2 families. We therefore determined breast and ovarian cancer penetrance in BRCA1/2 mutation families in the northern Netherlands and compared them with the incidence of cancers in the general population in this region. We identified 1188 female mutation carriers and first-degree female relatives in 185 families with a pathogenic BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. The occurrence of breast cancer, contralateral breast cancer and ovarian cancer was recorded. The cumulative incidence of breast cancer by age 70 was 71.4% (95% CI 67.2–82.4%) in BRCA1 and 87.5% (82.4–92.6%) in BRCA2 mutation carriers. For ovarian cancer at age 70, it was 58.9% (53.5–64.3%) in BRCA1 and 34.5% (25.0–44.0%) in BRCA2 mutation carriers. For breast cancer we saw a rise of 24.2% in the cumulative incidence in the seventh decade for BRCA2 mutation carriers versus 6.3% for BRCA1. For ovarian cancer the rise in the seventh decade was 17.3% for BRCA1 mutation carriers and 15.1% for BRCA2. The 10-year risk for contralateral breast cancer was 34.2% (29.4–39.0%) in BRCA1 families and 29.2% (22.9–35.5%) in BRCA2. We show that the incidence of breast and ovarian cancer in BRCA2 mutation carriers and of ovarian cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers is still high after 60 years. This may justify intensive breast screening as well as oophorectomy even after age 60. The risk of contralateral breast cancer rises approximately 3% per year, which may affect preventive choices.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Struikmans H, Nortier JW, Rutgers EJ, Zonderland HM, Bontenbal M, Elkhuizen PH, van Tienhoven G, Tjan-Heijnen VC, van Vegchel T, Tuut MK, Benraadt J (2008) Guideline ‘Treatment of breast cancer 2008’ (revision). Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 152:2507–2511
Burke W, Daly M, Garber J, Botkin J, Kahn MJ, Lynch P, McTiernan A, Offit K, Perlman J, Petersen G, Thomson E, Varricchio C (1997) Recommendations for follow-up care of individuals with an inherited predisposition to cancer. II. BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cancer Genetics Studies Consortium. JAMA 277:997–1003
van der Velde NM, Mourits MJ, Arts HJ, de Vries J, Leegte BK, Dijkhuis G, Oosterwijk JC, de Bock GH (2009) Time to stop ovarian cancer screening in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers? Int J Cancer 124:919–923
Rebbeck TR, Lynch HT, Neuhausen SL, Narod SA, Van’t Veer L, Garber JE, Evans G, Isaacs C, Daly MB, Matloff E, Olopade OI, Weber BL (2002) Prophylactic oophorectomy in carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. N Engl J Med 346:1616–1622
Meijers-Heijboer H, van Geel B, van Putten WL, Henzen-Logmans SC, Seynaeve C, Menke-Pluymers MB, Bartels CC, Verhoog LC, van den Ouweland AM, Niermeijer MF, Brekelmans CT, Klijn JG (2001) Breast cancer after prophylactic bilateral mastectomy in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. N Engl J Med 345:159–164
Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P et al (2003) Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet 72:1117–1130
Chen S, Parmigiani G (2007) Meta-analysis of BRCA1 and BRCA2 penetrance. J Clin Oncol 25:1329–1333
Easton DF, Ford D, Bishop DT (1995) Breast and ovarian cancer incidence in BRCA1-mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 56:265–271
Evans DG, Shenton A, Woodward E, Lalloo F, Howell A, Maher ER (2008) Penetrance estimates for BRCA1 and BRCA2 based on genetic testing in a clinical cancer genetics service setting: risks of breast/ovarian cancer quoted should reflect the cancer burden in the family. BMC Cancer 8:155
Ford D, Easton DF, Stratton M, Narod S, Goldgar D, Devilee P, Bishop DT, Weber B, Lenoir G, Chang-Claude J, Sobol H, Teare MD et al (1998) Genetic heterogeneity and penetrance analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in breast cancer families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 62:676–689
King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB (2003) Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 302:643–646
Brekelmans CT, Seynaeve C, Menke-Pluymers M, Bruggenwirth HT, Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Bartels CC, Kriege M, van Geel AN, Crepin CM, Blom JC, Meijers-Heijboer H, Klijn JG (2006) Survival and prognostic factors in BRCA1-associated breast cancer. Ann Oncol 17:391–400
Haffty BG, Harrold E, Khan AJ, Pathare P, Smith TE, Turner BC, Glazer PM, Ward B, Carter D, Matloff E, Bale AE, Alvarez-Franco M (2002) Outcome of conservatively managed early-onset breast cancer by BRCA1/2 status. Lancet 359:1471–1477
