Abstract
Introduction. A cadaveric study was undertaken to investigate the usefulness and reliability of a microscope based navigation system (NS) for skull base surgery.
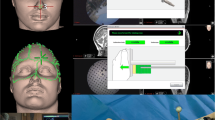
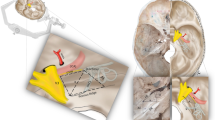
Material and Methods. CT-scans (1 mm slices) were performed in 10 fixed cadaver heads after implantation of fiducials. There upon, various skull base dissections were undertaken: transethmoidal-transsphenoidal approach to sella and clivus, retrosigmoidal approach to the internal auditory canal (IAC) and to the posterior semicircular canal (PSCC). The navigated dissections were performed with the MKMTM, a microscope based navigation system of Carl Zeiss© (Oberkochen, Germany).
Results. The registration assessment by the NS yielded a mean deviation of 0.23 mm±0.03 mm (mean±SD, n=7, range 0.19 to 0.27 mm). The real anatomical deviation during dissection was 0.67 mm±0.2 mm for navigation to the IAC and 0.71 mm±0.37 mm to the PSCC. This accuracy was achieved with three fiducials (4*1 mm titanium screws) arranged as a triangle (side length 4–6 cm) nearby the surgical field. Navigation data on current position, direction and distance to a target structure were helpful in the transethmoidal-transsphenoidal approach to the clivus, as well as for accessing deep seated structures (C1–C2 junction, petrous bone tip). The contouring feature was beneficial for identifying structures embedded in the bone. However, due to inaccurate 3-D modelling this feature has a restricted reliability.
Discussion. Our cadaveric skull base study has shown that the MKMTM is a reliable tool with high anatomical accuracy and usefulness of most navigation features. However, in order to effectively and reliably use any NS the surgeon must be familiar with its potential features and limitations as is demonstrated in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinker, T., Arango, G., Kaminsky, J. et al. An Experimental Approach to Image Guided Skull Base Surgery Employing a Microscope-Based Neuronavigation System. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140, 883–889 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050189