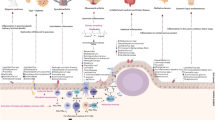
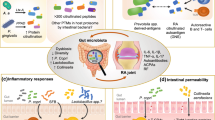
Abstract
Rheumatic diseases refer to many diseases with a loss of immune self-tolerance, leading to a chronic inflammation, degeneration, or metabolic derangement in multiple organs or tissues. The cause of rheumatic diseases remains to be elucidated, though both environmental and genetic factors are required for the development of rheumatic diseases. Over the past decades, emerging studies suggested that alteration of intestinal microbiota, known as gut dysbiosis, contributed to the occurrence or development of a range of rheumatic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ankylosing spondylitis, systemic sclerosis, and Sjogren’s syndrome, through profoundly affecting the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory immune responses. In this article, we discussed the role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases based on a large number of experimental and clinical materials, thereby providing a new insight for microbiota-targeted therapies to prevent or cure rheumatic diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C et al (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65
Kverka M, Tlaskalova-Hogenova H (2017) Intestinal microbiota: facts and fiction. Dig Dis 35:139–147
Koboziev I, Reinoso WC, Furr KL, Grisham MB (2014) Role of the enteric microbiota in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 68:122–133
Rajilic-Stojanovic M, de Vos WM (2014) The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:996–1047
Clooney AG, Fouhy F, Sleator RD, O' Driscoll A, Stanton C, Cotter PD et al (2016) Comparing apples and oranges?: next generation sequencing and its impact on microbiome analysis. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148028
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M et al (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308:1635–1638
Kamada N, Seo SU, Chen GY, Nunez G (2013) Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 13:321–335
Sparks JA, Costenbader KH (2014) Genetics, environment, and gene-environment interactions in the development of systemic rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 40:637–657
Benson AK, Kelly SA, Legge R, Ma F, Low SJ, Kim J et al (2010) Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:18933–18938
Mizuno M, Noto D, Kaga N, Chiba A, Miyake S (2017) The dual role of short fatty acid chains in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease models. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173032
Amarilyo G, Lourenco EV, Shi FD, La Cava A (2014) IL-17 promotes murine lupus. J Immunol 193:540–543
Chen DY, Chen YM, Wen MC, Hsieh TY, Hung WT, Lan JL (2012) The potential role of Th17 cells and Th17-related cytokines in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Lupus 21:1385–1396
Gomez A, Luckey D, Yeoman CJ, Marietta EV, Berg Miller ME, Murray JA et al (2012) Loss of sex and age driven differences in the gut microbiome characterize arthritis-susceptible 0401 mice but not arthritis-resistant 0402 mice. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal
Wu HJ, Ivanov II, Darce J, Hattori K, Shima T, Umesaki Y et al (2010) Gut-residing segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune arthritis via Th17 cells. Immunity 32:815–827
Flannigan KL, Ngo VL, Geem D, Harusato A, Hirota SA, Parkos CA et al (2016) IL-17A-mediated neutrophil recruitment limits expansion of segmented filamentous bacteria. Mucosal Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2016.80
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly YM et al (2013) The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 341:569–573
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van der Veeken J, DeRoos P et al (2013) Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 504:451–455
Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, Endo TA, Nakato G, Takahashi D et al (2013) Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 504:446–450
Rivière A, Selak M, Lantin D, Leroy F, De Vuyst L (2016) Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut. Front Microbiol 7:979
Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL (2005) An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell 122:107–118
Proal AD, Lindseth IA, Marshall TG (2017) Microbe-microbe and host-microbe interactions drive microbiome dysbiosis and inflammatory processes. Disco Med 23:51–60
Chen J, Wright K, Davis JM, Jeraldo P, Marietta EV, Murray J et al (2016) An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med 8:43
Liu X, Zeng B, Zhang J, Li W, Mou F, Wang H et al (2016) Role of the gut microbiome in modulating arthritis progression in mice. Sci Rep 6:30594
Liu X, Zou Q, Zeng B, Fang Y, Wei H (2013) Analysis of fecal Lactobacillus community structure in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Microbiol 67:170–176
Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata N, Ubeda C, Bielski C et al (2013) Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01202
Gul'neva MI, Noskov SM (2011) Colonic microbial biocenosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Klin Med (Mosk) 89:45–48
Vaahtovuo J, Munukka E, Korkeamaki M, Luukkainen R, Toivanen P (2008) Fecal microbiota in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35:1500–1505
Eerola E, Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Luukkainen R, Kantola I, Vuori K et al (1990) Intestinal anaerobic bacteria in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Br J Rheumatol 33:1030–1038
Severijnen AJ, Kool J, Swaak AJ, Hazenberg MP (1990) Intestinal flora of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: induction of chronic arthritis in rats by cell wall fragments from isolated Eubacterium aerofaciens strains. Br J Rheumatol 29:433–439
Olhagen B, Månsson I (1968) Intestinal Clostridium perfringens in rheumatoid arthritis and other collagen diseases. Acta Med Scand 184:395–402
He Z, Shao T, Li H, Xie Z, Wen C (2016) Alterations of the gut microbiome in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Gut Pathog 8:64
Johnson BM, Gaudreau MC, Al-Gadban MM, Gudi R, Vasu C (2015) Impact of dietary deviation on disease progression and gut microbiome composition in lupus-prone SNF1 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 181:323–337
Zhang H, Liao X, Sparks JB, Luo XM (2014) Dynamics of gut microbiota in autoimmune lupus. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7551–7560
Hevia A, Milani C, Lopez P, Cuervo A, Arboleya S, Duranti S et al (2014) Intestinal dysbiosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. mBio 5:e1514–e1548
Mehta HE, Goulet PO, Mashiko S, Desjardins J, Pérez G, Koenig M et al (2017) Early life antibiotic exposure causes intestinal dysbiosis and exacerbates skin and lung pathology in experimental systemic sclerosis. J Invest Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.06.019
Andreasson K, Alrawi Z, Persson A, Jonsson G, Marsal J (2016) Intestinal dysbiosis is common in systemic sclerosis and associated with gastrointestinal and extraintestinal features of disease. Arthritis Res Ther 18:278
Volkmann ER, Chang YL, Barroso N, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Gorn AH et al (2016) Association of systemic sclerosis with a unique colonic microbial consortium. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:1483–1492
Costello ME, Ciccia F, Willner D, Warrington N, Robinson PC, Gardiner B et al (2014) Intestinal dysbiosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:686–691
Lin P, Bach M, Asquith M, Lee AY, Akileswaran L, Stauffer P et al (2014) HLA-B27 and human beta2-microglobulin affect the gut microbiota of transgenic rats. PLoS One 9:e105684
Stebbings S, Munro K, Simon MA, Tannock G, Highton J, Harmsen H et al (2002) Comparison of the faecal microflora of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and controls using molecular methods of analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1395–1401
Taurog JD, Richardson JA, Croft JT, Simmons WA, Zhou M, Fernandez-Sueiro JL et al (1994) The germfree state prevents development of gut and joint inflammatory disease in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. J Exp Med 180:2359–2364
de Paiva CS, Jones DB, Stern ME, Bian F, Moore QL, Corbiere S et al (2016) Altered mucosal microbiome diversity and disease severity in Sjogren syndrome. Sci Rep 6:23561
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 388:2023–2038
Bessis N, Decker P, Assier E, Semerano L, Boissier MC (2017) Arthritis models: usefulness and interpretation. Semin Immunopathol 39:469–486
Trentham DE, Townes AS, Kang AH (1977) Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med 146:857–868
Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Koenders MI, Devesa I, Roelofs MF, Radstake TR et al (2008) Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. J Clin Invest 118:205–216
Wu W, Liu HP, Chen F, Liu H, Cao AT, Yao S et al (2016) Commensal A4 bacteria inhibit intestinal Th2-cell responses through induction of dendritic cell TGF-beta production. Eur J Immunol 46:1162–1167
Liu X, Zhang J, Zou Q, Zhong B, Wang H, Mou F et al (2016) Lactobacillus salivarius isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis suppresses collagen-induced arthritis and increases Treg frequency in mice. J Interf Cytokine Res 36:706–712
