Abstract
Purpose
The gut–liver interaction suggests that modification of gut bacterial flora using probiotics and synbiotics may improve liver function. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to clarify the effect of probiotics and synbiotics consumption on the serum concentration of liver function enzymes.
Methods
PubMed (MEDLINE), Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, and Cochrane Library (Central) were searched from 1980 to August 2017 for studies where adults consumed probiotics and/or synbiotics in controlled trials and changes in liver function enzymes were examined.
Results
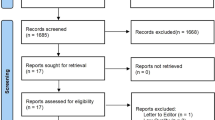
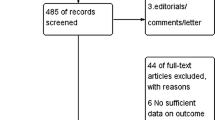
A total of 17 studies (19 trials) were included in the meta-analysis. Random effects meta-analyses were applied. Probiotics and synbiotics significantly reduced serum alanine aminotransferase [− 8.05 IU/L, 95% confidence interval (CI) − 13.07 to − 3.04; p = 0.002]; aspartate aminotransferase (− 7.79 IU/L, 95% CI: − 13.93 to − 1.65; p = 0.02) and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (− 8.40 IU/L, 95% CI − 12.61 to − 4.20; p < 0.001). Changes in the serum concentration of alkaline phosphatase and albumin did not reach a statistically significant level. Changes to bilirubin levels were in favour of the control group (0.95 μmol/L, 95% CI 0.48–1.42; p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis suggested the existence of liver disease at baseline, synbiotics supplementation and duration of supplementation ≥ 8 weeks resulted in more pronounced improvement in liver function enzymes than their counterparts.
Conclusions
Probiotics and synbiotics may be suggested as supplements to improve serum concentration of liver enzymes, especially when synbiotics administered for a period ≥ 8 weeks and in individuals with liver disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engen PA, Green SJ, Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Keshavarzian A (2015) The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Alcohol Effects on the Composition of Intestinal Microbiota. Alcohol Res Curr Rev 37 (2): 223–236
Iannitti T, Palmieri B (2010) Therapeutical use of probiotic formulations in clinical practice. Clin Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland) 29(6):701–725. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2010.05.004
Aureli P, Capurso L, Castellazzi AM, Clerici M, Giovannini M, Morelli L, Poli A, Pregliasco F, Salvini F, Zuccotti GV (2011) Probiotics and health: an evidence-based review. Pharmacol Res 63(5):366–376. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.02.006
Conlon MA, Bird AR (2015) The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 7(1):17–44. doi:10.3390/nu7010017
Sung H, Kim SW, Hong M, Suk KT (2016) Microbiota-based treatments in alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 22(29):6673–6682. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6673
Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Wang B, Chen Y, Lei D, Wang Y, Zhu B, Li L (2011) Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 54(2):562–572. doi:10.1002/hep.24423
Sharma V, Garg S, Aggarwal S (2013) Probiotics and liver disease. Perm J 17(4):62–67. doi:10.7812/tpp/12-144
Liu J, Wu D, Ahmed A, Li X, Ma Y, Tang L, Mo D, Ma Y, Xin Y (2012) Comparison of the gut microbe profiles and numbers between patients with liver cirrhosis and healthy individuals. Curr Microbiol 65(1):7–13. doi:10.1007/s00284-012-0105-8
Boursier J, Mueller O, Barret M, Machado M, Fizanne L, Araujo-Perez F, Guy CD, Seed PC, Rawls JF, David LA, Hunault G, Oberti F, Cales P, Diehl AM (2016) The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 63(3):764–775. doi:10.1002/hep.28356
Gkolfakis P, Dimitriadis G, Triantafyllou K (2015) Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int HBPD INT 14(6):572–581
Zhu L, Baker SS, Gill C, Liu W, Alkhouri R, Baker RD, Gill SR (2013) Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: a connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 57(2):601–609. doi:10.1002/hep.26093
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C, Burcelin RG, Tuohy KM, Gibson GR, Delzenne NM (2007) Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 50(11):2374–2383. doi:10.1007/s00125-007-0791-0
Kirpich IA, Marsano LS, McClain CJ (2015) Gut-liver axis, nutrition, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Biochem 48(13–14): 923–930. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.06.023
Pereira DI, Gibson GR (2002) Cholesterol assimilation by lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from the human gut. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(9):4689–4693
Rodes L, Khan A, Paul A, Coussa-Charley M, Marinescu D, Tomaro-Duchesneau C, Shao W, Kahouli I, Prakash S (2013) Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and inflammatory cytokines: an in vitro study using a human colonic microbiota model. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4):518 – 26
Madsen K, Cornish A, Soper P, McKaigney C, Jijon H, Yachimec C, Doyle J, Jewell L, De Simone C (2001) Probiotic bacteria enhance murine and human intestinal epithelial barrier function. Gastroenterology 121(3):580–591
Gratz SW, Mykkanen H, El-Nezami HS (2010) Probiotics and gut health: a special focus on liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 16(4):403–410
Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Hylemon PB, Sanyal AJ, Puri P, Sterling RK, Luketic V, Stravitz RT, Siddiqui MS, Fuchs M, Thacker LR, Wade JB, Daita K, Sistrun S, White MB, Noble NA, Thorpe C, Kakiyama G, Pandak WM, Sikaroodi M, Gillevet PM (2014) Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 39(10):1113–1125. doi:10.1111/apt.12695
Eslamparast T, Poustchi H, Zamani F, Sharafkhah M, Malekzadeh R, Hekmatdoost A (2014) Synbiotic supplementation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am J Clin Nutr 99(3):535–542. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.068890
Sang Hak H, Ki Tae S, Dong Joon K, Moon Young K, Soon Koo B, Young Don K, Gab Jin C, Dae Hee C, Young Lim H, Dong Hoon S, Eun Ji K, Han SH, Suk KT, Kim DJ, Kim MY, Baik SK, Kim YD, Cheon GJ, Choi DH, Ham YL (2015) Effects of probiotics (cultured Lactobacillus subtilis/Streptococcus faecium) in the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis: randomized-controlled multicenter study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(11):1300–1306. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000458
Khalesi S, Sun J, Buys N, Jayasinghe R (2014) Effect of probiotics on blood pressure a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled Trials. Hypertension 64(4):897–903
Menaa F Are Probiotics Pro-Obesity or Potential Anti-Obesity Agents?(2015) J Food Nutr Sci 2 (1): 1
FAO/WHO (2002) Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food, vol 30. World Health Organization, London, Ontario, Canada
Lenoir-Wijnkoop I, Sanders ME, Cabana MD, Caglar E, Corthier G, Rayes N, Sherman PM, Timmerman HM, Vaneechoutte M, Van Loo J, Wolvers DA (2007) Probiotic and prebiotic influence beyond the intestinal tract. Nutr Rev 65(11):469–489
Aller R, Luis DA, Izaola O, Conde R, Gonzalez Sagrado M, Primo D, Fuente B, Gonzalez J (2011) Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 15(9):1090–1095
Kirpich IA, Solovieva NV, Leikhter SN, Shidakova NA, Lebedeva OV, Sidorov PI, Bazhukova TA, Soloviev AG, Barve SS, McClain CJ, Cave M (2008) Probiotics restore bowel flora and improve liver enzymes in human alcohol-induced liver injury: a pilot study. Alcohol (Fayetteville NY) 42(8):675–682. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.08.006
Wolf BW, Wheeler KB, Ataya DG, Garleb KA (1998) Safety and tolerance of Lactobacillus reuteri supplementation to a population infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Food Chem Toxicol 36(12):1085–1094
Ziada DH, Soliman HH, Yamany SA, Hamisa MF, Hasan AM (2013) Can Lactobacillus acidophilus improve minimal hepatic encephalopathy? A neurometabolite study using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arab J Gastroenterol 14(3):116–122. doi:10.1016/j.ajg.2013.08.002
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
van Rosendal SP, Osborne MA, Fassett RG, Coombes JS (2010) Guidelines for glycerol use in hyperhydration and rehydration associated with exercise. Sports Med 40(2):113 – 39
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA (2011) The Cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 343:d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Higgins JP, Green S (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, vol 5. Wiley Online Library
Wong VW, Won GL, Chim AM, Chu WC, Yeung DK, Li KC, Chan HL (2013) Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probiotics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann Hepatol 12(2):256–262
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Nikbakht E, Khalesi S, Singh I, Williams LT, West NP, Colson N (2016) Effect of probiotics and synbiotics on blood glucose: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. Eur J Nutr. doi:10.1007/s00394-016-1300-3
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Fei X (2016) Effect of probiotics on glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicina (B Aires) 52(1):28–34. doi:10.1016/j.medici.2015.11.008
Minelli EB, Benini A (2008) Relationship between number of bacteria and their probiotic effects. Microb Ecol Health Dis 20(4):180–183
Hayes SR, Vargas AJ (2016) Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Explore (New York NY) 12(6):463–466. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2016.08.015
Irwin C, Khalesi S, Cox AJ, Grant G, Davey AK, Bulmer AC, Desbrow B (2017) Effect of 8-weeks prebiotics/probiotics supplementation on alcohol metabolism and blood biomarkers of healthy adults: a Pilot Study. Eur J Nutr. doi:10.1007/s00394-017-1437-8
Cox AJ, West NP, Horn PL, Lehtinen MJ, Koerbin G, Pyne DB, Lahtinen SJ, Fricker PA, Cripps AW (2014) Effects of probiotic supplementation over 5 months on routine haematology and clinical chemistry measures in healthy active adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 68(11):1255–1257. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2014.137
Liu Q, Duan ZP, Ha DK, Bengmark S, Kurtovic J, Riordan SM (2004) Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology (Baltimore Md) 39(5):1441–1449. doi:10.1002/hep.20194
Nabavi S, Rafraf M, Somi MH, Homayouni-Rad A, Asghari-Jafarabadi M (2014) Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on metabolic factors in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Dairy Sci 97(12):7386–7393. doi:10.3168/jds.2014-8500
Vleggaar FP, Monkelbaan JF, van Erpecum KJ (2008) Probiotics in primary sclerosing cholangitis: a randomized placebo-controlled crossover pilot study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(7):688–692. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f5197e
