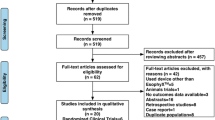
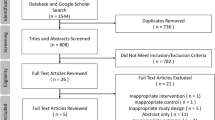
Abstract
Purpose
We aim to review and quantitatively compare laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication (LTF), Nissen fundoplication (LNF), anterior partial fundoplication (APF), magnetic augmentation sphincter (MSA), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF), proton pump inhibitor (PPI), and placebo for the treatment of GERD. A number of meta-analyses compared the efficacy of surgical and endoscopic procedures for recalcitrant GERD, but considerable debate on the effectiveness of operative strategies remains.
Methods
A systematic review of MEDLINE databases, EMBASE, and Web of Science for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the aforementioned surgical and endoscopic GERD treatments was performed. Risk ratio and weighted mean difference were used as pooled effect size measures, whereas 95% credible intervals (CrI) were used to assess relative inference.
Results
Thirty-three RCTs were included. Surgical and endoscopic treatments have similar RR for heartburn, regurgitation, bloating. LTF has a lower RR of post-operative dysphagia when compared to APF (RR 3.3; Crl 1.4–7.1) and LNF (RR 2.5; Crl 1.3–4.4). The pooled network meta-analysis did not observe any significant improvement regarding LES pressure and pH < from baseline. LTF, APF, LNF, MSA, RFA, and TIF had have a similar post-operative PPI discontinuation rate.
Conclusion
LTF has a lower rate of post-operative dysphagia when compared to APF and LNF. The pre-post effects, such as GERD-HQRL, LES pressure, and pH <4, should be avoided in meta-analyses because results may be biased. Last, a consensus about the evaluation of GERD treatments’ efficacy and their outcomes is needed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J (2014) Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 63(6):871–880. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269
Sandhu DS, Fass R (2018) Current trends in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gut Liver 12(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl16615
Gyawali CP, Fass R. Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. Jan 2018;154(2):302-318. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.049
Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF (2013) Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 108(3):308–328; quiz 329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.444
Gotley DC, Smithers BM, Rhodes M, Menzies B, Branicki FJ, Nathanson L (1996) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication—200 consecutive cases. Gut. 38(4):487–491. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.38.4.487
Bessell JR, Finch R, Gotley DC, Smithers BM, Nathanson L, Menzies B (2000) Chronic dysphagia following laparoscopic fundoplication. Br J Surg 87(10):1341–1345. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2168.2000.01634.x
Nissen R (1956) Gastropexy as the lone procedure in the surgical repair of hiatus hernia. Am J Surg 92(3):389–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(56)80111-6
Toupet A (1963) Technic of esophago-gastroplasty with phrenogastropexy used in radical treatment of hiatal hernias as a supplement to Heller's operation in cardiospasms. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 89:384–389
Hopkins RJ, Irvine T, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Watson DI (2020) Long-term follow-up of two randomized trials comparing laparoscopic Nissen 360° with anterior 90° partial fundoplication. Br J Surg 107(1):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.11327
Spechler SJ, Hunter JG, Jones KM et al (2019) Randomized trial of medical versus surgical treatment for refractory heartburn. N Engl J Med 381(16):1513–1523. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1811424
Richter JE (2013) Gastroesophageal reflux disease treatment: side effects and complications of fundoplication. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(5):465–471; quiz e39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2012.12.006
Ganz RA, Peters JH, Horgan S et al (2013) Esophageal sphincter device for gastroesophageal reflux disease. N Engl J Med 368(8):719–727. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1205544
Aziz AM, El-Khayat HR, Sadek A et al (2010) A prospective randomized trial of sham, single-dose Stretta, and double-dose Stretta for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 24(4):818–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0671-4
Hunter JG, Kahrilas PJ, Bell RC et al (2015) Efficacy of transoral fundoplication vs omeprazole for treatment of regurgitation in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 148(2):324–333.e5. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.009
Xie P, Yan J, Ye L et al (2021) Efficacy of different endoscopic treatments in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 35(4):1500–1510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08386-1
Skubleny D, Switzer NJ, Dang J et al (2017) LINX(®) magnetic esophageal sphincter augmentation versus Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 31(8):3078–3084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5370-3
Tian ZC, Wang B, Shan CX, Zhang W, Jiang DZ, Qiu M (2015) A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to compare long-term outcomes of Nissen and Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. PLoS One 10(6):e0127627. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127627
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. Bmj. 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR et al (1999) Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 45(2):172–180. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.45.2.172
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj. 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Mills EJ, Thorlund K, Ioannidis JP (2013) Demystifying trial networks and network meta-analysis. Bmj. 346:f2914. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f2914
Rausa E, Kelly ME, Asti E, Aiolfi A, Bonitta G, Bonavina L (2019) Right hemicolectomy: a network meta-analysis comparing open, laparoscopic-assisted, total laparoscopic, and robotic approach. Surg Endosc 33(4):1020–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6592-3
Warn DE, Thompson SG, Spiegelhalter DJ (2002) Bayesian random effects meta-analysis of trials with binary outcomes: methods for the absolute risk difference and relative risk scales. Stat Med 21(11):1601–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1189
Friede T, Rover C, Wandel S, Neuenschwander B (2017) Meta-analysis of few small studies in orphan diseases. Res Synth Methods 8(1):79–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1217
Turner RM, Davey J, Clarke MJ, Thompson SG, Higgins JP (2012) Predicting the extent of heterogeneity in meta-analysis, using empirical data from the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Int J Epidemiol 41(3):818–827. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dys041
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj. 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Smith BJ (2007) boa: an R package for MCMC output convergence assessment and posterior inference. J Stat Softw 21:1–37. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v021.i11
Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE (2010) Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. Stat Med 29(7-8):932–944. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3767
Salanti G, Del Giovane C, Chaimani A, Caldwell DM, Higgins JP (2014) Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS One 9(7):e99682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099682
Higgins JPT GSCHfSRoIVuMTCC, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Plummer, Gibbs MJApfaoBgmu, sampling, Distributed PotrIWo, Computing S, Vienna AM
R Development Core Team (2015) A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Anvari M, Allen C, Marshall J et al (2006) A randomized controlled trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitors for treatment of patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease: one-year follow-up. Surg Innov 13(4):238–249. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350606296389
Baigrie RJ, Cullis SN, Ndhluni AJ, Cariem A (2005) Randomized double-blind trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus anterior partial fundoplication. Br J Surg 92(7):819–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4803
Bell R, Lipham J, Louie BE et al (2020) Magnetic sphincter augmentation superior to proton pump inhibitors for regurgitation in a 1-year randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(8):1736–1743.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.056
Booth MI, Stratford J, Jones L, Dehn TC (2008) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic total (Nissen) versus posterior partial (Toupet) fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease based on preoperative oesophageal manometry. Br J Surg 95(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6047
Chrysos E, Tsiaoussis J, Zoras OJ et al (2003) Laparoscopic surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease patients with impaired esophageal peristalsis: total or partial fundoplication? J Am Coll Surg 197(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1072-7515(03)00151-0
Corley DA, Katz P, Wo JM et al (2003) Improvement of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms after radiofrequency energy: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 125(3):668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01052-7
Coron E, Sebille V, Cadiot G et al (2008) Clinical trial: radiofrequency energy delivery in proton pump inhibitor-dependent gastro-oesophageal reflux disease patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28(9):1147–1158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03790.x
Daud WN, Thompson SK, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Martin IJ, Watson DI (2015) Randomized controlled trial of laparoscopic anterior 180° partial versus posterior 270° partial fundoplication. ANZ J Surg 85(9):668–672. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.12476
