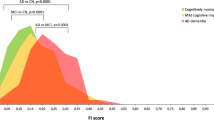
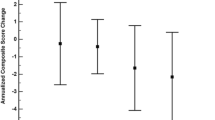Abstract
The diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the oldest-old is complicated by the increasing prevalence of age-related neurofibrillary tangles, plaques and non-AD pathologies such as cerebrovascular disease (CVD), hippocampal sclerosis (HS), aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG), as well as TDP-43 and Lewy pathology. The contribution of these non-AD pathologies to dementia and cognitive resilience is unclear. We assessed the level of AD neuropathologic change (ADNPC) and non-AD pathology in 185 participants enrolled in The 90+ Study with available cognitive assessments and brain tissue. Logistic regression models—adjusting for age, sex and education—determined the association between each pathology and dementia or between subgroups. 53% had dementia, primarily AD or mixed AD; 23% had cognitive impairment without dementia (CIND); 23% were not impaired. Both AD and non-AD pathology was prevalent. 100% had tangles, 81% had plaques, and both tangles and plaques associated with dementia. ARTAG distributed across limbic (70%), brainstem (39%) and cortical regions (24%). 49% had possible CVD and 26% had definite CVD, while HS was noted in 15%. Cortical ARTAG, CVD and HS were each associated with dementia, but limbic and brainstem ARTAGs were not. TDP-43 and Lewy pathologies were found in 36 and 17% and both associated with dementia. No pathology distinguished CIND and the not impaired. By NIA-AA criteria and dementia status, the cohort was subdivided into four groups: those with minimal ADNPC included the not dementia (ND) and Not AD dementia groups; and those with significant ADNPC included the Resilient without dementia and AD dementia groups. Compared to the ND group, the Not AD dementia group had more HS, cortical ARTAG, TDP-43, and Lewy pathology. Compared to the AD dementia group, the Resilient group had less CVD, no HS and less cortical ARTAG, TDP-43 and Lewy pathology. Our findings imply that reductions in non-AD pathologies including CVD contribute to cognitive resilience in the oldest-old.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell CC (1994) DSM-IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. JAMA 272:828–829. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1994.03520100096046
Bender R, Lange S (2001) Adjusting for multiple testing–when and how? J Clin Epidemiol 54:343–349
Boluda S, Iba M, Zhang B, Raible KM, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2015) Differential induction and spread of tau pathology in young PS19 tau transgenic mice following intracerebral injections of pathological tau from Alzheimer’s disease or corticobasal degeneration brains. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 129:221–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1373-0
Boluda S, Toledo JB, Irwin DJ, Raible KM, Byrne MD, Lee EB, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2014) A comparison of Aβ amyloid pathology staging systems and correlation with clinical diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 128:543–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1308-9
Braak H, Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K (2011) Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease: age categories from 1 to 100 years. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70:960–969. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e318232a379
Brenowitz WD, Monsell SE, Schmitt FA, Kukull WA, Nelson PT (2014) Hippocampal sclerosis of aging is a key Alzheimer’s disease mimic: clinical-pathologic correlations and comparisons with both alzheimer’s disease and non-tauopathic frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Alzheimers Dis JAD 39:691–702. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-131880
Buchman AS, Shulman JM, Nag S, Leurgans SE, Arnold SE, Morris MC, Schneider JA, Bennett DA (2012) Nigral pathology and parkinsonian signs in elders without Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 71:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22588
Clavaguera F, Akatsu H, Fraser G, Crowther RA, Frank S, Hench J, Probst A, Winkler DT, Reichwald J, Staufenbiel M, Ghetti B, Goedert M, Tolnay M (2013) Brain homogenates from human tauopathies induce tau inclusions in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:9535–9540. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1301175110
Corrada MM, Berlau DJ, Kawas CH (2012) A population-based clinicopathological study in the oldest-old: the 90+ study. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:709–717
