Abstract
Background
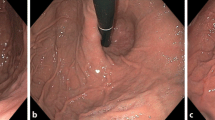
Barium swallow is considered essential in the preoperative assessment of gastroesophaeal reflux disease and hiatal hernias. The objective of this study was to investigate the effective value of a barium swallow if complementary to the commonly recommended endoscopy before laparoscopic antireflux and hiatal hernia surgery.
Methods
We prospectively evaluated 40 consecutive patients who were tested with preoperative barium swallow and endoscopy before laparoscopic surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease and/or symptomatic hiatal hernia. Results regarding the presence and the type of hiatal hernia found by barium swallow and endoscopy were correlated with the intraoperative finding as the reference standard.
Results
Intraoperative findings revealed 21 axial, 7 paraesophageal, and 12 mixed hiatal hernias. Barium swallow and endoscopy allowed the diagnosis of hiatal hernia in 75% and 97.5%, respectively (p = 0.003). The correct classification of hiatal hernia was confirmed in 50% by barium swallow and 80% by endoscopy (p = 0.005).
Conclusions
Although barium swallow is recommended as an important diagnostic tool in the workup before surgical antireflux and hiatal hernia therapy, our results suggest that if mandatory endoscopy is performed preoperatively, a barium swallow does not provide any further essential information. It seems that barium swallow can be omitted as a basic diagnostic test before primary laparoscopic antireflux and hiatal hernia surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canon CL, Morgan DE, Einstein DM, Herts BR, Hawn MT, Johnson LF (2005) Surgical approach to gastroesophageal reflux disease: what the radiologist needs to know. Radiographics 25:1485–1499
Holscher AH, Bollschweiler E, Gutschow C, Malfertheiner P (2005) Correct diagnosis for indication in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Chirurg 76:345–352
Patti MG, Fisichella PM, Perretta S (2001) Preoperative evaluation of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 11:327–331
Watson TJ, Peters JH (2005) Evaluation of esophageal function for antireflux surgery. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 15:347–360
Consensus Development Conference (1997) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Results of a Consensus Development Conference. Held at the Fourth International Congress of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (E.A.E.S.), Trondheim, Norway, June 21–24, 1996. Surg Endosc 11:413–26
Neugebauer EA, Sauerland S, Fingerhut A, Millat B (2006) EAES Guidelines for Endoscopic Surgery—Twelve Years Evidence-Based Surgery in Europe. Springer, Berlin
Armstrong D, Blum AL, Savary M (1992) Reflux disease and Barrett’s oesophagus. Endoscopy 24:9–17
Campos GM, Peters JH, Demeester TR, Oberg S, Crookes PF, Tan S, Demeester SR, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1999) Multivariate analysis of factors predicting outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 3:292–300
Maziak DE, Todd TR, Pearson FG (1998) Massive hiatus hernia: evaluation and surgical management. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 115:53–60
Sloan S, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ (1992) Determinants of gastroesophageal junction incompetence: hiatal hernia, lower esophageal sphincter, or both? Ann Intern Med 117:977–982
DeVault KR, Castell DO (2005) Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 100:190–200
Chen YM, Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Munitz HA (1985) Multiphasic examination of the esophagogastric region for strictures, rings, and hiatal hernia: evaluation of the individual techniques. Gastrointest Radiol 10:311–316
Boyce HW (2000) Endoscopic definitions of esophagogastric junction regional anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc 51:586–592
Allison PR (1951) Reflux esophagitis, sliding hiatus hernia and the anatomy of repair. Surg Gynecol Obstet 92:419–431
Hill LD (1967) An effective operation for hiatal hernia: an eight year appraisal. Ann Surg 166:681–692
Narbona-Arnau B, Olavarietta L, Lioris JM, Narbona-Calvo B (1980) Reflujo gastroesofagico hernia hiatal. Rehabilitacion quirurgica del musculo esofagico mediante pexia con el ligamento redondo. Resultados (1143 operados en 15 anos). Bol Soc Val Digest 1:21–28
Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, Bergman JJ, Gossner L, Hoshihara Y, Jankowski JA, Junghard O, Lundell L, Tytgat GN, Vieth M (2006) The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett’s esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology 131:1392–1399
Kahrilas PJ, Lin S, Chen J, Manka M (1999) The effect of hiatus hernia on gastro-oesophageal junction pressure. Gut 44:476–482
Berstad A, Weberg R, Froyshov Larsen I, Hoel B, Hauer-Jensen M (1986) Relationship of hiatus hernia to reflux oesophagitis. A prospective study of coincidence, using endoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol 21:55–58
Jones MP, Sloan SS, Rabine JC, Ebert CC, Huang CF, Kahrilas PJ (2001) Hiatal hernia size is the dominant determinant of esophagitis presence and severity in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 96:1711–1717
Frazzoni M, De ME, Grisendi A, Savarino V (2002) Hiatal hernia is the key factor determining the lansoprazole dosage required for effective intra-oesophageal acid suppression. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:881–886
Streets CG, Demeester TR (2003) Ambulatory 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring: why, when, and what to do. J Clin Gastroenterol 37:14–22
Johnsson F, Hatlebakk JG, Klintenberg AC, Roman J, Toth E, Stubberod A, Falk A, Edin R (2003) One-week esomeprazole treatment: an effective confirmatory test in patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 38:354–359
Johnston BT, Troshinsky MB, Castell JA, Castell DO (1996) Comparison of barium radiology with esophageal pH monitoring in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 91:1181–1185
Ott DJ, McManus CM, Ledbetter MS, Chen MY, Gelfand DW (1997) Heartburn correlated to 24-hour pH monitoring and radiographic examination of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 92:1827–1830
Mittal SK, Awad ZT, Tasset M, Filipi CJ, Dickason TJ, Shinno Y, Marsh RE, Tomonaga TJ, Lerner C (2000) The preoperative predictability of the short esophagus in patients with stricture or paraesophageal hernia. Surg Endosc 14:464–468
Horvath KD, Swanstrom LL, Jobe BA (2000) The short esophagus: pathophysiology, incidence, presentation, and treatment in the era of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Ann Surg 232:630–640
Levine MS, Rubesin SE (2005) Diseases of the esophagus: diagnosis with esophagography. Radiology 237:414–427
Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Wu WC (1983) Sensitivity of single-contrast radiology in esophageal disease: a study of 240 patients with endoscopically verified abnormality. Gastrointest Radiol 8:105–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linke, G.R., Borovicka, J., Schneider, P. et al. Is a barium swallow complementary to endoscopy essential in the preoperative assessment of laparoscopic antireflux and hiatal hernia surgery?. Surg Endosc 22, 96–100 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9379-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9379-5