Horvath A, Leber B, Schmerboeck B, Tawdrous M, Zettel G, Hartl A, Madl T, Stryeck S, Fuchs D, Lemesch S, Douschan P, Krones E, Spindelboeck W, Durchschein F, Rainer F, Zollner G, Stauber RE, Fickert P, Stiegler P, Stadlbauer V (2016) Randomised clinical trial: the effects of a multispecies probiotic vs. placebo on innate immune function, bacterial translocation and gut permeability in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 44(9):926–935. doi:10.1111/apt.13788
Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Dong P, Chen M, Duan Z (2010) Probiotic yogurt effects on intestinal flora of patients with chronic liver disease. Nurs Res 59(6):426–432. doi:10.1097/NNR.0b013c3181fa4dc6
Sharma P, Sharma BC, Puri V, Sarin SK (2008) An open-label randomized controlled trial of lactulose and probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(6):506–511. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f3e6f5
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Antic T, Giordano M, Chisari G, Acquaviva R, Mastrojeni S, Malaguarnera G, Mistretta A, Li Volti G, Galvano F (2012) Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 57(2):545–553. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1887-4
Firouzi S, Mohd-Yusof B-N, Majid H-A, Ismail A, Kamaruddin N-A (2015) Effect of microbial cell preparation on renal profile and liver function among type 2 diabetics: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:1–10. doi:10.1186/s12906-015-0952-5
Lefevre M, Racedo SM, Denayrolles M, Ripert G, Desfougeres T, Lobach AR, Simon R, Pelerin F, Justen P, Urdaci MC (2017) Safety assessment of Bacillus subtilis CU1 for use as a probiotic in humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol RTP 83:54–65. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.11.010
Pereg D, Kotliroff A, Gadoth N, Hadary R, Lishner M, Kitay-Cohen Y (2011) Probiotics for patients with compensated liver cirrhosis: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Nutrition (Burbank Los Angeles County Calif) 27(2):177–181. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2010.01.006
Kwak DS, Jun DW, Seo JG, Chung WS, Park S-E, Lee KN, Khalid-Saeed W, Lee HL, Lee OY, Yoon BC, Choi HS (2014) Short-term probiotic therapy alleviates small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, but does not improve intestinal permeability in chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(12):1353–1359. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000214
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Controlled Clin Trials 17(1):1–12
Khalesi S, Irwin C, Schubert M (2015) Flaxseed consumption may reduce blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. J Nutr 145(4):758–765. doi:10.3945/jn.114.205302
Patel R, DuPont HL (2015) New approaches for bacteriotherapy: prebiotics, new-generation probiotics, and synbiotics. Clin infect Dis 60(Suppl 2):S108–S121. doi:10.1093/cid/civ177
Commane DM, Shortt CT, Silvi S, Cresci A, Hughes RM, Rowland IR (2005) Effects of fermentation products of pro- and prebiotics on trans-epithelial electrical resistance in an in vitro model of the colon. Nutr Cancer 51(1):102–109. doi:10.1207/s15327914nc5101_14
Loguercio C, De Simone T, Federico A, Terracciano F, Tuccillo C, Di Chicco M, Carteni M (2002) Gut-liver axis: a new point of attack to treat chronic liver damage? Am J Gastroenterol 97(8):2144–2146. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05942.x
Berg RD, Garlington AW (1979) Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun 23(2):403–411
Wiest R, Lawson M, Geuking M (2014) Pathological bacterial translocation in liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol 60(1):197–209. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.044
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Reddy DN (2015) Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol WJG 21(29):8787–8803. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8787
Li S, Tan H-Y, Wang N, Zhang Z-J, Lao L, Wong C-W, Feng Y (2015) The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16(11):26087–26124. doi:10.3390/ijms161125942
Behnsen J, Deriu E, Sassone-Corsi M, Raffatellu M (2013) Probiotics: properties, examples, and specific applications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3(3):a010074. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a010074
Osman N, Adawi D, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G (2007) Endotoxin- and d-galactosamine-induced liver injury improved by the administration of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and blueberry. Dig Liver Dis 39 (9):849–856. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2007.06.001
Konickova R, Jiraskova A, Zelenka J, Leseticky L, Sticha M, Vitek L (2012) Reduction of bilirubin ditaurate by the intestinal bacterium Clostridium perfringens. Acta Biochim Pol 59(2):289–92
Gasteyger C, Larsen TM, Vercruysse F, Astrup A (2008) Effect of a dietary-induced weight loss on liver enzymes in obese subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 87(5):1141–1147
Rodriguez-Hernandez H, Cervantes-Huerta M, Rodriguez-Moran M, Guerrero-Romero F (2011) Decrease of aminotransferase levels in obese women is related to body weight reduction, irrespective of type of diet. Ann Hepatol 10 (4):486–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalesi, S., Johnson, D.W., Campbell, K. et al. Effect of probiotics and synbiotics consumption on serum concentrations of liver function test enzymes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr 57, 2037–2053 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1568-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1568-y