Abstract
Purpose
To establish the prognostic significance of C-reactive protein (CRP) and albumin in octogenarians with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) based on the study of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery (JACS 1303).
Methods
A total of 618 octogenarians with pathological stage I NSCLC, who underwent pulmonary resection, were included in the analysis. We conducted multivariable Cox regression analysis to evaluate the CRP to albumin ratio (CAR) as a potential prognostic factor. Other clinicopathological factors were also evaluated.
Results
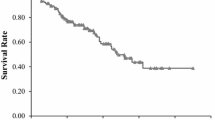
The median age was 82 years. Operations included lobectomy (n = 388; 62.8%) segmentectomy (n = 95; 15%), and wedge resection (n = 135; 22%). Pathological stage IA was diagnosed in 380 (61.5%) patients. The 3-year (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CS) rates were 86.7% and 94.6%, respectively. OS was significantly higher for patients with low CAR (< 0.106) than for those with high CAR (≥ 0.106) (hazard ratio = 3.13, 95% confidence interval: 1.99–4.93, p < 0.0001). Univariate analysis identified sex, poor performance status, smoking status, comorbidity, solid tumor, histology, high Glasgow prognostic scale, and high CAR as significant prognostic factors. Multivariate analysis identified only the CAR as a significant prognostic factor for both OS and CS.
Conclusions
Our analysis of the nationwide data demonstrated that the CAR is a useful prognostic factor for elderly patients with stage I NSCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Abridged life table 2019 https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/life/life19/dl/life19-02.pdf. Accessed 24 May 2021.
Shimizu H, Okada M, Toh Y, Doki Y, Endo S, Fukuda H, et al. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgeries in Japan during 2018: Annual Report by the Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;69:179–212.
Saji H, Ueno T, Nakamura H. Prospective observational cohort study of postoperative risk and prognosis scoring for elderly patients with medically operable lung cancer (JACS1303). Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;64:634–5.
Saji H, Ueno T, Nakamura H, Okumura N, Tsuchida M, Sonobe M, et al. A proposal for a comprehensive risk scoring system for predicting postoperative complications in octogenarian patients with medically operable lung cancer: JACS1303. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53:835–41.
Hino H, Karasaki T, Yoshida Y, Fukami T, Sano A, Tanaka M, et al. Risk factors for postoperative complications and long-term survival in lung cancer patients older than 80 years. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53:980–6.
Okami J, Higashiyama M, Asamura H, Goya H, Koshiishi Y, Sohara Y, et al. Pulmonary resection in patients aged 80 years or over with clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer: Prognostic factors for overall survival and risk factors for postoperative complications. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:1247–53.
Miyazaki T, Yamasaki N, Tsuchiya T, Matsumoto K, Kunizaki M, Taniguchi D, et al. Inflammation-based scoring is a useful prognostic predictor of pulmonary resection for elderly patients with clinical stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015;47:e140–5.
Kobayashi S, Karube Y, Matsumura Y, Nishiura M, Inoue T, Araki O, et al. Inflammatory risk factors for early recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer within one year following curative resection. World J Surg. 2020;44:3510–21.
Wang J, Hui Z, Men Y, Kan J, Sun X, Deng L, et al. Systemic inflammation-immune status predicts survival in stage III-n2 non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108:1701–9.
Proctor MJ, Morrison DS, Talwar D, Balmer SM, O’Reilly DSJ, Foulis AK, et al. An inflammation-based prognostic score (mGPS) predicts cancer survival independent of tumour site: A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Br J Cancer. 2011;104:726–34.
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N, Iwaku A, Oishi M, Tanaka K, et al. The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, a novel inflammation-based prognostic score, predicts outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:803–10.
Baldessari C, Guaitoli G, Valoriani F, Bonacini R, Marcheselli R, Reverberi L, et al. Impact of body composition, nutritional and inflammatory status on outcome of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immunotherapy. Clinical Nutrit ESPEN. 2021;43:64–75.
Ni XF, Wu J, Ji M, Shao YJ, Xu B, Jiang JT, et al. Effect of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio on prognosis in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018;14:402–9.
Zhang F, Ying L, Jin J, Chen K, Zhang N, Wu J, et al. The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts long-term outcomes of patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:8835–42.