Corrada MM, Sonnen JA, Kim RC, Kawas CH (2016) Microinfarcts are common and strongly related to dementia in the oldest-old: the 90 + study. Alzheimers Dement J Alzheimers Assoc 12:900–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.04.006
Crary JF, Trojanowski JQ, Schneider JA, Abisambra JF, Abner EL, Alafuzoff I, Arnold SE, Attems J, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW, Gearing M, Grinberg LT, Hof PR, Hyman BT, Jellinger K, Jicha GA, Kovacs GG, Knopman DS, Kofler J, Kukull WA, Mackenzie IR, Masliah E, McKee A, Montine TJ, Murray ME, Neltner JH, Santa-Maria I, Seeley WW, Serrano-Pozo A, Shelanski ML, Stein T, Takao M, Thal DR, Toledo JB, Troncoso JC, Vonsattel JP, White CL, Wisniewski T, Woltjer RL, Yamada M, Nelson PT (2014) Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 128:755–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1349-0
Cykowski MD, Powell SZ, Schulz PE, Takei H, Rivera AL, Jackson RE, Roman G, Jicha GA, Nelson PT (2017) Hippocampal sclerosis in older patients: practical examples and guidance with a focus on cerebral age-related TDP-43 with sclerosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 141:1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2016-0469-SA
Deramecourt V, Slade JY, Oakley AE, Perry RH, Ince PG, Maurage C-A, Kalaria RN (2012) Staging and natural history of cerebrovascular pathology in dementia. Neurology 78:1043–1050. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824e8e7f
Dolan D, Troncoso J, Resnick SM, Crain BJ, Zonderman AB, O’Brien RJ (2010) Age, Alzheimer’s disease and dementia in the Baltimore Longitudinal study of ageing. Brain J Neurol 133:2225–2231. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq141
Elobeid A, Libard S, Leino M, Popova SN, Alafuzoff I (2016) Altered proteins in the aging brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75:316–325. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlw002
Flanagan M, Larson EB, Latimer CS, Cholerton B, Crane PK, Montine KS, White LR, Keene CD, Montine TJ (2016) Clinical-pathologic correlations in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:945–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.08.019
He Z, Guo JL, McBride JD, Narasimhan S, Kim H, Changolkar L, Zhang B, Gathagan RJ, Yue C, Dengler C, Stieber A, Nitla M, Coulter DA, Abel T, Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2017) Amyloid-β plaques enhance Alzheimer’s brain tau-seeded pathologies by facilitating neuritic plaque tau aggregation. Nat Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4443
Hokkanen SRK, Hunter S, Polvikoski TM, Keage HAD, Minett T, Matthews FE, Brayne C, MRC CFAS and CC75C Study Group (2017) Hippocampal sclerosis, hippocampal neuron loss patterns and Tdp-43 in the aged population. Brain Pathol Zurich Switz. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12556
Josephs KA, Murray ME, Whitwell JL, Parisi JE, Petrucelli L, Jack CR, Petersen RC, Dickson DW (2014) Staging TDP-43 pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 127:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1211-9
Kapasi A, DeCarli C, Schneider JA (2017) Impact of multiple pathologies on the threshold for clinically overt dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1717-7
Kawas CH, Kim RC, Sonnen JA, Bullain SS, Trieu T, Corrada MM (2015) Multiple pathologies are common and related to dementia in the oldest-old: the 90+ study. Neurology 85:535–542. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001831
Kent DM, Rothwell PM, Ioannidis JPA, Altman DG, Hayward RA (2010) Assessing and reporting heterogeneity in treatment effects in clinical trials: a proposal. Trials 11:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-11-85
Kovacs GG, Ferrer I, Grinberg LT, Alafuzoff I, Attems J, Budka H, Cairns NJ, Crary JF, Duyckaerts C, Ghetti B, Halliday GM, Ironside JW, Love S, Mackenzie IR, Munoz DG, Murray ME, Nelson PT, Takahashi H, Trojanowski JQ, Ansorge O, Arzberger T, Baborie A, Beach TG, Bieniek KF, Bigio EH, Bodi I, Dugger BN, Feany M, Gelpi E, Gentleman SM, Giaccone G, Hatanpaa KJ, Heale R, Hof PR, Hofer M, Hortobágyi T, Jellinger K, Jicha GA, Ince P, Kofler J, Kövari E, Kril JJ, Mann DM, Matej R, McKee AC, McLean C, Milenkovic I, Montine TJ, Murayama S, Lee EB, Rahimi J, Rodriguez RD, Rozemüller A, Schneider JA, Schultz C, Seeley W, Seilhean D, Smith C, Tagliavini F, Takao M, Thal DR, Toledo JB, Tolnay M, Troncoso JC, Vinters HV, Weis S, Wharton SB, White CL, Wisniewski T, Woulfe JM, Yamada M, Dickson DW (2016) Aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG): harmonized evaluation strategy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 131:87–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1509-x
Kovacs GG, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2017) Protein astrogliopathies in human neurodegenerative diseases and aging. Brain Pathol Zurich Switz 27:675–690. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12536
Kovacs GG, Molnár K, László L, Ströbel T, Botond G, Hönigschnabl S, Reiner-Concin A, Palkovits M, Fischer P, Budka H (2011) A peculiar constellation of tau pathology defines a subset of dementia in the elderly. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 122:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0819-x
Kovacs GG, Robinson JL, Xie SX, Lee EB, Grossman M, Wolk DA, Irwin DJ, Weintraub D, Kim CF, Schuck T, Yousef A, Wagner ST, Suh E, Van Deerlin VM, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2017) Evaluating the patterns of aging-related tau astrogliopathy unravels novel insights into brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76:270–288. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlx007
Kovacs GG, Xie SX, Lee EB, Robinson JL, Caswell C, Irwin DJ, Toledo JB, Johnson VE, Smith DH, Alafuzoff I, Attems J, Bencze J, Bieniek KF, Bigio EH, Bodi I, Budka H, Dickson DW, Dugger BN, Duyckaerts C, Ferrer I, Forrest SL, Gelpi E, Gentleman SM, Giaccone G, Grinberg LT, Halliday GM, Hatanpaa KJ, Hof PR, Hofer M, Hortobágyi T, Ironside JW, King A, Kofler J, Kövari E, Kril JJ, Love S, Mackenzie IR, Mao Q, Matej R, McLean C, Munoz DG, Murray ME, Neltner J, Nelson PT, Ritchie D, Rodriguez RD, Rohan Z, Rozemuller A, Sakai K, Schultz C, Seilhean D, Smith V, Tacik P, Takahashi H, Takao M, Rudolf Thal D, Weis S, Wharton SB, White CL, Woulfe JM, Yamada M, Trojanowski JQ (2017) Multisite assessment of aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76:605–619. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlx041
Lace G, Ince PG, Brayne C, Savva GM, Matthews FE, de Silva R, Simpson JE, Wharton SB (2012) Mesial temporal astrocyte tau pathology in the MRC-CFAS ageing brain cohort. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 34:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1159/000341581
McKeith IG, Boeve BF, Dickson DW, Halliday G, Taylor J-P, Weintraub D, Aarsland D, Galvin J, Attems J, Ballard CG, Bayston A, Beach TG, Blanc F, Bohnen N, Bonanni L, Bras J, Brundin P, Burn D, Chen-Plotkin A, Duda JE, El-Agnaf O, Feldman H, Ferman TJ, Ffytche D, Fujishiro H, Galasko D, Goldman JG, Gomperts SN, Graff-Radford NR, Honig LS, Iranzo A, Kantarci K, Kaufer D, Kukull W, Lee VMY, Leverenz JB, Lewis S, Lippa C, Lunde A, Masellis M, Masliah E, McLean P, Mollenhauer B, Montine TJ, Moreno E, Mori E, Murray M, O’Brien JT, Orimo S, Postuma RB, Ramaswamy S, Ross OA, Salmon DP, Singleton A, Taylor A, Thomas A, Tiraboschi P, Toledo JB, Trojanowski JQ, Tsuang D, Walker Z, Yamada M, Kosaka K (2017) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: fourth consensus report of the DLB consortium. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004058
Montine TJ, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW, Duyckaerts C, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Mirra SS, Nelson PT, Schneider JA, Thal DR, Trojanowski JQ, Vinters HV, Hyman BT, National Institute on Aging, Alzheimer’s Association (2012) National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 123:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0910-3
Munoz DG, Woulfe J, Kertesz A (2007) Argyrophilic thorny astrocyte clusters in association with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in possible primary progressive aphasia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 114:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0266-x
Narasimhan S, Guo JL, Changolkar L, Stieber A, McBride JD, Silva LV, He Z, Zhang B, Gathagan RJ, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2017) Pathological tau strains from human brains recapitulate the diversity of tauopathies in nontransgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 37:11406–11423. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1230-17.2017
Nelson PT, Alafuzoff I, Bigio EH, Bouras C, Braak H, Cairns NJ, Castellani RJ, Crain BJ, Davies P, Del Tredici K, Duyckaerts C, Frosch MP, Haroutunian V, Hof PR, Hulette CM, Hyman BT, Iwatsubo T, Jellinger KA, Jicha GA, Kövari E, Kukull WA, Leverenz JB, Love S, Mackenzie IR, Mann DM, Masliah E, McKee AC, Montine TJ, Morris JC, Schneider JA, Sonnen JA, Thal DR, Trojanowski JQ, Troncoso JC, Wisniewski T, Woltjer RL, Beach TG (2012) Correlation of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes with cognitive status: a review of the literature. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:362–381. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e31825018f7
