Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to report on sirolimus activity in a series of patients with hemangioendothelioma (HE) treated at the National Cancer Institute, Milan (Istituto Nazionale Tumori; INT) and within the Italian Rare Cancer Network (“Rete Tumori Rari”; RTR).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed patients with advanced and progressing epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) treated with sirolimus at the INT and/or within the RTR. Pathologic review and molecular analysis for WWTR1 rearrangement were performed. Sirolimus was administered until unacceptable toxicity or progression, with the dose being adjusted to reach target plasma levels of 15–20 ng/dL. Responses were assessed using the Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria.
Results
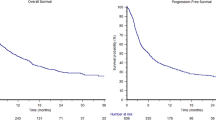
Since 2005, 18 patients (17 EHE, 1 retiform HE; 1 locally advanced, 17 metastatic; WWTR1 rearrangement: 16) have been identified, with 17/18 patients being evaluable for response. Mean sirolimus daily dose was 4.5 mg. According to RECIST, best responses in EHE were 1 partial response (PR), 12 stable disease (SD), and 3 progressive disease (PD); the patient with retiform HE also achieved a PR, lasting >2 years. Four patients with a reversed interval progression on interruption were observed. Median overall survival was 16 months, and median progression-free survival was 12 months (range 1–45), with four patients progression-free at 24 months. The clinical benefit (complete response [CR] + PR + SD >6 months) was 56 %. Seven patients receiving sirolimus experienced an increase in pleural/peritoneal effusion plus worsening of tumor-related symptoms; six of these patients died within 1–8 months from evidence of effusion progression, while a RECIST PD was assessed in two of seven patients.
Conclusions
A clinical benefit was achieved in 56 % of patients receiving sirolimus, which lasted >24 months in four patients. Most patients with pleural effusion did not benefit from sirolimus and had a poor outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a vascular tumor often mistaken for a carcinoma. Cancer. 1982;50:970–81.
Fletcher DM, Krishnan Unni K, Mertens F, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC Press; 2013, p. 80–82.
Tanas MR, Sboner A, Oliveira AM, et al. Identification of a disease-defining gene fusion in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:98ra82.
Errani C, Zhang L, Sung YS, et al. A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2011;50:644–53.
Antonescu CR, Le Loarer F, Mosquera JM, et al. Novel YAP1-TFE3 fusion defines a distinct subset of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2013;52:775–84.
Doyle LA, Fletcher CD, Hornick JL. Nuclear expression of CAMTA1 distinguishes epithelioid hemangioendothelioma from histologic mimics. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:94–102.
Deyrup AT, Tighiouart M, Montag AG, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of soft tissue: a proposal for risk stratification based on 49 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:924–7.
Anderson T, Zhang L, Hameed M, et al. Thoracic epithelioid malignant vascular tumors: a clinicopathologic study of 52 cases with emphasis on pathologic grading and molecular studies of WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39:132–9.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaertsc J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:257–63.
Chevreau C, Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, et al. Sorafenib in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a phase 2 study by the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Cancer. 2013;119:2639–44.
Saada E, Saint Paul MC, Gugenheim J, et al. Metastatic hepatic epithelioid hemangio-endothelioma: long-term response to sunitinib malate. Oncol Res Treat. 2014;3:124–6.
Prochilo T, Savelli G, Bertocchi P, et al. Targeting VEGF-VEGFR pathway by sunitinib in peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor, paraganglioma and epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: three case reports. Case Rep Oncol. 2013;6:90–7.
Bally O, Tassy L, Richioud B, et al. Eight years tumor control with pazopanib for a metastatic resistant epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2015;5:12.
Semenisty V, Naroditsky I, Keidar Z, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma—a suitable treatment option: case report and review of anti-angiogenic treatment options. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:402.
Radzikowska E, Szczepulska-Wójcik E, Chabowski M, et al. Pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma—interferon 2-alpha treatment: case report. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2008;76:281–5.
Yousaf N, Maruzzo M, Judson I, et al. Systemic treatment options for epithelioid haemangioendothelioma: the Royal Marsden Hospital experience. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:473–80.
Soape MP, Verma R, Payne JD, Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: finding uses for thalidomide in a new era of medicine. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2015;2015:326795.
Riou S, Morelon E, Guibaud L, et al. Efficacy of rapamycin for refractory hemangioendotheliomas in Maffucci’s syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:e213–5.
Cohen EE, Wu K, Hartford C, et al. Phase I studies of sirolimus alone or in combination with pharmacokinetic modulators in advanced cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4785–93.
Hernando E, Charytonowicz E, Dudas ME, et al. The AKT-mTOR pathway plays a critical role in the development of leiomyosarcomas. Nat Med. 2007;13: 748–53.
Gutierrez A, Snyder EL, Marino-Enriquez A, et al. Aberrant AKT activation drives well-differentiated liposarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:16386–91.
Barretina J, Taylor BS, Banerji S, et al. Subtype-specific genomic alterations define new targets for soft-tissue sarcoma therapy. Nat Genet. 2010;42:715–21.
Schuetze SM, Zhao L, Chugh R, et al. Results of a phase II study of sirolimus and cyclophosphamide in patients with advanced sarcoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1347–53.
Demetri GD, Chawla SP, Ray-Coquard I, et al. Results of an international randomized phase III trial of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor ridaforolimus versus placebo to control metastatic sarcomas in patients after benefit from prior chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2485–92.
Wagner AJ, Malinowska-Kolodziej I, Morgan JA, et al. Clinical activity of mTOR inhibition with sirolimus in malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: targeting the pathogenic activation of mTORC1 in tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:835–40.
Chaoul N, Fayolle C, Desrues B, et al. Rapamycin impairs antitumor CD8 + T-cell responses and vaccine-induced tumor eradication. Cancer Res. 2015;75:3279–91.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the following pathologists who kindly contributed case material: L. Ambrosiani, Anatomia ed Istologia Patologica e Citodiagnostica, Ospedale Valduce, Como, Italy; M. Paulli, Medicina di Laboratorio-Anatomia Patologica, Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy; and C. Cattaneo, Anatomia Patologica, Azienda Ospedaliera di Desio e Vimercate, Vimercate, Italy.
Disclosures
Silvia Stacchiotti, Vittoria Colia, Michela Libertini, and Elena Palassini: Pfizer, research funding. Alessandro Gronchi: Pfizer, advisory (compensated). Angelo P. Dei Tos: Pfizer, honoraria. Paolo G. Casali: Pfizer, advisory (compensated) and research funding. Salvatore Provenzano, Gianpaolo Dagrada, Tiziana Negri, Silvia Brich, Umberto Basso, Antonella Brunello, Federica Grosso, Luca Galli, Flavio Crippa, Carlo Morosi, and Silvana Pilotti have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stacchiotti, S., Provenzano, S., Dagrada, G. et al. Sirolimus in Advanced Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: A Retrospective Case-Series Analysis from the Italian Rare Cancer Network Database. Ann Surg Oncol 23, 2735–2744 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5331-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5331-z