Miyazaki T, Yamasaki N, Tsuchiya T, Matsumoto K, Kunizaki M, Kamohara R, et al. Ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin is a prognostic factor for operable non-small-cell lung cancer in elderly patients. Surg Today. 2017;47:836–43.
Worrall SF. TNM Classification of malignant tumours. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;38:244.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Takamori S, Toyokawa G, Shimokawa M, Kinoshita F, Kozuma Y, Matsubara T, et al. A novel prognostic marker in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Musculo-immuno-nutritional score calculated by controlling nutritional status and creatine kinase. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11:927–35.
Matsubara T, Takamori S, Haratake N, Fujishita T, Toyozawa R, Ito K, et al. Identification of the best prognostic marker among immunonutritional parameters using serum C-reactive protein and albumin in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28:3046–54.
Tomita M, Ayabe T, Maeda R, Nakamura K. The prognostic values of a novel preoperative inflammation-based score in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2019;10:176–80.
Gallus S, Lugo A, Suatoni P, Taverna F, Bertocchi E, Boffi R, et al. Effect of tobacco smoking cessation on C-reactive protein levels in a cohort of low-dose computed tomography screening participants. Sci Rep. 2018;8:6–12.
Razi SS, Kodia K, Alnajar A, Block MI, Tarrazzi F, Nguyen D, et al. Lobectomy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy in healthy octogenarians with stage I lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;111:1659–65.
Cao C, Wang D, Chung C, Tian D, Rimner A, Huang J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of stereotactic body radiation therapy versus surgery for patients with non–small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:362-73.e8.
Mimae T, Saji H, Nakamura H, Okumura N, Tsuchida M, Sonobe M, et al. Survival of octogenarians with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer is comparable between wedge resection and lobectomy/segmentectomy: JACS1303. Ann Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-021-09835-w.
Shoji F, Miura N, Matsubara T, Akamine T, Kozuma Y, Haratake N, et al. Prognostic significance of immune-nutritional parameters for surgically resected elderly lung cancer patients: A multicentre retrospective study. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;26:389–94.
Fukumoto K, Mori S, Shintani Y, Okami J, Ito H, Ohtsuka T, et al. Impact of the preoperative body mass index on the postoperative outcomes in patients with completely resected non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis of 16,503 cases in a Japanese Lung Cancer Registry Study. Lung Cancer. 2020;149:120–9.
Tsukioka T, Nishiyama N, Izumi N, Mizuguchi S, Komatsu H, Okada S, et al. Sarcopenia is a novel poor prognostic factor in male patients with pathological Stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017;47:363–8.
Batchelor TJP, Rasburn NJ, Abdelnour-Berchtold E, Brunelli A, Cerfolio RJ, Gonzalez M, et al. Guidelines for enhanced recovery after lung surgery: Recommendations of the Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS®) Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55:91–115.
Wu Y-L, Tsuboi M, He J, John T, Grohe C, Majem M, et al. Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1711–23.
Yoh K, Takamochi K, Shukuya T, Hishida T, Tsuboi M, Sakurai H, et al. Pattern of care in adjuvant therapy for resected Stage I non-small cell lung cancer: Real-world data from Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019;49:63–8.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shuntaro Sato, Ph.D., Clinical Research Center, Nagasaki University Hospital for statistical advice.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hisashi Saji received honoraria from MSD, Boehringer Ingelheim, ETHICON, Covidien, Chugai-pharm, Astellas Pharma, FUJIFILM Medical, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Hiroshige Nakamura received honoraria from Intuitive Surgical Corp, Johnson & Johnson C.C. and research funding from Covidien Japan C.C., Johnson & Johnson C., Co. Morihito Okada received honoraria from Ethicon, Astra Zeneca, Chugai, Covidien, Pfizer, MSD, Daiichi-Sankyo, Bristol-Myers and research funding from Ethicon, Covidien, Daiichi-Sankyo, Chugai, Ono, Lilly, Astra Zeneca, Kirin-Kyowa, and Medi-Physics.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, T., Saji, H., Nakamura, H. et al. The C-reactive protein to albumin ratio is a prognostic factor for stage I non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients: JACS1303. Surg Today 52, 1463–1471 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-022-02485-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-022-02485-9