Metcalfe K, Lynch HT, Ghadirian P, Tung N, Olivotto I, Warner E, Olopade OI, Eisen A, Weber B, McLennan J, Sun P, Foulkes WD et al (2004) Contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. J Clin Oncol 22:2328–2335
Pierce LJ, Levin AM, Rebbeck TR, Ben David MA, Friedman E, Solin LJ, Harris EE, Gaffney DK, Haffty BG, Dawson LA, Narod SA, Olivotto IA et al (2006) Ten-year multi-institutional results of breast-conserving surgery and radiotherapy in BRCA1/2-associated stage I/II breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:2437–2443
Robson M, Gilewski T, Haas B, Levin D, Borgen P, Rajan P, Hirschaut Y, Pressman P, Rosen PP, Lesser ML, Norton L, Offit K (1998) BRCA-associated breast cancer in young women. J Clin Oncol 16:1642–1649
Robson M, Svahn T, McCormick B, Borgen P, Hudis CA, Norton L, Offit K (2005) Appropriateness of breast-conserving treatment of breast carcinoma in women with germline mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2: a clinic-based series. Cancer 103:44–51
The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium (1999) Cancer risks in BRCA2 mutation carriers. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1310–1316
Graeser MK, Engel C, Rhiem K, Gadzicki D, Bick U, Kast K, Froster UG, Schlehe B, Bechtold A, Arnold N, Preisler-Adams S, Nestle-Kraemling C et al (2009) Contralateral breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. J Clin Oncol 27:5887–5892
Gronwald J, Tung N, Foulkes WD, Offit K, Gershoni R, Daly M, Kim-Sing C, Olsson H, Ainsworth P, Eisen A, Saal H, Friedman E et al (2006) Tamoxifen and contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers: an update. Int J Cancer 118:2281–2284
Hopper JL, Southey MC, Dite GS, Jolley DJ, Giles GG, McCredie MR, Easton DF, Venter DJ (1999) Population-based estimate of the average age-specific cumulative risk of breast cancer for a defined set of protein-truncating mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Australian Breast Cancer Family Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 8:741–747
Satagopan JM, Offit K, Foulkes W, Robson ME, Wacholder S, Eng CM, Karp SE, Begg CB (2001) The lifetime risks of breast cancer in Ashkenazi Jewish carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10:467–473
Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, Baker SM, Berlin M, McAdams M, Timmerman MM, Brody LC, Tucker MA (1997) The risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med 336:1401–1408
Warner E, Foulkes W, Goodwin P, Meschino W, Blondal J, Paterson C, Ozcelik H, Goss P, Allingham-Hawkins D, Hamel N, Di Prospero L, Contiga V et al (1999) Prevalence and penetrance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations in unselected Ashkenazi Jewish women with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1241–1247
van der Hout AH, van den Ouweland AM, van der Luijt RB, Gille HJ, Bodmer D, Bruggenwirth H, Mulder IM, van der Vlies P, Elfferich P, Huisman MT, ten Berge AM, Kromosoeto J et al (2006) A DGGE system for comprehensive mutation screening of BRCA1 and BRCA2: application in a Dutch cancer clinic setting. Hum Mutat 27:654–666
Comprehensive Cancer Center, The Netherlands. http://www.ikcnet.nl
Kiemeney LA, Lemmers FA, Verhoeven RH, Aben KK, Honing C, de Nooijer J, Peeters PH, Visser O, Vlems FA (2008) The risk of cancer in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 152:2233–2241
Smith A, Moran A, Boyd MC, Bulman M, Shenton A, Smith L, Iddenden R, Woodward ER, Lalloo F, Maher ER, Evans DG (2007) Phenocopies in BRCA1 and BRCA2 families: evidence for modifier genes and implications for screening. J Med Genet 44:10–15
Robson ME, Chappuis PO, Satagopan J, Wong N, Boyd J, Goffin JR, Hudis C, Roberge D, Norton L, Begin LR, Offit K, Foulkes WD (2004) A combined analysis of outcome following breast cancer: differences in survival based on BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation status and administration of adjuvant treatment. Breast Cancer Res 6:R8–R17
Oei AL, Massuger LF, Bulten J, Ligtenberg MJ, Hoogerbrugge N, de Hullu JA (2006) Surveillance of women at high risk for hereditary ovarian cancer is inefficient. Br J Cancer 94:814–819
Acknowledgements
We thank Rob H. A. Verhoeven and Maaike van der Aa for providing breast and ovarian cancer incidences in the female population in the Netherlands. We thank Jackie Senior for editorial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Kolk, D.M., de Bock, G.H., Leegte, B.K. et al. Penetrance of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 families: high cancer incidence at older age. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124, 643–651 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0805-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0805-3