Djerf P, Montgomery A, Hallerbäck B, Håkansson HO, Johnsson F (2016) One- and ten-year outcome of laparoscopic anterior 120° versus total fundoplication: a double-blind, randomized multicenter study. Surg Endosc 30(1):168–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4177-y
Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S et al (2011) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery vs esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. Jama. 305(19):1969–1977. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.626
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Granderath UM, Pointner R (2007) Gas-related symptoms after laparoscopic 360 degrees Nissen or 270 degrees Toupet fundoplication in gastrooesophageal reflux disease patients with aerophagia as comorbidity. Dig Liver Dis 39(4):312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2006.11.011
Guérin E, Bétroune K, Closset J et al (2007) Nissen versus Toupet fundoplication: results of a randomized and multicenter trial. Surg Endosc 21(11):1985–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9474-7
Hagedorn C, Jönson C, Lönroth H, Ruth M, Thune A, Lundell L (2003) Efficacy of an anterior as compared with a posterior laparoscopic partial fundoplication: results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg 238(2):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000080821.08262.53
Håkanson BS, Lundell L, Bylund A, Thorell A (2019) Comparison of laparoscopic 270° posterior partial fundoplication vs total fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg 154(6):479–486. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0047
Håkansson B, Montgomery M, Cadiere GB et al (2015) Randomised clinical trial: transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. sham intervention to control chronic GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 42(11-12):1261–1270. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13427
Kalapala R, Shah H, Nabi Z, Darisetty S, Talukdar R, Nageshwar RD (2017) Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease using radiofrequency ablation (Stretta procedure): an interim analysis of a randomized trial. Indian J Gastroenterol 36(5):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-017-0796-7
Koch OO, Kaindlstorfer A, Antoniou SA, Luketina RR, Emmanuel K, Pointner R (2013) Comparison of results from a randomized trial 1 year after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplications. Surg Endosc 27(7):2383–2390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2803-0
Laws HL, Clements RH, Swillie CM (1997) A randomized, prospective comparison of the Nissen fundoplication versus the Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 225(6):647–653; discussion 654. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199706000-00002
Mahon D, Rhodes M, Decadt B et al (2005) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication compared with proton-pump inhibitors for treatment of chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 92(6):695–699. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4934
Mickevicius A, Endzinas Z, Kiudelis M et al (2008) Influence of wrap length on the effectiveness of Nissen and Toupet fundoplication: a prospective randomized study. Surg Endosc 22(10):2269–2276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9852-9
Mucio M, Rojano M, Herrera JJ et al (2012) Novel surgical concept in antireflux surgery: long-term outcomes comparing 3 different laparoscopic approaches. Surgery. 151(1):84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2011.06.024
Qin M, Ding G, Yang H (2013) A clinical comparison of laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23(7):601–604. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2012.0485
Raue W, Ordemann J, Jacobi CA, Menenakos C, Buchholz A, Hartmann J (2011) Nissen versus Dor fundoplication for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a blinded randomized clinical trial. Dig Surg 28(1):80–86. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323630
Roks DJ, Koetje JH, Oor JE, Broeders JA, Nieuwenhuijs VB, Hazebroek EJ (2017) Randomized clinical trial of 270° posterior versus 180° anterior partial laparoscopic fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 104(7):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10500
Rydberg L, Ruth M, Abrahamsson H, Lundell L (1999) Tailoring antireflux surgery: a randomized clinical trial. World J Surg 23(6):612–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00012356
Shaw JM, Bornman PC, Callanan MD, Beckingham IJ, Metz DC (2010) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic Nissen and laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a prospective, randomized trial. Surg Endosc 24(4):924–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0700-3
Trad KS, Barnes WE, Simoni G et al (2015) Transoral incisionless fundoplication effective in eliminating GERD symptoms in partial responders to proton pump inhibitor therapy at 6 months: the TEMPO Randomized Clinical Trial. Surg Innov 22(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350614526788
Wang B, Zhang W, Liu S, Du Z, Shan C, Qiu M (2015) A Chinese randomized prospective trial of floppy Nissen and Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal disease. Int J Surg 23(Pt A):35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.08.074
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Lally C et al (2004) Multicenter, prospective, double-blind, randomized trial of laparoscopic nissen vs anterior 90 degrees partial fundoplication. Arch Surg 139(11):1160–1167. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.139.11.1160
Witteman BP, Conchillo JM, Rinsma NF et al (2015) Randomized controlled trial of transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. proton pump inhibitors for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 110(4):531–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2015.28
Cuijpers P, Weitz E, Cristea IA, Twisk J (2017) Pre-post effect sizes should be avoided in meta-analyses. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci 26(4):364–368. https://doi.org/10.1017/s2045796016000809
Bittner HB, Meyers WC, Brazer SR, Pappas TN (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: operative results and short-term follow-up. Am J Surg 167(1):193–198; discussion 199-200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9610(94)90073-6
Strate U, Emmermann A, Fibbe C, Layer P, Zornig C (2008) Laparoscopic fundoplication: Nissen versus Toupet two-year outcome of a prospective randomized study of 200 patients regarding preoperative esophageal motility. Surg Endosc 22(1):21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9546-8
Watson A, Jenkinson LR, Ball CS, Barlow AP, Norris TL (1991) A more physiological alternative to total fundoplication for the surgical correction of resistant gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 78(9):1088–1094. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.1800780918
Mittal RK, Rochester DF, McCallum RW (1987) Effect of the diaphragmatic contraction on lower oesophageal sphincter pressure in man. Gut. 28(12):1564–1568. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.28.12.1564
Riegler M, Schoppman SF, Bonavina L, Ashton D, Horbach T, Kemen M (2015) Magnetic sphincter augmentation and fundoplication for GERD in clinical practice: one-year results of a multicenter, prospective observational study. Surg Endosc 29(5):1123–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3772-7
Rona KA, Reynolds J, Schwameis K et al (2017) Efficacy of magnetic sphincter augmentation in patients with large hiatal hernias. Surg Endosc 31(5):2096–2102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5204-3
Buckley FP 3rd, Bell RCW, Freeman K, Doggett S, Heidrick R (2018) Favorable results from a prospective evaluation of 200 patients with large hiatal hernias undergoing LINX magnetic sphincter augmentation. Surg Endosc 32(4):1762–1768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5859-4
Alicuben ET, Bell RCW, Jobe BA et al (2018) Worldwide experience with erosion of the magnetic sphincter augmentation device. J Gastrointest Surg 22(8):1442–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-018-3775-0
Lipham JC, Taiganides PA, Louie BE, Ganz RA, DeMeester TR (2015) Safety analysis of first 1000 patients treated with magnetic sphincter augmentation for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus 28(4):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/dote.12199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ER, MR, and AA did the literature search. ER, MK, and MV formed the study design. Data collection done by AA, DF. ER, GB, DB analyzed the data. ER, MV, and GB interpreted the data. ER, MV, and MR wrote the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Paper is containing original research and has not been submitted/published earlier in any journal and is not being considered for publication elsewhere.
Supplementary information

Supplementary Figure 1.
Forest plots of network meta-analysis estimates the RR for E improvement in pH<4, F improvement in LES pressure and, D PPI discontinuation (PNG 90 kb)

Supplementary Figure 2.
The Ranking plot created using the rankogram function from R package applied to the three surgical approaches illustrating the empirical probability that each treatment is ranked 1st through 7th (left to right) for (E) improvement in pH<4 and (G) PPI discontinuation; and ranked 1st through 5th for (F) improvement in LES pressure. The abscissa axis shows the different treatments. The ordinate axis shows the probability (%) of ranking better (higher rankings associated with smaller outcomes values). (PNG 49 kb)
Supplementary Table 1.
Definition for treatment failure for each enrolled study (DOCX 16 kb)
Supplementary Table 2.
Description of the assessment tools for subjective symptoms in each enrolled study (DOCX 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rausa, E., Ferrari, D., Kelly, M.E. et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication compared to endoscopic and surgical procedures for GERD treatment: a randomized trials network meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 408, 52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-023-02774-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-023-02774-y