Abstract
Background
The Prodige-7 trial has questioned the role of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in the treatment of peritoneal metastases from colorectal cancer (CRC-PM).
Patients and Methods
We compared a prospectively collected group of 48 patients undergoing oxaliplatin/irinotecan-based perioperative systemic chemotherapy (s-CT) with targeted agents, and cytoreductive surgery (CRS) (no-HIPEC group) with 48 controls undergoing the same perioperative s-CT and CRS/HIPEC (HIPEC group). Patients were matched (1:1) according to the Peritoneal Surface Disease Severity Score, completeness of cytoreduction, history of extraperitoneal disease (EPD), and Peritoneal Cancer Index.
Results
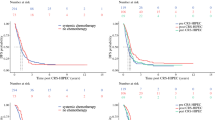
The groups were comparable, except for a higher number of patients in the HIPEC group with World Health Organization performance status 0, pN2 stage primary tumor, and treated with preoperative s-CT. Forty-one patients in the no-HIPEC group and 43 patients in the HIPEC group had optimal comprehensive treatment (P = 0.759), defined as complete cytoreduction of PM and margin-negative EPD resection. Median follow-up was 31.6 months in the no-HIPEC group and 39.9 months in the HIPEC group. Median overall survival was 39.3 months in the no-HIPEC group and 34.8 months in the HIPEC group (P = 0.702). In the two groups, severe morbidity occurred in 14 (29.2%) and 13 (27.1%) patients, respectively (P = 1.000), with no operative deaths. On multivariate analysis, left-sided primary and curative treatment independently correlated with better survival while HIPEC did not (hazard ratio 0.73; 95% confidence interval 0.47–1.15; P = 0.178).
Conclusions
Our results confirmed that, in selected patients, perioperative s-CT and surgical treatment of CRC-PM resulted in unexpectedly high survival rates. Mitomycin C-based HIPEC did not increase morbidity but did not impact prognosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lemmens VE, Klaver YL, Verwaal VJ, et al. Predictors and survival of synchronous peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin: a population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:2717–25.
Segelman J, Granath F, Holm T, et al. Incidence, prevalence and risk factors for peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 2012;99:699–705.
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Pietrantonio F, Guaglio M, Niger M, Deraco M. Progress in treatments for colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases during the years 2010–2015: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;100:209–22.
Franko J, Shi Q, Goldman CD, et al. Treatment of colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis with systemic chemotherapy: a pooled analysis of north central cancer treatment group phase III trials N9741 and N9841. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:263–7.
Klaver YL, Simkens LH, Lemmens VE, et al. Outcomes of colorectal cancer patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis treated with chemotherapy with and without targeted therapy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38:617–23.
Elias D, Lefevre JH, Chevalier J, et al. Complete cytoreductive surgery plus intraperitoneal chemohyperthermia with oxaliplatin for peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:681–85.
Elias D, Gilly F, Boutitie F, et al. Peritoneal colorectal carcinomatosis treated with surgery and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: retrospective analysis of 523 patients from a multicentric French study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:63–8.
Sugarbaker PH, Ryan DP. Cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic perioperative chemotherapy to treat peritoneal metastases from colorectal cancer: standard of care or an experimental approach? Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:e362–9.
Verwaal VJ, van Ruth S, de Bree E, et al. Randomized trial of cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy versus systemic chemotherapy and palliative surgery in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3737–43.
Gremonprez F, Willaert W, Ceelen W. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy (IPC) for peritoneal carcinomatosis: review of animal models. J Surg Oncol. 2014;109:110–6.
Yang XJ, Huang CQ, Suo T, et al. Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy improves survival of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer: final results of a phase III randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:1575–81.
van Driel WJ, Koole SN, Sikorska K, et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:230–40.
http://ascopubs.org/doi/abs/10.1200/JCO.2018.36.18_suppl.LBA3503?af=R.
Ceelen W. HIPEC with oxaliplatin for colorectal peritoneal metastasis: The end of the road? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019;45:400–2.
Elias D, Delperro JR, Sideris L, et al. Treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer: impact of complete cytoreductive surgery and difficulties in conducting randomized trials. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;11:518–21.
