Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate two methods of sentinel node navigation surgery (SNNS) using blue dye with and without indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence imaging (FI) to determine the usefulness of combined ICG and blue dye.
Methods
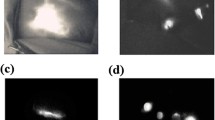
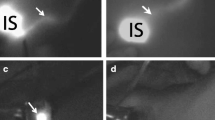
Between 2005 and 2010, a total of 501 patients underwent SNNS in our hospital. Detection of sentinel lymph node (SLN) was performed with sulfan blue (SB) alone until 2008 and with a combination of SB and ICG-FI since 2009. ICG 5 mg and SB 15 mg were injected in the subareolar region, and FI was obtained by a fluorescence imaging device.
Results
We attempted to identify SLNs in 393 patients by SB alone and in 108 patients by a combination of SB and FI. The mean number of SLNs detected was 1.6 (0–5) for SB alone and 2.2 (1–6) for the combination method. The SLN identification rate was 95.7 % for SB alone and 100 % for the combination method so that the combination was significantly superior to SB in terms of the identification rate (p = 0.0037). In patients who received the combination method, detection of SLN was made through only SB in 1 patient, only ICG in 8 patients, and both in 99 patients. Lymph node metastasis was found in 56 patients with SB alone and in 16 patients with the combination method. Recurrence of an axillary node was observed in 3 patients (0.8 %) with SB alone and in no patients with the combination method.
Conclusions
ICG-FI is a useful method and is especially recommended in cases where no radiotracers are available.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krag DN, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer—a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med. 1988;339:941–6.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Galber RD, et al. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1133–44.
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:927–33.
Cox CE, Pendas S, Cox JM, et al. Guidelines for sentinel node biopsy and lymphatic mapping of patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1998;227:645–53.
Rutgers EJ. Guidelines to assure quality in breast cancer surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005;31:568–76.
Sanidas EE, de Bree E, Tsiftsis DD. How many cases are enough for accreditation in sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer? Am J Surg. 2003;185:202–10.
Schwartz GF, Giuliano AE, Veronesi U; Consensus Conference Committee. Proceedings of the consensus conference on the role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in carcinoma of the breast, April 19 to 22, 2001, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Hum Pathol. 2002;33:579–89.
Sanidas EE, Daskalakis M, Sbyrakis N, et al. Modifications of the learning curve guidelines for breast cancer sentinel node biopsy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005;31:357–63.
Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M, Shikayama T. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:211–5.
Tagaya N, Yamazaki R, Nakagawa A, et al. Intraoperative identification of sentinel lymph nodes by near-infrared fluorescence imaging in patients with breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2008;195:850–3.
McMasters KM, Wong SL, Martin RCG II, et al. Dermal injection of radioactive colloid is superior to peritumoral injection for breast cancer sentinel lymph node biopsy: results of a multiinstitutional study. Ann Surg. 2001;233:676–87.
Kang SW, Chung SE, Shin WJ, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and late geographic hyperfluorescence on indocyanine green angiography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:759–64.
Schneider PD. Preoperative assessment of liver function. Surg Clin North Am. 2004;84:355–73.
Vogt PR, Bauer EP, Graves K. Novadaq SPY Intraoperative imaging system—current status. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;51:49–51.
Hirsche C, Murawa D, Mohr Z, Kneif S, Hunerbein M. ICG fluorescent–guided sentinel node biopsy for axillary nodal staging in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;121:373–8.
Tagaya N, Tsumuraya M, Nakagawa A, et al. 2010 Indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence imaging versus radioactive colloid for sentinel lymph node identification in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:674.
Aoyama K, Kamio T, Nishizawa M, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer patients using fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:157.
Bass SS, Cox CE, Reintgen DS, et al. Learning curves and certification for breast cancer lymphatic mapping. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 1999;8:497–509.
Dupont E, Cox C, Shivers S, et al. Learning curves and breast cancer lymphatic mapping: Institutional volume index. J Surg Res. 2001;97:92–6.
Hojo T, Nagao T, Kikuyama M, et al. Evaluation of sentinel node biopsy by combined fluorescent and dye method and lymph flow for breast cancer. Breast. 2010;19:210–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, A., Kamimura, M., Ogura, K. et al. A Comparison of Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Imaging Plus Blue Dye and Blue Dye Alone for Sentinel Node Navigation Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients. Ann Surg Oncol 19, 4112–4116 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2478-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2478-0