Nelson PT, Jicha GA, Schmitt FA, Liu H, Davis DG, Mendiondo MS, Abner EL, Markesbery WR (2007) Clinicopathologic correlations in a large Alzheimer disease center autopsy cohort: neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles “do count” when staging disease severity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:1136–1146. https://doi.org/10.1097/nen.0b013e31815c5efb
Nelson PT, Trojanowski JQ, Abner EL, Al-Janabi OM, Jicha GA, Schmitt FA, Smith CD, Fardo DW, Wang W-X, Kryscio RJ, Neltner JH, Kukull WA, Cykowski MD, Van Eldik LJ, Ighodaro ET (2016) “New Old Pathologies”: Ad, PART, and Cerebral Age-Related TDP-43 With Sclerosis (CARTS). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75:482–498. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlw033
Neltner JH, Abner EL, Jicha GA, Schmitt FA, Patel E, Poon LW, Marla G, Green RC, Davey A, Johnson MA, Jazwinski SM, Kim S, Davis D, Woodard JL, Kryscio RJ, Van Eldik LJ, Nelson PT (2016) Brain pathologies in extreme old age. Neurobiol Aging 37:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.009
Neuropathology Group. Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Aging Study (2001) Pathological correlates of late-onset dementia in a multicentre, community-based population in England and Wales. Neuropathology Group of the Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study (MRC CFAS). Lancet Lond Engl 357:169–175
Robinson JL, Geser F, Corrada MM, Berlau DJ, Arnold SE, Lee VM-Y, Kawas CH, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Neocortical and hippocampal amyloid-β and tau measures associate with dementia in the oldest-old. Brain J Neurol 134:3708–3715. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr308
Robinson JL, Molina-Porcel L, Corrada MM, Raible K, Lee EB, Lee VM-Y, Kawas CH, Trojanowski JQ (2014) Perforant path synaptic loss correlates with cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease in the oldest-old. Brain J Neurol 137:2578–2587. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu190
Santos CY, Snyder PJ, Wu W-C, Zhang M, Echeverria A, Alber J (2017) Pathophysiologic relationship between Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular disease, and cardiovascular risk: a review and synthesis. Alzheimers Dement Diagn Assess Dis Monit 7:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2017.01.005
Savva GM, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study (2009) Age, neuropathology, and dementia. N Engl J Med 360:2302–2309. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa0806142
Schmidt ML, DiDario AG, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1994) An extensive network of PHF tau-rich dystrophic neurites permeates neocortex and nearly all neuritic and diffuse amyloid plaques in Alzheimer disease. FEBS Lett 344:69–73
Schultz C, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, Braak H (2004) High prevalence of thorn-shaped astrocytes in the aged human medial temporal lobe. Neurobiol Aging 25:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00113-1
Thal DR, Capetillo-Zarate E, Del Tredici K, Braak H (2006) The development of amyloid beta protein deposits in the aged brain. Sci Aging Knowl Environ SAGE KE 2006:re1. https://doi.org/10.1126/sageke.2006.6.re1
Vos SJB, van Boxtel MPJ, Schiepers OJG, Deckers K, de Vugt M, Carrière I, Dartigues J-F, Peres K, Artero S, Ritchie K, Galluzzo L, Scafato E, Frisoni GB, Huisman M, Comijs HC, Sacuiu SF, Skoog I, Irving K, O’Donnell CA, Verhey FRJ, Visser PJ, Köhler S (2017) Modifiable risk factors for prevention of dementia in midlife, late life and the oldest-old: validation of the LIBRA index. J Alzheimers Dis JAD 58:537–547. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-161208
Wharton SB, Minett T, Drew D, Forster G, Matthews F, Brayne C, Ince PG, MRC Cognitive Function and Ageing Neuropathology Study Group (2016) Epidemiological pathology of Tau in the ageing brain: application of staging for neuropil threads (BrainNet Europe protocol) to the MRC cognitive function and ageing brain study. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0275-x
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the participants and their relatives, testers and examiners of The 90+ Study, and the staff of the UCI brain repository for making this study possible. We also thank Terry Schuck and Katie Casalnova for their assistance with this study. Funding from the National Institutes of Health (AG10124, AG16573, AG17586, R01AG021055, R01AG042444, P50AG16573 and MH64045) supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, J.L., Corrada, M.M., Kovacs, G.G. et al. Non-Alzheimer’s contributions to dementia and cognitive resilience in The 90+ Study. Acta Neuropathol 136, 377–388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1872-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1872-5