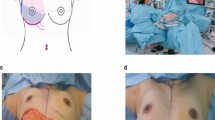
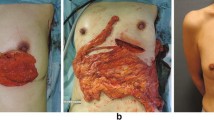
Abstract
Background
To determine the therapeutic and cosmetic outcomes of patients with breast cancer treated with endoscopic axillary lymphadenectomy (EAL) combined with laparoscopically harvested pedicled omentum (LHPO) for immediate breast reconstruction.
Methods
Forty patients with early breast cancer underwent EAL, followed by quadrantectomy and LHPO for immediate breast reconstruction. All patients were evaluated for operating time, blood loss, postoperative hospital stay, complications, etc. The cosmetic outcomes were evaluated 6 months after the surgery, according to the Harris criteria.
Results
The average operating time was 308 min, including 39 min for EAL, 63 min for quadrantectomy, and 58 min for LHPO. The average blood loss was 70 ml, and was mainly incurred during breast resection. On average, the patients were discharged 9.5 days after the surgery. Partial graft necrosis and omental fat liquefaction occurred in one patient each. No other complications occurred after the surgery. No local recurrence or distant metastasis was found during the follow-up. The cosmetic results were mostly satisfactory. No size reduction of the reconstructed breast occurred after radiation therapy. Esthetic evaluation of the reconstructed breast showed that the cosmetic outcome was “excellent” in 35 patients, “good” in 4 patients, and “fair” in 1 patient.
Conclusions
EAL combined with LHPO for breast reconstruction is a viable, safe procedure that causes minimal surgical trauma and results in a soft, shapely breast postoperatively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veronesi U, Salvadori B, Luini A, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Del VM, Mariani L, Zurrida S, Rilke F (1995) Breast conservation is a safe method in patients with small cancer of the breast. Long-term results of three randomised trials on 1,973 patients. Eur J Cancer 31A:1574–1579
Caffo O, Amichetti M, Ferro A, Lucenti A, Valduga F, Galligioni E (2003) Pain and quality of life after surgery for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80:39–48
Krekel N, Zonderhuis B, Muller S, Bril H, van Slooten HJ, de Lange DKE, van den Tol P, Meijer S (2011) Excessive resections in breast-conserving surgery: a retrospective multicentre study. Breast J 17:602–609
Cyriac C, Sharma RK, Singh G (2010) Assessment of the abdominal wall function after pedicled TRAM flap surgery for breast reconstruction: use of modified mesh repair for the donor defect. Indian J Plast Surg 43:166–172
Rezai M, Darsow M, Kummel S, Kramer S (2008) Autologous and alloplastic breast reconstruction-overview of techniques, indications and results. Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch 48:68–75
Kiricuta I (1963) The use of the great omentum in the surgery of breast cancer. Presse Med 71:15–17
Jimenez AG, St GP, Sirois M, Hatheway M, Lethbridge R (2002) Free omental flap for skin-sparing breast reconstruction harvested laparoscopically. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:545–551
Zaha H, Inamine S (2010) Laparoscopically harvested omental flap: results for 96 patients. Surg Endosc 24:103–107
Zaha H, Onomura M, Nomura H, Umekawa K, Oki M, Asato H (2012) Free omental flap for partial breast reconstruction after breast-conserving surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:583–587
Zaha H, Sunagawa H, Kawakami K, Touyama T, Yonaha T, Ohshiro N (2010) Partial breast reconstruction for an inferomedial breast carcinoma using an omental flap. World J Surg 34:1782–1787
Harris JR, Levene MB, Svensson G, Hellman S (1979) Analysis of cosmetic results following primary radiation therapy for stages I and II carcinoma of the breast. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 5:257–261
Luo C, Guo W, Yang J, Sun Q, Wei W, Wu S, Fang S, Zeng Q, Zhao Z, Meng F, Huang X, Zhang X, Li R, Ma X, Luo C, Yang Y (2012) Comparison of mastoscopic and conventional axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: long-term results from a randomized, multicenter trial. Mayo Clin Proc 87:1153–1161
Zaha H, Inamine S, Naito T, Nomura H (2006) Laparoscopically harvested omental flap for immediate breast reconstruction. Am J Surg 192:556–558
Gomatos IP, Filippakis G, Albanopoulos K, Zografos G, Leandros E, Bramis J, Konstadoulakis MM (2006) Complete endoscopic axillary lymph node dissection without liposuction for breast cancer: initial experience and mid-term outcome. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Technol 16:232–236
de Wilde RL, Schmidt EH, Hesseling M, Mildner R, Frank V, Tenger M (2003) Comparison of classic and endoscopic lymphadenectomy for staging breast cancer. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc 10:75–79
Chengyu L, Yongqiao Z, Hua L, Xiaoxin J, Chen G, Jing L, Jian Z (2005) A standardized surgical technique for mastoscopic axillary lymph node dissection. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Technol 15:153–159
Cothier-Savey I, Tamtawi B, Dohnt F, Raulo Y, Baruch J (2001) Immediate breast reconstruction using a laparoscopically harvested omental flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 107(1156–1163):1164–1165
van Garderen JA, Wiggers T, van Geel AN (1991) Complications of the pedicled omentoplasty. Neth J Surg 43:171–174
Disclosures
Pusheng Zhang, Yunfeng Luo, Jianwen Deng, Guoli Shao, Shuai Han and Zonghai Huang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pusheng Zhang and Yunfeng Luo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Luo, Y., Deng, J. et al. Endoscopic axillary lymphadenectomy combined with laparoscopically harvested pedicled omentum for immediate breast reconstruction. Surg Endosc 29, 1376–1383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3808-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3808-z