Abstract
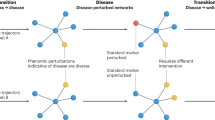
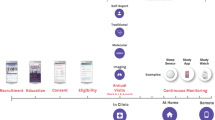
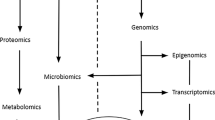
The WHOLE approach to personalized medicine represents an effort to integrate clinical and genomic profiling jointly into preventative health care and the promotion of wellness. Our premise is that genotypes alone are insufficient to predict health outcomes, since they fail to account for individualized responses to the environment and life history. Instead, integrative genomic approaches incorporating whole genome sequences and transcriptome and epigenome profiles, all combined with extensive clinical data obtained at annual health evaluations, have the potential to provide more informative wellness classification. As with traditional medicine where the physician interprets subclinical signs in light of the person’s health history, truly personalized medicine will be founded on algorithms that extract relevant information from genomes but will also require interpretation in light of the triggers, behaviors, and environment that are unique to each person. This chapter discusses some of the major obstacles to implementation, from development of risk scores through integration of diverse omic data types to presentation of results in a format that fosters development of personal health action plans.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham G, Kowalczyk A, Zobel J, Inouye M (2012) Performance and robustness of penalized and unpenalized methods for genetic prediction of complex human disease. Genet Epidemiol 2012 Epub ahead of print
Ashley EA, Butte AJ, Wheeler MT, Chen R, Klein TE et al (2010) Clinical assessment incorporating a personal genome. Lancet 375:1525–1535
Ayers KL, Cordell HJ (2010) SNP selection in genome-wide and candidate gene studies via penalized logistic regression. Genet Epidemiol 34:879–891
Bick D, Dimmock D (2011) Whole exome and whole genome sequencing. Curr Opin Pediatr 23:594–600
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Sterk PJ, Adcock IM, Chung KF et al (2011) Systems medicine and integrated care to combat chronic noncommunicable diseases. Genome Med 3:43
Brigham KL (2010) Predictive health: the imminent revolution in health care. J Am Geriatr Soc 58(Suppl 2):S298–S302
Brigham KL, Johns MME (2012) Predictive health: how we can reinvent medicine to extend our best years? Basic Books, New York, NY
Brindle P, Emberson J, Lampe F, Walker M, Whincup P, Fahey T, Ebrahim S (2003) Predictive accuracy of the Framingham coronary risk score in British men: prospective cohort study. BMJ 327:1267
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2011) Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 474:609–615
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012) Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 487:330–337
Casper ML, Wing S, Anda RF, Knowles M, Pollard RA (1995) The shifting stroke belt: changes in the geographic pattern of stroke mortality in the United States, 1962 to 1988. Stroke 26:755–760
Chaussabel D, Quinn C, Shen J, Patel P, Glaser C et al (2008) A modular analysis framework for blood genomics studies: application to systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 29:150–164
Chen R, Butte AJ (2011) The reference human genome demonstrates high risk of type 1 diabetes and other disorders. Pac Symp Biocomput 2011:231–242
Clayton DG (2009) Prediction and interaction in complex disease genetics: experience in type 1 diabetes. PLoS Genet 5:e1000540
de Roos AP, Hayes BJ, Goddard ME (2009) Reliability of genomic predictions across multiple populations. Genetics 183:1545–1553
Dewey FE, Chen R, Cordero SP, Ormond KE, Caleshu C et al (2011) Phased whole-genome genetic risk in a family quartet using a major allele reference sequence. PLoS Genet 7:e1002280
Do CB, Hinds DA, Francke U, Eriksson N (2012) Comparison of family history and SNPs for predicting risk of complex disease. PLoS Genet 8:e1002973
Ellis MJ, Ding L, Shen D, Luo J, Suman VJ et al (2012) Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition. Nature 486:353–360
Emilsson V, Thorleifsson G, Zhang B, Leonardson AS, Zink F et al (2008) Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature 452:423–428
