Abstract
Purpose
Evaluation of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scoring system for classifying multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging findings of the prostate using whole-mount step-section slides as reference standard.
Materials and methods
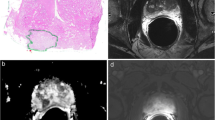
Prospective inclusion of 50 consecutive patients with biopsy-proven prostate cancer (PCa). All patients received a multi-parametric MRI of the prostate, consisting of T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. After prostatectomy, all prostates were prepared as whole-mount step-section slides. For each patient, six lesions were predefined on whole-mount step-sections according to a distinct scheme and the corresponding regions were identified on MRI. Each lesion then was scored on MRI according to PI-RADS by an experienced blinded uro-radiologist and compared with histopathological findings.
Results
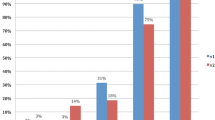
PCa received significant (p < 0.01) higher overall PI-RADS scores (4.10 ± 0.75) compared with benign changes (2.00 ± 0.74). In the peripheral zone, each single modality score showed good diagnostic accuracy for PCa detection (area under the curve [AUC] > 0.90). When combining all single modality scores, an even higher discriminative ability of PCa detection (AUC = 0.97, 95 % CI 0.95–0.99) could be achieved. In contrast, in the transitional zone, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE) showed very low diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.60). Regarding tumor malignancy, no high-grade PCa (Gleason >7a) was present at PI-RADS scores <4 and no Gleason 6 PCa at a PI-RADS score of 5.
Conclusion
The PI-RADS scoring system showed good diagnostic accuracy: Only PI-RADS 4 and 5 showed high-grade PCa. However, it seems necessary to revise the PI-RADS scoring system concerning DCE in the transitional zone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Rooij M, Hamoen EH, Fütterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM (2014) Accuracy of Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection: a meta-AnalysisMaarten. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202(2):343–351. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.11046
Murphy G, Haider M, Ghai S, Sreeharsha B (2013) The expanding role of MRI in prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201(6):1229–1238. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.10178
Dickinson L, Ahmed HU, Allen C, Barentsz JO, Carey B, Futterer JJ, Heijmink SW, Hoskin P, Kirkham AP, Padhani AR, Persad R, Puech P, Punwani S, Sohaib A, Tombal B, Villers A, Emberton M (2012) Scoring systems used for the interpretation and reporting of multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection, localization, and characterization: could standardization lead to improved utilization of imaging within the diagnostic pathway? J Magn Reson Imaging 37(1):48–58. doi:10.1002/jmri.23689
Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G, Rouviere O, Logager V, Fütterer JJ (2012) ESUR prostate MR guidelines. Eur Radiol 22(4):746–757. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2377-y
Schimmöller L, Quentin M, Arsov C, Lanzman RS, Hiester A, Rabenalt R, Antoch G, Albers P, Blondin D (2013) Inter-reader agreement of the ESUR score for prostate MRI using in-bore MRI-guided biopsies as the reference standard. Eur Radiol 23(11):3185–3190. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-2922-y
Rosenkrantz AB, Lim RP, Haghighi M, Somberg MB, Babb JS, Taneja SS (2013) Comparison of interreader reproducibility of the prostate imaging reporting and data system and likert scales for evaluation of multiparametric prostate MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201(4):W612–W618. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.10173
Kuru TH, Roethke MC, Rieker P, Roth W, Fenchel M, Hohenfellner M, Schlemmer HP, Hadaschik BA (2013) Histology core-specific evaluation of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) standardised scoring system of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) of the prostate. BJU Int 112(8):1054–1055. doi:10.1111/bju.12307
Portalez D, Mozer P, Cornud F, Renard-Penna R, Misrai V, Thoulouzan M, Malavaud B (2012) Validation of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology scoring system for prostate cancer diagnosis on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in a cohort of repeat biopsy patients. Eur Urol 62(6):986–996. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.044
Roethke MC, Kuru TH, Schultze S, Tichy D, Kopp-Schneider A, Fenchel M, Schlemmer HP, Hadaschik BA (2014) Evaluation of the ESUR PI-RADS scoring system for multiparametric MRI of the prostate with targeted MR/TRUS fusion-guided biopsy at 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol 24(2):344–352. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-3017-5
Junker D, Schäfer G, Edlinger M, Kremser C, Bektic J, Horninger W, Jaschke W, Aigner F (2013) Evaluation of the PI-RADS scoring system for classifying mpMRI findings in men with suspicion of prostate cancer. Biomed Res Int 2013:252939. doi:10.1155/2013/252939
Roethke M, Blondin D, Schlemmer HP, Franiel T (2013) PI-RADS classification: structured reporting for MRI of the prostate. RoFo. Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Rontgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin 185(3):253–261. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1330270
Hoeks CM, Somford DM, van Oort IM, Vergunst H, Oddens JR, Smits GA, Roobol MJ, Bul M, Hambrock T, Witjes JA, Fütterer JJ, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Barentsz JO (2014) Value of 3-T multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance-guided biopsy for early risk restratification in active surveillance of low-risk prostate cancer: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Invest Radiol 49(3):165–172. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000008
D’Orsi CJ, Newell MS (2007) BI-RADS decoded: detailed guidance on potentially confusing issues. Radiol Clin North Am 45:751–763
Moore CM, Robertson NL, Arsanious N, Middleton T, Villers A, Klotz L, Taneja SS, Emberton M (2013) Image-guided prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance imaging-derived targets: a systematic review. Eur Urol 63(1):125–140. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.004
Haffner J, Lemaitre L, Puech P, Haber GP, Leroy X, Jones JS, Villers A (2011) Role of magnetic resonance imaging before initial biopsy: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging-targeted and systematic biopsy for significant prostate cancer detection. BJU Int 108(8 Pt 2):E171–E178. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10112.x
Parker C, Muston D, Melia J, Moss S, Dearnaley D (2006) A model of the natural history of screen-detected prostate cancer, and the effect of radical treatment on overall survival. Br J Cancer 94(10):1361–1368
Wolters T, Roobol MJ, Leeuwen PJV, van den Bergh RC, Hoedemaeker RF, van Leenders GJ, Schröder FH, van der Kwast TH (2011) A Critical analysis of the tumor volume threshold for clinically insignificant prostate cancer using a data set of a randomized screening trial. J Urol 185(1):121–125. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.08.082
Kirkham AP, Haslam P, Keanie JY, McCafferty I, Padhani AR, Punwani S, Richenberg J, Rottenberg G, Sohaib A, Thompson P, Turnbull LW, Kurban L, Sahdev A, Clements R, Carey BM, Allen C (2013) Prostate MRI: who, when, and how? Report from a UK consensus meeting. Clin Radiol 68(10):1016–1023. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2013.03.030
Langer DL, van der Kwast TH, Evans AJ, Trachtenberg J, Wilson BC, Haider MA (2009) Prostate cancer detection with multi-parametric MRI: logistic regression analysis of quantitative T2, diffusion-weighted imaging, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(2):327–334. doi:10.1002/jmri.21824
Oto A, Kayhan A, Jiang Y, Tretiakova M, Yang C, Antic T, Dahi F, Shalhav AL, Karczmar G, Stadler WM (2010) Prostate cancer: differentiation of central gland cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia by using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 257(3):715–723. doi:10.1148/radiol.10100021
Rosenkrantz AB, Kim S, Lim RP, Hindman N, Deng FM, Babb JS, Taneja SS (2013) Prostate cancer localization using multiparametric MR imaging: comparison of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) and Likert scales. Radiology 269(2):482–492. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122233
Westphalen AC, Rosenkrantz AB (2014) Prostate imaging reporting and data system (PI-RADS): reflections on early experience with a standardized interpretation scheme for multiparametric prostate MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202(1):121–123. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.10889
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standard
The current study has been approved by the local ethics committee in Innsbruck (Study number: AN4468 304/4.17) and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All patients gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Daniel Junker and Michael Quentin equally contributed for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junker, D., Quentin, M., Nagele, U. et al. Evaluation of the PI-RADS scoring system for mpMRI of the prostate: a whole-mount step-section analysis. World J Urol 33, 1023–1030 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1370-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1370-x