Abstract
Purpose
Chronic inguinodynia is one of the most frequent complications after groin herniorrhaphy. We investigated the retroperitoneal anatomy of the iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve to prevent direct nerve injury during hernia repairs and to find the most advantageous approach for posterior triple neurectomy.
Methods
We dissected the inguinal nerves in 30 human anatomic specimens bilaterally. The distances from each nerve and their entry points in the abdominal wall were measured in relation to the posterior superior iliac spine, anterior superior iliac spine, and the midpoint between the two iliac spines on the iliac crest. We evaluated our findings by creating high-resolution summation images.
Results
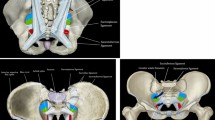
The courses of the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerve are most consistent on the anterior surface of the quadratus lumborum muscle. The genitofemoral nerve always runs on the psoas muscle. The entry points of the nerves in the abdominal wall are located as follows: the iliohypogastric nerve is above the iliac crest and lateral from the anterior superior iliac spine, the ilioinguinal nerve is with great variability, either above or below the iliac crest and lateral from the anterior superior iliac spine, the genital branch is around the internal inguinal ring, the femoral branch is either cranial or caudal to the iliopubic tract, and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is either medial or lateral to the anterior superior iliac spine.
Conclusion
Nerve injury during inguinal hernia repairs can be avoided by taking the topographic anatomy of the inguinal nerves into consideration. The most advantageous plane to look for the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerve during posterior neurectomy is on the anterior surface of the quadratus lumborum muscle. For the surgical treatment of severe chronic inguinodynia, especially after posterior open or endoscopic mesh repair (TAPP/TEP), the retroperitoneoscopic or open retroperitoneal approach for posterior triple neurectomy can be considered.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bay-Nielsen M, Perkins FM, Kehlet H (2001) Pain and functional impairment 1 year after inguinal herniorrhaphy: a nationwide questionnaire study. Ann Surg 233:1–7
Fränneby U, Sandblom G, Nordin P, Nyrén O, Gunnarsson U (2006) Risk factors for long-term pain after hernia surgery. Ann Surg 244:212–219
Reinpold WM, Nehls J, Eggert A (2011) Nerve management and chronic pain after open inguinal hernia repair: a prospective two phase study. Ann Surg 254:163–168
Bittner R, Sauerland S, Schmedt CG (2005) Comparison of endoscopic techniques vs Shouldice and other open nonmesh techniques for inguinal hernia repair: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Surg Endosc 19:605–615
Singh AN, Bansal VK, Misra MC, Kumar S, Rajeshwari S, Kumar A, Sagar R, Kumar A (2012) Testicular functions, chronic groin pain, and quality of life after laparoscopic and open mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 26:1304–1317
McCormack K, Scott NW, Go PM, Ross S, Grant AM (2003) Laparoscopic techniques versus open techniques for inguinal hernia repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD001785
Neumayer L, Giobbie-Hurder A, Jonasson O, Fitzgibbons R Jr, Dunlop D, Gibbs J, Reda D, Henderson W (2004) Open mesh versus laparoscopic mesh repair of inguinal hernia. N Engl J Med 350:1819–1827
Alfieri S, Amid PK, Campanelli G, Izard G, Kehlet H, Wijsmuller AR, Di Miceli D, Doglietto GB (2011) International guidelines for prevention and management of post-operative chronic pain following inguinal hernia surgery. Hernia 15:239–249
Amid PK, Hiatt JR (2007) New understanding of the causes and surgical treatment of postherniorrhaphy inguinodynia and orchalgia. J Am Coll Surg 205:381–385
Amid PK (2004) Causes, prevention, and surgical treatment of postherniorrhaphy neuropathic inguinodynia: triple neurectomy with proximal end implantation. Hernia 8:343–349
Chen DC, Hiatt JR, Amid PK (2013) Operative management of refractory neuropathic inguinodynia by a laparoscopic retroperitoneal approach. JAMA Surg 148:962–967
O’Malley KJ, Monkhouse WS, Qureshi MA, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (1997) Anatomy of the peritoneal aspect of the deep inguinal ring: implications for laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy. Clin Anat 10:313–317
Bittner R, Arregui ME, Bisgaard T, Dudai M, Ferzli GS, Fitzgibbons RJ, Fortelny RH, Klinge U, Kockerling F, Kuhry E, Kukleta J, Lomanto D, Misra MC, Montgomery A, Morales-Conde S, Reinpold W, Rosenberg J, Sauerland S, Schug-Pass C, Singh K, Timoney M, Weyhe D, Chowbey P (2011) Guidelines for laparoscopic (TAPP) and endoscopic (TEP) treatment of inguinal hernia [International Endohernia Society (IEHS)]. Surg Endosc 25:2773–2843
Miserez M, Peeters E, Aufenacker T, Bouillot JL, Campanelli G, Conze J, Fortelny R, Heikkinen T, Jorgensen LN, Kukleta J, Morales-Conde S, Nordin P, Schumpelick V, Smedberg S, Smietanski M, Weber G, Simons MP (2014) Update with level 1 studies of the European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients. Hernia 18:151–163
Kehlet H, Roumen RM, Reinpold W, Miserez M (2013) Invited commentary: persistent pain after inguinal hernia repair: what do we know and what do we need to know? Hernia 17:293–297
Campanelli G, Bertocchi V, Cavalli M, Bombini G, Biondi A, Tentorio T, Sfeclan C, Canziani M (2013) Surgical treatment of chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair. Hernia 17:347–353
Schu S, Gulve A, Eldabe S, Baranidharan G, Wolf K, Demmel W, Rasche D, Sharma M, Klase D, Jahnichen G, Wahlstedt A, Nijhuis H, Liem L (2014) Spinal cord stimulation of the dorsal root ganglion for groin pain—a retrospective review. Pain Pract. doi: 10.1111/papr.12194 [Epub ahead of print]
Wijsmuller AR, Lange JF, Kleinrensink GJ, van Geldere D, Simons MP, Huygen FJ, Jeekel J, Lange JF (2007) Nerve-identifying inguinal hernia repair: a surgical anatomical study. World J Surg 31:414–420
Amid PK, Chen DC (2011) Surgical treatment of chronic groin and testicular pain after laparoscopic and open preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair. J Am Coll Surg 213:531–536
Al-dabbagh AKR (2002) Anatomical variations of the inguinal nerves and risks of injury in 110 hernia repairs. Surg Radiol Anat 24:102–107
Klaassen Z, Marshall E, Tubbs RS, Louis RG Jr, Wartmann CT, Loukas M (2011) Anatomy of the ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves with observations of their spinal nerve contributions. Clin Anat 24:454–461
Mandelkow H, Loeweneck H (1988) The iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves. Distribution in the abdominal wall, danger areas in surgical incisions in the inguinal and pubic regions and reflected visceral pain in their dermatomes. Surg Radiol Anat 10:145–149
Rosenberger RJ, Loeweneck H, Meyer G (2000) The cutaneous nerves encountered during laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia. Surg Endosc 14:731–735
Conflict of interest
WR, AS, MS, CB, MR, and UW declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinpold, W., Schroeder, A.D., Schroeder, M. et al. Retroperitoneal anatomy of the iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: consequences for prevention and treatment of chronic inguinodynia. Hernia 19, 539–548 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-015-1396-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-015-1396-z