Scaringi S, Leo F, Canonico G, Batignani G, Ficari F, Tonelli F. The role of cytoreductive surgery alone for the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin: a retrospective analysis with regard to multimodal treatments. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009;56:650–5.
Mulsow J, Merkel S, Agaimy A, Hohenberger W. Outcomes following surgery for colorectal cancer with synchronous peritoneal metastases. Br J Surg. 2011;98:1785–91.
Kobayashi H, Enomoto M, Higushi T, et al. Validation and clinical use of the Japanese classification of colorectal carcinomatosis: benefit of surgical cytoreduction, even without intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Dig Surg. 2010;27:473–80.
Kobayashi H, Kotak, K., Sugihara, K, et al. Outcomes of surgery without HIPEC for synchronous peritoneal metastasis from colorectal cancer: data from a multi-center registry. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014;19:98–105.
Pelz O, Stojadinovic A, Nissan A, Hohenberger W, Esquivel J. Evaluation of a Peritoneal Surface Disease Severity Score in patients with colon cancer and peritoneal dissemination. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99:9–15.
Chua TC, Morris DL, Saxena A, et al. Influence of modern systemic therapies as adjunct to cytoreduction and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for patients with colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis: a multicenter study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:1560-7.
Prada-Villaverde A, Esquivel J, Lowy AM, et al. The American Society of Peritoneal Surface Malignancies evaluation of HIPEC with mitomycin C versus oxaliplatin in 539 patients with colon cancer undergoing a complete cytoreductive surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2014;110:779–85.
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Iusco D, et al. Postoperative complications after cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy affect long-term outcome of patients with peritoneal metastases from colorectal cancer: a two-center study of 101 patients. Dis Colon Rectum. 2014;57:858–68.
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Iusco D, et al. Should a history of extra-peritoneal disease be a contraindication to cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases? Dis Colon Rectum. 2018;61:1026–34.
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1386–422.
Deraco M, Baratti D, Kusamura S, Laterza B, Balestra MR. Surgical technique of parietal and visceral peritonectomy for peritoneal surface malignancies. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:321–8.
Jaquet P, Sugarbaker PH. Current methodologies for clinical assessment of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 1996;15:49–58.
http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_4.03_2010-06-14_QuickReference_5x7.pdf.
Désolneux G, Mazière C, Vara J, et al. Cytoreductive surgery of colorectal peritoneal metastases: outcomes aftercomplete cytoreductive surgery and systemic chemotherapy only. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0122816.
Bushati M, Rovers KP, Sommariva A, et al. The current practice of cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC for colorectal peritoneal metastases: results of a worldwide web-based survey of the Peritoneal Surface Oncology Group International (PSOGI). Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:1942–48.
Hompes D, D’Hoore A, Wolthuis A, et al. The use of oxaliplatin or mitomycin C in HIPEC treatment for peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer: a comparative study. J Surg Oncol. 2014;109:527–32.
Leung V, Huo YR, Liauw W, Morris DL. Oxaliplatin versus mitomycin C for HIPEC in colorectal cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017;43:144–9.
Votanopoulos K, Ihemelandu C, Shen P, Stewart J, Russell G, Levine EA. A comparison of hematologic toxicity profiles after heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy with oxaliplatin and mitomycin C. J Surg Res. 2013;179:e133–9.
van Eden WJ, Kok NFM, Woensdregt K, Huitema ADR, Boot H, Aalbers AGJ. Safety of intraperitoneal Mitomycin C versus intraperitoneal oxaliplatin in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal cancer undergoing cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:220–7.
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Iusco D, et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) at the time of primary curative surgery in patients with colorectal cancer at high risk for metachronous peritoneal metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:167–75.
Ubink I, Bolhaqueiro ACF, Elias SG, et al. Organoids from colorectal peritoneal metastases as a platform for improving hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Br J Surg. [Epub ahead of print].
Acknowledgments
N.A. is a fellow of the European School of Peritoneal Surface Oncology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors have no financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baratti, D., Kusamura, S., Azmi, N. et al. Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases Treated by Perioperative Systemic Chemotherapy and Cytoreductive Surgery With or Without Mitomycin C-Based HIPEC: A Comparative Study Using the Peritoneal Surface Disease Severity Score (PSDSS). Ann Surg Oncol 27, 98–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07935-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07935-2