Glatt SJ, Tsuang MT, Winn M, Chandler SD, Collins M et al (2012) Blood-based gene expression signatures of infants and toddlers with autism. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51:934–944
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Cooper C, Thornburg KL (2008) Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N Engl J Med 359:61–73
Gullapalli RR, Desai KV, Santana-Santos L, Kant JA, Becich MJ (2012) Next generation sequencing in clinical medicine: challenges and lessons for pathology and biomedical informatics. J Pathol Inform 3:40
Hamburg MA, Collins FS (2010) The path to personalized medicine. N Engl J Med 363:301–304
Han F, Pan W (2010) Powerful multi-marker association tests: unifying genomic distance-based regression and logistic regression. Genet Epidemiol 34:680–688
Hood L, Balling R, Auffray C (2012) Revolutionizing medicine in the 21st century through systems approaches. Biotechnol J 7:992–1001
Idaghdour Y, Czika W, Shianna KV, Lee SH, Visscher PM et al (2010) Geographical genomics of human leukocyte gene expression variation in southern Morocco. Nat Genet 42:62–67
Karagas MR, Andrew AS, Nelson HH, Li Z, Punshon T et al (2012) SLC39A2 and FSIP1 polymorphisms as potential modifiers of arsenic-related bladder cancer. Hum Genet 131:453–461
Kooperberg C, LeBlanc M, Obenchain V (2010) Risk prediction using genome-wide association studies. Genet Epidemiol 34:643–652
Kruppa J, Ziegler A, König IR (2012) Risk estimation and risk prediction using machine-learning methods. Hum Genet 131:1639–1654
Lango H; UK Type 2 Diabetes Genetics Consortium, Palmer CN, Morris AD, Zeggini E et al (2008) Assessing the combined impact of 18 common genetic variants of modest effect sizes on type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes 57: 3129–3135
Le-Niculescu H, Kurian SM, Yehyawi N, Dike C, Patel SD et al (2009) Identifying blood biomarkers for mood disorders using convergent functional genomics. Mol Psychiatry 14:156–174
Lettre G, Rioux JD (2008) Autoimmune diseases: insights from genome-wide association studies. Hum Mol Genet 17(R2):R116–R121
Lusis AJ, Attie AD, Reue K (2008) Metabolic syndrome: from epidemiology to systems biology. Nat Rev Genet 9:819–830
Miller GE, Chen E, Fok AK, Walker H, Lim A, Nicholls EF, Cole S, Kobor MS (2009) Low early-life social class leaves a biological residue manifested by decreased glucocorticoid and increased proinflammatory signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14716–14721
Morgan AA, Chen R, Butte AJ (2010) Likelihood ratios for genome medicine. Genome Med 2:30
Nath AP, Arafat D, Gibson G (2012) Using blood informative transcripts in geographical genomics: impact of lifestyle on gene expression in Fijians. Front Genet 3:243
Neale BM, Kou Y, Liu L, Ma'ayan A, Samocha KE et al (2012) Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 485:242–245
Nebert DW, Zhang G, Vesell ES (2008) From human genetics and genomics to pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics: past lessons, future directions. Drug Metab Rev 40:187–224
Need AC, McEvoy JP, Gennarelli M, Heinzen EL, Ge D et al (2012) Exome sequencing followed by large-scale genotyping suggests a limited role for moderately rare risk factors of strong effect in schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 91:303–312
Need AC, Shashi V, Hitomi Y, Schoch K, Shianna KV, McDonald MT, Meisler MH, Goldstein DB (2012) Clinical application of exome sequencing in undiagnosed genetic conditions. J Med Genet 49:353–361
Pace TWW, Mletzko TC, Alagbe O, Musselman DL, Nemeroff CB, Miller AH, Heim CM (2006) Increased stress-induced inflammatory responses in male patients with major depression and increased early life stress. Am J Psychiatry 163:1630–1633
Park S, Yang JS, Kim J, Shin YE, Hwang J, Park J, Jang SK, Kim S (2012) Evolutionary history of human disease genes reveals phenotypic connections and comorbidity among genetic diseases. Sci Rep 2:757
Patel CJ, Sivadas A, Tabassum R, Thanawadee P, Zhao J, Arafat D, Chen R, Morgan AA, Martin G, Brigham KL, Butte AJ, Gibson G (2013) Whole genome sequencing in support of wellness and health maintenance. Genome Med 5:58
Polychronakos C, Li Q (2011) Understanding type 1 diabetes through genetics: advances and prospects. Nat Rev Genet 12:781–792
