Abstract
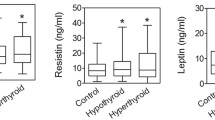
The aim of this controlled prospective study was to investigate resistin levels in hypothyroidism before and after restoration of euthyroidism and correlate the results with body weight (BW), body fat (BF), waist circumference (WC), body mass index (BMI) and serum insulin levels. Fifty-three hypothyroid patients with Hashimoto’s disease (6 males, 47 females) and 30 controls matched for age, BMI and BF were investigated. Anthropometric parameters, resistin and insulin levels were measured. All patients were started on levothyroxine treatment and 4 to 5 months after initiation of treatment the investigations were repeated. Hypothyroid patients exhibited normal resistin values, which were no different from controls (mean±SD 7.4±4.0 vs 5.1±3.5 ng/ml, p=0.063). Normalization of circulating thyroid hormone levels produced no significant change in resistin levels (7.4±4.0 vs 6.8±4.2 ng/ml, p=ns) and post-treatment resistin levels did not differ from euthyroid controls. Furthermore, no gender difference was demonstrated in resistin levels either before (6.4±3.7 for males vs 7.6±4.1 ng/ml for females, p=ns) or after therapy (7.9±4.3 vs 6.7±4.3 ng/ml, for males and females respectively, p=ns), nor was there a difference in resistin levels in either sex induced by treatment of hypothyroidism (6.4±3.7 vs 7.9±4.3 ng/ml for males, p=ns, and 7.6±4.1 vs 6.7±4.3 ng/ml for females, p=ns). However, a small but significant difference in resistin levels was found between female patients and female controls (7.6±4.1 vs 5.0±4.0 ng/ml, p=0.047). Insulin levels and homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index did not differ before and after treatment in hypothyroid patients (13.0±10.2 vs 12.6±11.8 μU/ml, 22.7±1.4 vs 21.8±1.3, respectively, p=ns for both) or between patients and controls. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that resistin levels are normal in hypothyroidism and remain within normal range after attainment of euthyroidism. Resistin is not associated with serum insulin and HOMA-IR index, as well as BMI, BF, WC and BW.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf G. Insulin resistance and obesity: resistin, a hormone secreted by adipose tissue. Nutr Rev 2004, 62: 389–94.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001, 409: 307–12.
Kim KH, Lee K, Moon YS, Sul HS. A cysteine-rich adipose tissue-specific secretory factor inhibits adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2001, 276: 11252–6.
Steppan CM, Brown EJ, Wright CM, et al. A family of tissue-specific resistin-like molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98: 502–6.
Steppan CM, Lazar MA. Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002, 13: 18–23.
Haugen F, Jorgensen A, Drevon CA, Trayhurn P. Inhibition by insulin of resistin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett 2001, 507: 105–8.
Ukkola O. Resistin — a mediator of obesity-associated insulin resistance or an innocent bystander? Eur J Endocrinol 2002, 147: 571–4.
Sentinelli F, Romeo S, Arca M, et al. Human resistin gene, obesity, and type 2 diabetes: mutation analysis and population study. Diabetes 2002, 51: 860–2.
Osawa H, Onuma H, Murakami A, et al. Systematic search for single nucleotide polymorphisms in the resistin gene: the absence of evidence for the association of three identified single nucleotide polymorphisms with Japanese type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51: 863–6.
Lee JH, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, et al. Circulating resistin levels are not associated with obesity or insulin resistance in humans and are not regulated by fasting or leptin administration: cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal, insulin-resistant, and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4848–56.
Rajala MW, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue-derived hormones: their role in energy homeostasis and pathophysiology. Topical Endocrinol 2004, 24: 6–9.
Weetman AP. Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med 2000, 343: 1236–48.
Duntas LH. Thyroid disease and lipids. Thyroid 2002, 12: 287–93.
Iglesias P, Alvarez Fidalgo P, Codoceo R, Diez JJ. Serum concentrations of adipocytokines in patients with hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism before and after control of thyroid function. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2003, 59: 621–9.
Krassas GE, Pontikides N, Loustis K, Koliakos G, Constantinidis T, Panidis D. Resistin levels in hyperthyroid patients before and after restoration of thyroid function: relationship with body weight and body composition. Eur J Endocrinol 2005, 153: 217–21.
Utter AC, Nieman DC, Ward AN, Butterworth DE. Use of the leg-to-leg bioelectrical impedance method in assessing body-composition change in obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 1999, 69: 603–7.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28: 412–9.
Pfutzner A, Langenfeld M, Kunt T, Lobig M, Forst T. Evaluation of human resistin assays with serum from patients with type 2 diabetes and different degrees of insulin resistance. Clin Lab 2003, 49: 571–6.
Azuma K, Katsukawa F, Oguchi S, et al. Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obes Res 2003, 11: 997–1001.
Schaffler A, Buchler C, Muller-Ladner U, et al. Identification of variables influencing resistin serum levels in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res 2004, 36: 702–7.
Yaturu S, Prado S, Grimes SR. Changes in adipocyte hormones leptin, resistin, and adiponectin in thyroid dysfunction. J Cell Biochem 2004, 93: 491–6.
Nogueiras R, Gualillo O, Caminos JE, Casanueva FF, Dieguez C. Regulation of resistin by gonadal, thyroid hormone, and nutritional status. Obes Res 2003, 11: 408–14.
Endo T, Ohta K, Haraguchi K, Onaya T. Cloning and functional expression of a thyrotropin receptor cDNA from rat fat cells. J Biol Chem 1995, 270: 10833–7.
Savage DB, Sewter CP, Klenk ES, et al. Resistin / Fizz3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma action in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50: 2199–202.
Hotamisligil GS. The irresistible biology of resistin. J Clin Invest 2003, 111: 173–4.
Banerjee RR, Rangwala SM, Shapiro JS, et al. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science 2004, 303: 1195–8.
Mueller A, O’Rourke J, Chu P, et al. Protective immunity against Helicobacter is characterized by a unique transcriptional signature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100: 12289–94.
Lehrke M, Reilly MP, Millington SC, Iqbal N, Rader DJ, Lazar MA. An inflammatory cascade leading to hyperresistinemia in humans. PLoS Med 2004, 1: e45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krassas, G.E., Pontikides, N., Loustis, K. et al. Resistin levels are normal in hypothyroidism and remain unchanged after attainment of euthyroidism: Relationship with insulin levels and anthropometric parameters. J Endocrinol Invest 29, 606–612 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344159
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344159