Abstract
Background
The prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer is poor, even among those who undergo potentially curative esophagectomy. The neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is hypothesized to reflect the systemic inflammatory response created by a tumor and is possibly predictive of tumor aggressiveness and propensity for metastasis.
Methods
We performed a single-center retrospective analysis of esophageal cancer patients who underwent attempted curative esophagectomy at Weill Cornell Medical Center between 1996 and 2009. We collected data on patient demographics, clinical characteristics, and receipt of neoadjuvant treatment. Preoperative blood tests were used to calculate NLR. Elevated NLR was defined a priori as ≥5.0. Logistic regression modeling was performed to analyze characteristics associated with elevated NLR. We conducted Kaplan-Meier analyses and Cox regression modeling to determine estimates and predictors of disease-free and overall survival.
Results
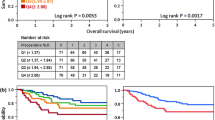
We identified a total of 295 patients who underwent esophagectomy. The median duration of follow-up was 31 months (interquartile range [IQR] 13–61). There were 56 patients (18.9%) who had elevated NLR preoperatively. Receipt of neoadjuvant therapy was independently associated with high NLR (odds ratio [OR] 2.14, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.02–4.51). In multivariable analyses, elevated NLR was associated with significantly worse disease-free (hazard ratio [HR] 2.26, 95% CI 1.43–3.55) and overall survival (HR 2.31, 95% CI 1.53–3.50).
Conclusions
Preoperative NLR is a potential prognostic marker for recurrence and death after esophagectomy. It is unclear whether NLR reflects the degree of inflammatory response to the primary tumor or other patient-specific or tumor characteristics that predispose to recurrence. Further investigation is warranted to clarify the mechanisms explaining the observed associations between elevated NLR and poor outcomes in esophageal cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society. Global cancer facts and figures. http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/Global_Facts_and_Figures_2007_rev2.pdf (2007). Accessed 30 Mar 2010.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49.
DeNardo DG, Johansson M, Coussens LM. Immune cells as mediators of solid tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:11–8.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–45.
Roxburgh CS, McMillan DC. Role of systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol. 2010;6:149–63.
Halazun KJ, Aldoori A, Malik HZ, Al-Mukhtar A, Prasad KR, Toogood GJ, et al. Elevated preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts survival following hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34:55–60.
Malik HZ, Gomez D, Wong V, Al-Mukthar A, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, et al. Predictors of early disease recurrence following hepatic resection for colorectal cancer metastasis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007;33:1003–9.
AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th edn. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2002.
Walsh SR, Cook EJ, Goulder F, Justin TA, Keeling NJ. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:181–4.
Malik HZ, Prasad KR, Halazun KJ, Aldoori A, Al-Mukhtar A, Gomez D, et al. Preoperative prognostic score for predicting survival after hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg. 2007;246:806–14.
Kishi Y, Kopetz S, Chun YS, Palavecino M, Abdalla EK, Vauthey JN. Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases treated with systemic chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:614–22.
Halazun KJ, Hardy MA, Rana AA, Woodland DC IV, Luyten EJ, Mahadev S, et al. Negative impact of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio on outcome after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2009;250:141–51.
Gomez D, Farid S, Malik HZ, Young AL, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2008;32:1757–62.
Gomez D, Morris-Stiff G, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, Prasad KR. Impact of systemic inflammation on outcome following resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:513–8.
Nakahara K, Monden Y, Ohno K, Fujii Y, Hashimoto J, Kitagawa Y, et al. Importance of biologic status to the postoperative prognosis of patients with stage III nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol. 1987;36:155–60.
Sarraf KM, Belcher E, Raevsky E, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P, Lim E. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and its association with survival after complete resection in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;137:425–8.
Gomez D, Morris-Stiff G, Wyatt J, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, Prasad KR. Surgical technique and systemic inflammation influences long-term disease-free survival following hepatic resection for colorectal metastasis. J Surg Oncol. 2008;98:371–6.
Cho H, Hur HW, Kim SW, Kim SH, Kim JH, Kim YT, et al. Pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer and predicts survival after treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58:15–23.
Rashid F, Waraich N, Bhatti I, Saha S, Khan RN, Ahmed J, et al. A pre-operative elevated neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio does not predict survival from oesophageal cancer resection. World J Surg Oncol. 2010;8:1.
Aliustaoglu M, Bilici A, Ustaalioglu BB, Konya V, Gucun M, Seker M, et al. The effect of peripheral blood values on prognosis of patients with locally advanced gastric cancer before treatment. Med Oncol. 2010;27:1060–5.
Liao Q, Zhao YP, Yang YC, Li LJ, Long X, Han SM. Combined detection of serum tumor markers for differential diagnosis of solid lesions located at the pancreatic head. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007;6:641–5.
Nozoe T, Saeki H, Sugimachi K. Significance of preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein as an indicator of prognosis in esophageal carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182:197–201.
Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Shiratori T, Aoki T, et al. Elevation of preoperative serum C-reactive protein level is related to poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2003;83:248–52.
Guillem P, Triboulet JP. Elevated serum levels of C-reactive protein are indicative of a poor prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2005;18:146–50.
Kobayashi T, Teruya M, Kishiki T, Kaneko S, Endo D, Takenaka Y, et al. Inflammation-based prognostic score, prior to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, predicts postoperative outcome in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 2008;144:729–35.
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L, et al. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:183–94.
AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2010.
Acknowledgment
Dr. Abrams is supported in part by a career development award from the National Cancer Institute (K07 CA132892). Dr. Sharaiha is supported in part by a training grant from the National Cancer Institute (T32-CA 09529).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharaiha, R.Z., Halazun, K.J., Mirza, F. et al. Elevated Preoperative Neutrophil:Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Postoperative Disease Recurrence in Esophageal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18, 3362–3369 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1754-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1754-8