Abstract
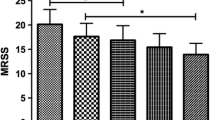
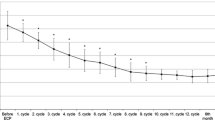
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disease which involves the skin, as well as several internal organs. Most therapies available in this disease are symptomatic. Authors present a case of diffuse SSc with progressive disease not responding to currently available treatments. Therefore a 12-month protocol of repeated plasmapheresis and high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment was administered with good clinical efficacy. Apart from monitoring the clinical symptoms throughout the treatment, authors also assessed a number of humoral and cellular immunolaboratory markers in order to obtain information on the immunomodulatory effects of this combined treatment in SSc.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seibold JR (2001) Scleroderma. In: Ruddy S, Harris ED Jr, Sledge CB, Budd RC, Sergent JS (eds) Kelley’s textbook of rheumatology, vol. 2., chapter 83, 6th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1211–1240
Mimori A, Nara H, Kaneko N et al (2000) Three patients with systemic sclerosis complicated by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 23:57–63
Levy T, Sherer Y, Langevitz P et al (2000) Skin score decrease in systemic sclerosis patients treated with intravenous immunoglobulin—a preliminary report. Clin Rheumatol 19:207–211
Omote A, Muramatsu M, Sugimoto Y et al (1997) Intern Med 36:508–513
Wach F, Ullrich H, Schmitz G et al (1995) Treatment of severe localized scleroderma by plasmapheresis—report of three cases. Br J Dermatol 133:605–609
Dau PC, Callahan JP (1994) Immune modulation during treatment of systemic sclerosis with plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drugs. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 70:159–165
Szücs G, Szamosi S, Aleksza M et al (2003) Plasmapheresis therapy in systemic sclerosis. Orv Hetil (Hung Med J) 144:2213–2217
Nacci F, Righi A, Conforti ML et al (2007) Intravenous immunoglobulins improve the function and ameliorate joint involvement in systemic sclerosis: a pilot study. Ann Rheum Dius 66:977–979
Levy Y, Amital H, Langevitz P et al (2004) Intravenous immunoglobulin modulates cutaneous involvement and reduces skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: an open-label study. Arthritis Rheum 50:1005–1007
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch P, Ng SC et al (1990) Skin score. A semiquantitative measure of cutaneous involvement that improves prediction of prognosis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1256–1262
Bollinger A, Fagrell B (1990) Clinical capillaroscopy. Hogrefe Huber, Toronto
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szekanecz, Z., Aleksza, M., Antal-Szalmás, P. et al. Combined plasmapheresis and high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in systemic sclerosis for 12 months: follow-up of immunopathological and clinical effects. Clin Rheumatol 28, 347–350 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1062-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1062-2