Abstract
Background
Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is a novel treatment for esophageal motility disorders such as achalasia. To date, the extent of the myotomy has been determined based on the subjective assessment of the endoscopist. We hypothesized that the real-time measurement of esophagogastric junction (EGJ) distensibility using a novel functional lumen-imaging probe would enable objective evaluation of POEM.
Methods
Patients diagnosed with achalasia disorders electively underwent POEM. Using impedance planimetry with a transorally inserted functional lumen-imaging probe (EndoFLIP®), cross-sectional areas (CSA) and distensibilities at the EGJ were measured intraoperatively immediately before and after the transoral myotomy (n = 4). All patients completed their 6-month follow-up and two patients had repeat distensibility tests at this time. Four healthy volunteers served as a control group.
Results
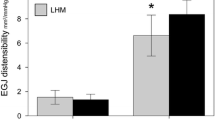
POEM was successfully performed in all patients (4/4). Premyotomy measurements (40-ml fill mode) showed a median diameter of 6.5 mm (range = 5.2–7.9 mm) at the narrowest location of the EGJ and was 10.1 mm (7.3–13.2 mm) following POEM. CSA increased from 41.5 mm2 (20–49 mm2) to 86 mm2 (41–137 mm2) at a similar median intraballoon pressure (40.3 vs. 38.6 mmHg). The increased EGJ distensibility (DI, 1.0 vs. 2.4 mm2/mmHg) was comparable to that of healthy volunteers (2.7 mm2/mmHg).
Conclusion
Functional lumen distensibility measures show that POEM can result in an immediate correction of the nonrelaxing lower esophageal sphincter, which appears similar to that of healthy controls. Intraoperative EGJ profiling may be an important tool to objectively guide the needed extent and completeness of the myotomy during POEM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pasricha PJ, Hawari R, Ahmed I, Chen J, Cotton PB, Hawes RH, Kalloo AN, Kantsevoy SV, Gostout CJ (2007) Submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy: a novel experimental approach for the treatment of achalasia. Endoscopy 39:761–764
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S (2010) Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42:265–271
Stavropoulos SN, Harris MD, Hida S, Brathwaite C, Demetriou C, Grendell J (2010) Endoscopic submucosal myotomy for the treatment of achalasia (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72:1309–1311
Swanstrom LL, Rieder E, Dunst CM (2011) A stepwise approach and early clinical experience in peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia and esophageal motility disorders. J Am Coll Surg 213:751–756
Rieder E, Dunst CM, Kastenmeier AS, Makris KI, Swanstrom LL (2011) Development and technique of per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for achalasia. Eur Surg 43:140–145
Von Renteln D, Inoue H, Minami H, Werner YB, Pace A, Kersten JF, Much CC, Schachschal G, Mann O, Keller J, Fuchs KH, Rösch T (2012) Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. Am J Gastroenterol 107(3):411–417
McMahon BP, Frøkjaer JB, Liao D, Kunwald P, Drewes AM, Gregersen H (2005) A new technique for evaluating sphincter function in visceral organs: application of the functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) for the evaluation of the oesophago-gastric junction. Physiol Meas 26:823–836
Pandolfino JE, Shi G, Curry J, Joehl RJ, Brasseur JG, Kahrilas PJ (2002) Esophagogastric junction distensibility: a factor contributing to sphincter incompetence. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G1052–G1058
Rohof WO, Hirsch DP, Boeckxstaens GE (2011) Impaired distensibility of the esophagogastric junction in patients with achalasia and persistent symptoms. Gastroenterology 140:S163
Jenkinson AD, Scott SM, Yazaki E et al (2001) Compliance measurement of lower esophageal sphincter and esophageal body in achalasia and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis Sci 46:1937–1942
Kwiatek MA, Pandolfino JE, Hirano I, Kahrilas PJ (2010) Esophagogastric junction distensibility assessed with an endoscopic functional luminal-imaging probe (EndoFLIP). Gastrointest Endosc 72:272–278
Kwiatek MA, Kahrilas K, Soper NJ, Bulsiewicz WJ, McMahon BP, Gregersen H, Pandolfino JE (2010) Esophagogastric junction distensibility after fundoplication assessed with a novel functional luminal-imaging probe. J Gastrointest Surg 14:268–276
Perretta S, Dallemagne B, Donatelli G, Diemunsch P, Marescaux J (2011) Transoral endoscopic esophageal myotomy based on esophageal function testing in a survival porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc 73:111–116
Perretta S, Dallemagne B, McMahon B, D’Agostino J, Marescaux J (2011) Improving functional esophageal surgery with a “smart” bougie: endoflip. Surg Endosc 25:3109
Kwiatek MA, Hirano I, Kahrilas PJ, Rothe J, Luger D, Pandolfino JE (2011) Mechanical properties of the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 140:82–90
Nathanson LK, Brunott N, Cavallucci D (2012) Adult esophagogastric junction distensibility during general anesthesia assessed with an endoscopic functional luminal-imaging probe (EndoFLIP®). Surg Endosc 26(4):1051–1055
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Olympus, USA, for providing the high-resolution upper endoscope.
Disclosures
Drs. Rieder, Swanström, Perretta, Lenglinger, Riegler, and Dunst report no conflict of interest with regard to this article and particularly had no financial or editorial involvement from Crospon Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieder, E., Swanström, L.L., Perretta, S. et al. Intraoperative assessment of esophagogastric junction distensibility during per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal motility disorders. Surg Endosc 27, 400–405 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2484-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2484-0