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, Imaoka A, Kuwahara T, Momose Y et al (2011) Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 331:337–341
Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H, Feng Q, Wang D, Liang D et al (2015) The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat Med 21:895–905
Brisbin JT, Gong J, Parvizi P, Sharif S (2010) Effects of lactobacilli on cytokine expression by chicken spleen and cecal tonsil cells. Clin Vaccin Immunol 17:1337–1343
Sierra S, Lara-Villoslada F, Sempere L, Olivares M, Boza J, Xaus J (2010) Intestinal and immunological effects of daily oral administration of Lactobacillus salivarius CECT5713 to healthy adults. Anaerobe 16:195–200
Lee JM, Hwang KT, Jun WJ, Park CS, Lee MY (2008) Anti-inflammatory effect of lactic acid bacteria: inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by suppressing nuclear factor-kappaB in Raw264.7 macrophage cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1683–1688
Lee JH, Valeriano VD, Shin YR, Chae JP, Kim GB, Ham JS et al (2012) Genome sequence of Lactobacillus mucosae LM1, isolated from piglet feces. J Bacteriol 194:4766
Vaghef-Mehrabany E, Alipour B, Homayouni-Rad A, Sharif SK, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Zavvari S (2014) Probiotic supplementation improves inflammatory status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition 30:430–435
Pineda ML, Thompson SF, Summers K, de Leon F, Pope J, Reid G (2011) A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled pilot study of probiotics in active rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit 17:R347–R354
Amdekar S, Singh V, Singh R, Sharma P, Keshav P, Kumar A (2011) Lactobacillus casei reduces the inflammatory joint damage associated with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) by reducing the pro-inflammatory cytokines: lactobacillus casei: COX-2 inhibitor. J Clin Immunol 31:147–154
Costa-Reis P, Sullivan KE (2013) Genetics and epigenetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 15:369
Tsokos GC (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 365:2110–2121
Van Praet JT, Donovan E, Vanassche I, Drennan MB, Windels F, Dendooven A et al (2015) Commensal microbiota influence systemic autoimmune responses. EMBO J 34:466–474
Zimmerman MA, Singh N, Martin PM, Thangaraju M, Ganapathy V, Waller JL et al (2012) Butyrate suppresses colonic inflammation through HDAC1-dependent Fas upregulation and Fas-mediated apoptosis of T cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 302:G1405–G1415
López P, de Paz B, Rodríguez-Carrio J, Hevia A, Sánchez B, Margolles A et al (2016) Th17 responses and natural IgM antibodies are related to gut microbiota composition in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Sci Rep 6:24072
Volkmann ER, Hoffmann-Vold AM, Chang YL, Jacobs JP, Tillisch K, Mayer EA et al (2017) Systemic sclerosis is associated with specific alterations in gastrointestinal microbiota in two independent cohorts. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000134
Frech TM, Khanna D, Maranian P, Frech EJ, Sawitzke AD, Murtaugh MA (2011) Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/distention. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:S22–S25
Rath HC, Herfarth HH, Ikeda JS, Grenther WB, Hamm TJ, Balish E et al (1996) Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats. J Clin Invest 98:945–953
Asquith MJ, Stauffer P, Davin S, Mitchell C, Lin P, Rosenbaum JT (2016) Perturbed mucosal immunity and dysbiosis accompany clinical disease in a rat model of spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:2151–2162
Luckey D, Gomez A, Murray J, White B, Taneja V (2013) Bugs & us: the role of the gut in autoimmunity. Indian J Med Res 138:732–743
Dominguez-Lopez ML, Burgos-Vargas R, Galicia-Serrano H, Bonilla-Sanchez MT, Rangel-Acosta HH, Cancino-Diaz ME et al (2002) IgG antibodies to enterobacteria 60 kDa heat shock proteins in the sera of HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Scandinavian J Rheumatol 31:260–265
Montoya J, Matta NB, Suchon P, Guzian MC, Lambert NC, Mattei JP et al (2016) Patients with ankylosing spondylitis have been breast fed less often than healthy controls: a case-control retrospective study. Ann Rheum Dis 75:879–882
Mavragani CP, Moutsopoulos HM (2014) Sjogren's syndrome. Annu Rev Pathol 9:273–285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, D., Wu, C., Zeng, X. et al. The role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol 37, 25–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3821-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3821-4