Preininger M, Arafat D, Kim J, Nath A, Idaghdour Y, Brigham KL, Gibson G (2013) Blood-informative transcripts define nine common axes of peripheral blood gene expression. PLoS Genet 9:e1003362
Ramos PS, Criswell LA, Moser KL, Comeau ME, Williams AH et al (2011) A comprehensive analysis of shared loci between systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and sixteen autoimmune diseases reveals limited genetic overlap. PLoS Genet 7:e1002406
Rask KJ, Brigham KL, Johns MME (2011) Integrating comparative effectiveness research programs into predictive health: a unique role for academic health centers. Acad Med 86:718–723
Ritchie ND, Hahn LW, Moore JH (2003) Power of multifactor dimensionality reduction for detecting gene-gene interactions in the presence of genotyping error, missing data, phenocopy, and genetic heterogeneity. Genet Epidemiol 24:150–157
Roberts NJ, Vogelstein JT, Parmigiani G, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2012) The predictive capacity of personal genome sequencing. Sci Transl Med 4:133ra58
Rost S, Fregin A, Ivaskevicius V, Conzelmann E, Hörtnagel K et al (2004) Mutations in VKORC1 cause warfarin resistance and multiple coagulation factor deficiency type 2. Nature 427:537–541
Roychowdhury S, Iyer MK, Robinson DR, Lonigro RJ, Wu YM et al (2011) Personalized oncology through integrative high-throughput sequencing: a pilot study. Sci Transl Med 3:111ra121
Rzhetsky A, Wajngurt D, Park N, Zheng T (2007) Probing genetic overlap among complex human phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11694–11699
Salari K, Watkins H, Ashley EA (2012) Personalized medicine: hope or hype? Eur Heart J 33:1564–1570
Sankararaman S, Sridhar S, Kimmel G, Halperin E (2008) Estimating local ancestry in admixed populations. Am J Hum Genet 82:290–303
Shriner D, Adeyemo A, Rotimi CN (2011) Joint ancestry and association testing in admixed individuals. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002325
Talkowski ME, Ordulu Z, Pillalamarri V, Benson CB, Blumenthal I et al (2012) Clinical diagnosis by whole-genome sequencing of a prenatal sample. N Engl J Med 367:2226–2232
Visscher PM, Brown MA, McCarthy MI, Yang J (2012) Five years of GWAS discovery. Am J Hum Genet 90:7–24
Weedon MN, McCarthy MI, Hitman G, Walker M, Groves CJ et al (2006) Combining information from common type 2 diabetes risk polymorphisms improves disease prediction. PLoS Med 3:e374
Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB, Levy D, Belanger AM, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB (1998) Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation 97:1837–1847
Wilson PW, Meigs JB, Sullivan L, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB (2007) Prediction of incident diabetes mellitus in middle-aged adults: the Framingham Offspring Study. Arch Intern Med 167:1068–1074
Wray NR, Goddard ME (2010) Multi-locus models of genetic risk of disease. Genome Med 2:10
Wray NR, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2008) Prediction of individual genetic risk of complex disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18:257–263
Wray NR, Yang J, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2010) The genetic interpretation of area under the ROC curve in genomic profiling. PLoS Genet 6:e1000864
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG et al (2012) Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486:222–227
Yu K, Wacholder S, Wheeler W, Wang Z, Caporaso N, Landi MT, Liang F (2012) A flexible Bayesian model for studying gene-environment interaction. PLoS Genet 8:e1002482
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gibson, G. (2014). Wellness and Health Omics Linked to the Environment: The WHOLE Approach to Personalized Medicine. In: Maltsev, N., Rzhetsky, A., Gilliam, T. (eds) Systems Analysis of Human Multigene Disorders. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 799. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8778-4_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8778-4_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-8777-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-8778-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)