Abstract.
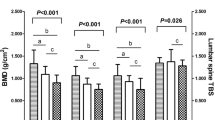
Quantitative ultrasound (QUS) of bone and new markers of bone remodeling have been poorly investigated in mild primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). In this study 26 patients (20 females and 6 males) were evaluated. BUA and SOS were measured by QUS at the heel. Markers of bone remodeling assessed were bone alkaline phosphatase (BAP), osteocalcin (OC), procollagen type I N- and C-terminal propeptides (PINP et PICP), and procollagen type I C-terminal telopeptide in blood and urine (ICTP and CTX). Bone mineral density (BMD) was measured at the lumbar spine (LS), femoral neck (FN), and Ward's triangle (WT). The control group comprised 35 sex- and age-matched subjects. The statistically significant variables between the two groups were (P < 0.05) BUA, BMDLS, BMDFN, BMDWT, BAP, and OC. Corresponding z-scores were −0.55 ± 0.75, −0.66 ± 0.77, −0.66 ± 0.71, −0.67 ± 0.52, 1.87 ± 3.87, and 1.93 ± 3.53, respectively. Although PICP and PINP levels were higher in PHPT patients as compared with controls, the difference was not significant. Several markers of bone turnover were moderately correlated with both QUS (r =−0.39 to −0.55) and BMD (r =−0.48 to 0.63). In conclusion QUS seems to be a relevant tool in the assessment of bone status for patients with mild PHPT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 October 1998 / Accepted: 1 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortet, B., Cortet, C., Blanckaert, F. et al. Bone Ultrasonometry and Turnover Markers in Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Calcif Tissue Int 66, 11–15 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002230050004
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002230050004