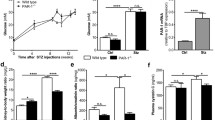
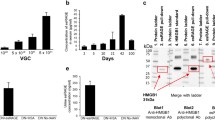
Abstract
Proteinuria is a major cause of morbidity in patients with glomerular disease. Nonselective protein filtration is now recognized as a significant contributing factor to the tubulo-interstitial injury which underlies and often predicts progressive renal insufficiency in patients with primary glomerular diseases. Increasing recognition of the mechanisms whereby proteinuria leads to tubule injury confirms the well-known clinical observation that the magnitude of proteinuria at diagnosis is a reliable predictor of prognosis in patients with glomerulonephritis and diabetes. For this reason, the search for safe and effective anti-proteinuric agents which do not reduce the glomerular filtration rate represents an urgent and critical need for physicians involved in the care of patients with glomerular disorders.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. K. Miller, J. W. Gillard, P. J. Vickers, S. Sadowski, C. Leveille, J. A. Mancini, P. Charleson, R. A. F. Dixon, A. W. Ford-Hutchinson, R. Fortin, J. Y. Gauthier, J. Rodkey, R. Rosen, C. Rouzer, I. S. Sigal, C. D. Strader, and J. F. Evans. Identification and isolation of a membrane protein necessary for leukotriene production.Nature343: 278–281, (1990).
R. A. F. Dixon, R. E. Diehl, E. Opas, E. Rands, P. J. Viskers, J. F. Evans, J. W. Gillard, and D. K. Miller. Requirement of a 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein for leukotriene synthesis.Nature343: 282–284, (1990).
S. Uda, K. A. Munger, and K. F. Badr. Glomerular localization of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) and 5-LO activating protein (FLAP) in a rat model of proliferative glomerulonephritis.J Am Soc Nephrol8, (1997).
A. Guash, C. F. Zayas, and K. F. Badr. MK-591 acutely restores glomerular size selectivity and reduces proteinuria in human glomerulonephritis.Kidney /nt56, (1999).
S. Shankland, and J. Scholey. Expression of transforming growth factor-(31 during diabetic renal hypertrophy.Kidney /nt46: 430–442, (1994).
J. Valdivielso, F. Perez-Barriocanal, J. García-Estañ, and J. López-Novoa. Role of nitric oxide in the early renal hemodynamic response after unilateral nephrectomy.American Journal of Physiology276: R1718- R1723, (1999).
K. Munger, A. Montero, M. Fukunaga, S. Uda, T. Yura, E. Imai, Y. Kaneda, J. Valdivielso, and K. Badr. Transfection of rat kidney with human 15-lipoxigenase suppresses inflammation and preserves function in experimental glomerulonephritis.PNAS96: 13375–13380, (1999).
R. Arison, E. Ciaccio, M. Glitzer, J. Cassaro, and M. Pruss. Light and electron microscopy of lesions in rats rendered diabetic with streptozotocin.Diabetes16: 51–56, (1967).
A. Junod, A. Lambert, L. Orci, R. Pictet, A. Gonet, and A. Renold. Studies of the diabetogenic action of streptozotocin.Proc Soc Exp Biol Med126: 201–205, (1967).
H. Selawry, J. Pennell, V. Pardo, D. Alzamora, and M. Millard. The effect of culture-mantained pancreatic islets on metabolic parameters, renal function, and glomerular lesions in the diabetic rat.Metabolism29: 261–269, (1980).
R. Weil, M. Nozawa, M. Koss, C. Weber, K. Reemstsama, and R. McIntosh. The kidney in streptozotocin diabetic rats.Arch Pathol Lab Med100: 37–49, (1976).
J. Sheth. Diabetes, micrfoalbuminuria and hypertension.Clin and Exper Hypertension21: 61–68, (1999).
V. Stewart, P. Whithing, A. Bell, and G. Hawsworth. Streptozotozin-induces diabetes is associated with increased renal lipoxygenase activity.Biochem Soc Transac26: S 134, (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Valdivielso, J.M., Montero, A., Munger, K.A., Badr, K.F. (2002). Inhibition of 5-lo Activating Protein (Flap) Activity Decreases Proteinuria in Streptozotocin(Stz)-induced Diabetic Rats.. In: Honn, K.V., Marnett, L.J., Nigam, S., Dennis, E., Serhan, C. (eds) Eicosanoids and Other Bioactive Lipids in Cancer, Inflammation, and Radiation Injury, 5. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 507. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0193-0_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0193-0_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-4960-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-0193-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive