Abstract
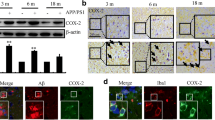
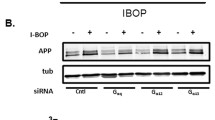
One of the early events in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the extracellular deposition of amyloid-beta peptide (An), a 39- to 43- amino acid cleavage product of the transmembrane glycoprotein, amyloid precursor protein. Excess A13 within the brain has long been thought to play a major role in AD pathogenesis, however, the mechanisms of its actions are highly debatable. Recent evidence suggests that inflammation may be the pathogenetic link between AP deposition and neuronal death (Halliday et al., 2000).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang J., Coleman P., O’Banion K., 1996, Prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) mRNA expression is decreased in Alzheimer’s diseaseNeurobiol. Aging.17:801.
Chiang C., Stalder A., Samimi A., Campbell I.L., 1994, Reactive gliosis as a consequence of interleukin-6 expression in the brain: Studies in transgenic miceDev. Neurosci.16:212.
Goodwin D., Landino L., Marnett L., 1999, Effects of nitric oxide and nitric oxide-derived species on prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase and prostaglandin biosynthesis, FASEB. 13:1121.
Halliday G., Robinson S., Shepherd C., Kril J., 2000, Alzheimer’s disease and inflammation: a review of cellular and therapeutic mechanismsClin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol.27:1.
Ho L., Pieroni C., Winger D., Purohit D., Aisen P., Pasinetti G., 1999, Regional distribution of cyclooxygenase-2 in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s diseaseJ. Neurosci. Res.57:295.
Hu J., Akama K., Krafft G., Chromy B., Van Eldik L., 1998, Amyloid-ß peptide activates cultured astrocytes: morphological alterations, cytokine induction and nitric oxide releaseBrain Res.785:195.
Johnstone M., Gearing A., Miller K., 1999, A central role for astrocytes in the inflammatory response to beta-amyloid; chemokines, cytokines and reactive oxygen species are producedJ. Neuroimmunol.93:182.
Landolfi C., Soldo L., Polenzani L., Apicella C., de Joannon A., Coletta I., Di Cesare F.M., Pinza, M., Milanese C.,1998, Inflammatory molecule release by ß-amyloid-treated T98G astrocytoma cells: role of prostaglandins and modulation by paracetamolEur. J. Pharmacol.360:55.
McGeer P., Schulzer M., McGeer E.,1996, Arthritis and anti-inflammatory agents as possible protective factors for Alzheimer’s disease: A review of 17 epidemiologic studiesNeurol.47:425.
Mitchell J. and Warner T., 1999, Cyclo-oxygenase-2: pharmacology, physiology, biochemistry and relevance to NSAID therapyBr. J. Pharmacol.128:1121.
Moore S.A., Strauch A., Yoder E., Rubenstein P., Hart M.,1984, Cerebral microvascular smooth muscle in tissue cultureIn Vitro.20:512.
Moore S.A., Yoder E., and Spector A.,1990, Role of the blood-brain barrier in the formation of long-chain w-3 and w-6 fatty acids from essential fatty acid precursors.J. Neurochem.55:391.
Moore S.A., Yoder E., Murphy S., Dutton G., Spector A.,1991, Astrocytes, not neurons, produce docosahexaenoic acid (22:6w-3) and arachidonic acid (20:4w-6)J. Neurochem.56:518.
Moore S.A., Yoder E., Rich G., Hilfers M., Albright J.,1999, Regulation of cerebrovascular cyclooxygenase-2 by pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.69:647.
O’Banion M., Miller J., Chang J., Kaplan M., Coleman P.,1996, Interleukin-113 induces prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) in primary mucine astrocyte culturesJ. Neurochem.66: 2532.
Pasinetti G.,1998, Cyclooxygenase and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Experimental approaches and clincial interventionsJ. Neurosci. Res.54:1.
Pasinetti G. and Aisen P., 1998, Cyclooxygnease-2 expression is increased in frontal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease brainNeurology87:319.
Price J., Sutton E., Hellermann A., Thomas T.,1997, (3 -amyloid induces cerebrovascular endothelial dysfunction in the rat brainNeurol. Res.19:534.
Su G., Arendash G., kalaria R., Bjugstad K., Mullan M.,1999, Intravascular infusions of soluble 13amyloid compromise the blood-brain barrier, activate CNS glial cells and induce peripheral hemorrhageBrain Res.818:105.
Weldon D., Rogers S., Ghilardi J., Finke M., Cleary J., O’Hare E., Esler W., Maggio J., Mantyh P.,1998, Fibrillar (3-amyloid induces microglial phagocytosis, expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, and loss of a select population of neurons in the rat CNS in vivoJ. Neuro.18:2161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bilunas, M.H., Moore, S.A. (2002). Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Activity are Induced by Amyloid-Beta 1-42 in Brain-Derived Cells. In: Honn, K.V., Marnett, L.J., Nigam, S., Dennis, E., Serhan, C. (eds) Eicosanoids and Other Bioactive Lipids in Cancer, Inflammation, and Radiation Injury, 5. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 507. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0193-0_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0193-0_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-4960-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-0193-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive