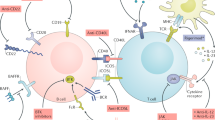
Abstract
In the past year there has been remarkable activity and some important success in the development of B cell-targeted therapies for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The most promising studies were BLISS-52 and BLISS-76, large phase III studies that demonstrated measurable efficacy for belimumab, a monoclonal antibody against B cell-activating factor (BAFF). The moderate-sized phase II/III trials EXPLORER and LUNAR that tested rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, for treatment of non-renal and renal lupus, disappointed many investigators with anecdotal success in refractory patients. These rituximab trials were intended to detect a large clinical effect in patients with very active disease and this was not found. Nevertheless, arguments can be made for additional studies in targeted populations or with a change in design to detect smaller or longer-term effects. Epratuzumab, a monoclonal antibody against the B cell surface antigen CD22, and atacicept, a chimeric molecule formed by a receptor for BAFF and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) with immunoglobulin (Ig)-G, have both been promising in initial small trials and now larger clinical trials are underway. Thus, recent clinical trial data show that B cell-targeting therapies are beginning to fulfil their promise as treatments for SLE and there are good reasons to hope for further progress in the near future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone J, Merkel P, Seo P, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for induction of remission in ANCA-associated vasculitis: a randomized controlled trial (RAVE) [abstract]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54(5): 1390–400
Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54(9): 2793–806
Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, et al. B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2008; 358(7): 676–88
Pescovitz M, Greenbaum C, Krause-Steinrauf H, et al. Rituximab, B-lymphocyte depletion, and preservation of beta-cell function. N Engl J Med 2009; 261: 2143–52
Looney RJ, Srinivasan R, Calabrese LH. The effects of rituximab on immunocompetency in patients with autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58(1): 5–14
Ahuja A, Anderson SM, Khalil A, et al. Maintenance of the plasma cell pool is independent of memory B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105(12): 4802–7
DiLillo DJ, Hamaguchi Y, Ueda Y, et al. Maintenance of long-lived plasma cells and serological memory despite mature and memory B cell depletion during CD20 immunotherapy in mice. J Immunol 2008; 180(1): 361–71
Chan O, Shlomchik MJ. A new role for B cells in systemic autoimmunity: B cells promote spontaneous T cell activation in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol 1998; 160(1): 51–9
Chan OT, Hannum LG, Haberman AM, et al. A novel mouse with B cells but lacking serum antibody reveals an antibody-independent role for B cells in murine lupus. J Exp Med 1999; 189(10): 1639–48
Chan OT, Madaio MP, Shlomchik MJ. The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 1999; 169: 107–21
Whitmire JK, Asano MS, Kaech SM, et al. Requirement of B cells for generating CD4+ T cell memory. J Immunol 2009; 182(4): 1868–76
Bouaziz J-D, Yanaba K, Venturi GM, et al. Therapeutic B cell depletion impairs adaptive and autoreactive CD4+ T cell activation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007; 104(52): 20878–83
Bekar D, Owen T, Dunn R, et al. Prolonged but variable effects of B cell depletion therapy in murine lupus nephritis [abstract no. 677]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
Ahuja A, Shupe J, Dunn R, et al. Depletion of B cells in murine lupus: efficacy and resistance. J Immunol 2007; 179(5): 3351–61
Merrill J, Neuwelt C, Wallace D, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: the randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 222–33
Furie R, Looney R, Rovin B, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in subjects with active proliferative lupus nephritis (LN): results from the randomized, double-blind phase III LUNAR study [abstract no. 1149]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
A Study to Evaluate Ocrelizumab in Patients With Nephritis Due to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (BELONG) [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00626197]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov [online]. Available from URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov [Accessed 2010 Feb 23]
Lu TYT, Ng KP, Cambridge G, et al. A retrospective seven-year analysis of the use of B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus at University College London Hospital: the first fifty patients. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 61(4): 482–7
Houssiau FA, Vasconcelos C, D'Cruz D, et al. Immuno-suppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: the Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46(8): 2121–31
Gourley M, Austin H, Scott D, et al. Methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide, alone or in combination, in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med 1996; 125: 549–57
Hill GS, Delahousse M, Nochy D, et al. Predictive power of the second renal biopsy in lupus nephritis: significance of macrophages. Kidney Int 2001; 59(1): 304–16
Hill GS, Delahousse M, Nochy D, et al. Outcome of relapse in lupus nephritis: roles of reversal of renal fibrosis and response of inflammation to therapy. Kidney Int 2002; 61(6): 2176–86
Hill GS, Delahousse M, Nochy D, et al. A new morphologic index for the evaluation of renal biopsies in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 2000; 58(3): 1160–73
Bonilla-Martinez ZL, Albrecht J, Troxel AB, et al. The cutaneous lupus erythematosus disease area and severity index: a responsive instrument to measure activity and damage in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol 2008; 144(2): 173–80
Krathen MS, Dunham J, Gaines E, et al. The Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity and Severity Index: expansion for rheumatology and dermatology. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 59(3): 338–44
Kreuter A, Tomi NS, Weiner SM, et al. Mycophenolate sodium for subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus resistant to standard therapy. Br J Dermatol 2007; 156(6): 1321–7
Merrill JT. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) is effective for systemic lupus (SLE) arthritis: final results of an organ-specific, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [abstract no. 264]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
Gong Q, Ou Q, Ye S, et al. Importance of cellular micro-environment and circulatory dynamics in B cell immunotherapy. J Immunol 2005; 174(2): 817–26
Merrill J, Neuwelt C, Wallace D, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with moderately to severely active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): results from the randomized, double-blind phase II/III study EXPLORER [abstract no. L12]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2008; 2008 Oct 25–29; San Francisco (CA)
Yanaba K, Bouaziz J-D, Haas KM, et al. A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 2008; 28(5): 639–50
Matsushita T, Yanaba K, Bouaziz J-D, et al. Regulatory B cells inhibit EAE initiation in mice while other B cells promote disease progression. J Clin Invest 2008; 118(10): 3420–30
McKay J, Chwalinska-Sadowska H, Boling E. Belimumab (BmAb), a fully human monoclonal antibody to B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), combined with standard of care therapy reduces the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in a heterogenous subject population [abstract no. 1920]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2005; 2005 Nov 13–17; San Diego (CA)
Daridon C, Burmester GR, Dorner T. Anticytokine therapy impacting on B cells in autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2009; 21(3): 205–10
Mackay F, Schneider P. Cracking the BAFF code. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9(7): 491–502
Ramanujam M, Davidson A. BAFF blockade for systemic lupus erythematosus: will the promise be fulfilled? Immunol Rev 2008; 223: 156–74
Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, et al. BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survival. Annu Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 231–64
Belnoue E, Pihlgren M, McGaha TL, et al. APRIL is critical for plasmablast survival in the bone marrow and poorly expressed by early-life bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 2008; 111(5): 2755–64
Chatham W, Furie R, Petri M, et al. Belimumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to BLyS) Improved or stabilized systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease activity over 3 years of therapy [abstract no. 1094]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2008; 2008 Oct 25–29; San Francisco (CA)
Petri M. Novel combined response endpoint and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) flare index (SFI) demonstrate belimumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to BLyS) improves or stabilizes SLE disease activity and reduces flare rate over 2.5 years of therapy [abstract no. 1316]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2007; 2007 Nov 6–11; Boston (MA)
Furie R, Lisse J, Merrill J, et al. Belimumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to b-lymphocyte stimulator [BLyS]) improves or stabilizes SLE activity in a multicenter phase 2 trial [abstract no. 535]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2006; 2006 Nov 11–15; Washington, DC
Furie R, MA P, Wallace D, et al. Novel evidence-based systemic lupus erythematosus responder index. Arthritis Care Res 2009; 61: 1143–51
Wallace DJ, Stohl W, Furie RA, et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 61(9): 1168–78
Navarra S, Guzman G, Gallacher A, et al. Belimumab, a BLyS-specific inhibitor, reduced disease activity, flares, and prednisone use in patients with SLE: efficacy and safety results from the phase 3 BLISS-52 study [late breaking abstract no. B1]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
Genovese M, Mociran E, Mare B, et al. Phase 2 study of safety and efficacy of a novel anti-BAFF monoclonal antibody, in patients with RA treated with methotrexate (MTX) [abstract no. 1923]. American College of Rheumatology National Meeting 2009; 2009 Oct 17–21; Philadelphia (PA)
Chang SK, Arendt BK, Darce JR, et al. A role for BLyS in the activation of innate immune cells. Blood 2006; 108(8): 2687–94
Dorner T, Kaufmann J, Wegener WA, et al. Initial clinical trial of epratuzumab (humanized anti-CD22 antibody) for immunotherapy of systemic lupus erythematosus [published erratum appears in Arthritis Res Ther 2008; 10(5): 406]. Arthritis Care Res 2006; 8 (3): R74
Jacobi AM, Goldenberg DM, Hiepe F, et al. Differential effects of epratuzumab on peripheral blood B cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus versus normal controls. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67(4): 450–7
Study of Epratuzumab in Serologically-positive Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With Active Disease [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00624351]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov [online]. Available from URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov [Accessed 2010 Feb 23]
Munafo A, Priestley A, Nestorov I, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of atacicept in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2007; 63(7): 647–56
Tak PP, Thurlings RM, Rossier C, et al. Atacicept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results of a multicenter, phase Ib, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalating, single- and repeated-dose study. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58(1): 61–72
Dall'Era M, Chakravarty E, Wallace D, et al. Reduced B lymphocyte and immunoglobulin levels after atacicept treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a multicenter, phase Ib, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalating trial. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56(12): 4142–50
The Efficacy and Safety of Atacicept in Combination With Mycophenolate Mofetil Used to Treat Lupus Nephritis [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00573157]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov [online]. Available from URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov [Accessed 2010 Feb 23]
Atacicept Phase II/III in Generalized Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00624338]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov [online]. Available from URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov [Accessed 2010 Feb 23]
Acknowledgements
Dr Looney is supported by the U19 Autoimmunity Center of Excellence AI56390 and the Lupus Clinical Trials Consortium. He has been an advisor for Genentech, IDEC/Biogen, Roche, Amgen, Novo Nordisk, Proteolix, Centocor, Pfizer and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has received funding for investigator-initiated studies from Genentech (2000) and Proteolix (2009). Dr Looney was one of the authors of the 2009 American College of Rheumatology abstract presenting the LUNAR (LUpus Nephritis Assessment with Rituximab) trial results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Looney, R.J. B Cell-Targeted Therapies for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Drugs 70, 529–540 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/11535420-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11535420-000000000-00000