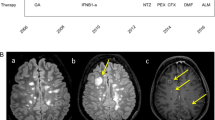
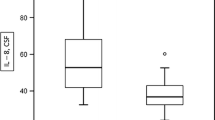
Abstract
Neurosarcoidosis (NS) represents an important differential diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS). However, thus far no reliable laboratory marker of neurosarcoidosis exists. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of soluble interleukin 2 receptor (sIL2-R) distinguish NS and other inflammatory disorders of the central nervous system. For this purpose, 139 paired CSF and serum samples from 11 patients with NS, 21 with MS, 10 with CNS vasculitis, 22 with bacterial meningitis, 17 with viral meningitis/encephalitis, seven with neurotuberculosis, and 18 healthy donors were assessed for sIL2-R using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We found that sIL2-R CSF levels above 150 pg/ml identified untreated NS patients with an overall accuracy of 93% against a group of non-infectious CNS-diseases. Furthermore, an increase in sIL2-R in the CSF was associated with and preceded the outbreak of new neurological symptoms. In conclusion, these findings suggest that sIL2-R measurement in the CSF may be a valuable tool in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with suspected and proven neurosarcoidosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitaichi M (1998) Prevalence of sarcoidosis around the world. Diffuse Lung Dis 15:16–18
Hagerstrand I, Linell F (1964) The prevalence of sarcoidosis in the autopsy material from a Swedish town. Acta Med Scand Suppl 425:171–174
Manz HJ (1983) Pathobiology of neurosarcoidosis and clinicopathologic correlation. Can J Neurol Sci 10:50–55
Mayock RL, Bertrand P, Morrison CE, Scott JH (1963) Manifestation of sarcoidosis: analysis of 145 Patients, with a review of nine series selected in the literature. Am J Med 35:67–89
Stern BJ, Krumholz A, Johns C et al (1985) Sarcoidosis and its neurological manifestations. Arch Neurol 42:909–917
Vinas FC, Rengachary S (2001) Diagnosis and management of neurosarcoidosis. J Clin Neurosci 8:505–513
Zajicek JP, Scolding NJ, Foster O et al (1999) Central nervous system sarcoidosis-diagnosis and management. Q J Med 92:103–117
Khoury J, Wellik KE, Demaerschalk BM, Wingerchuk DM (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme for diagnosis of central nervous system sarcoidosis. Neurologist 15:108–111
Marangoni S, Argentiero V, Tavolato B (2006) Neurosarcoidosis: clinical description of 7 cases with a proposal for a new diagnostic strategy. J Neurol 253:488–495
Joseph FG, Scolding NJ (2009) Neurosarcoidosis: a pilot study of 30 new cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:297–304
Ziegenhagen MW, Benner UK, Zissel G et al (1997) Sarcoidosis: TNF-alpha release from alveolar macrophages and serum level of sIL-2R are prognostic markers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:1586–1592
Grutters JC, Fellrath JM, Mulder L et al (2003) Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor measurement in patients with sarcoidosis: a clinical evaluation. Chest 124:186–195
Keicho N, Kitamura K, Takaku F, Yotsumoto H (1990) Serum concentration of soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a sensitive parameter of disease activity in sarcoidosis. Chest 98:1125–1129
Muller-Quernheim J, Pfeifer S, Strausz J, Ferlinz R (1991) Correlation of clinical and immunologic parameters of the inflammatory activity of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:1322–1329
Rubin LA, Kurman CC, Fritz ME et al (1985) Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol 135:3172–3177
Acknowledgments
We thank Hendrik Lindeman for excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petereit, HF., Reske, D., Tumani, H. et al. Soluble CSF interleukin 2 receptor as indicator of neurosarcoidosis. J Neurol 257, 1855–1863 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5623-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5623-3