Abstract
Background:
The relationships between adhesion molecules and measures of obesity and metabolic syndrome in different ethnic populations are unclear.
Objective:
Our aim was to study the association between body mass index (BMI), waist-hip ratio (WHR) and the parameters of the metabolic syndrome with four different adhesion molecules, adjusting for potential confounders, in men and women from different ethnic origins.
Methods:
Soluble plasma adhesion molecules (sP-selectin, sE-selectin, intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) were measured in 261 white (120 women), 188 African origin (99 women) and 215 South Asian (99 women) individuals living in South London. All were free from coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke and other cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, drug therapy for hypertension or high lipids, hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptive pill.
Results:
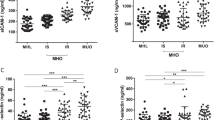
sE-selectin levels were positively and significantly associated with both BMI (P<0.001) and WHR (P<0.001). There were no major interactions with either sex or ethnicity. The strength of the association between sE-selectin and WHR was not affected by multiple adjustment for age, sex, ethnicity smoking, blood pressure, serum lipids and insulin (P<0.001), whereas the association with BMI was attenuated by multiple adjustments (P=0.037). An approximate 2% higher sE-selectin levels would be associated with a 1 unit higher BMI and a 0.01 unit greater WHR.
Conclusions:
The relationships between adhesion molecules and conventional measures of obesity are adhesion molecule specific and are strongest between sE-selectin and WHR.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krieglstein CF, Granger DN . Adhesion molecules and their role in vascular disease. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 44S–54S.
Pigott R, Dillon LP, Hemingway IH, Gearing AJ . Soluble forms of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 are present in the supernatants of cytokine activated cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992; 187: 584–589.
Leeuwenberg JF, Smeets EF, Neefjes JJ, Shaffer MA, Cinek T, Jeunhomme TM et al. E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 are released by activated human endothelial cells in vitro. Immunology 1992; 77: 543–549.
Miller MA, Sagnella GA, Kerry SM, Strazzullo P, Cook DG, Cappuccio FP . Ethnic differences in circulating soluble adhesion molecules. The Wandsworth heart and stroke study. Clin Sci (London) 2003; 104: 591–598.
Miller MA, Kerry SM, Cook DG, Cappuccio FP . Cellular adhesion molecules and blood pressure: interaction with sex in a multi-ethnic population. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 705–711.
Cappuccio FP . Ethnicity and cardiovascular risk: variations in people of African ancestry and South Asian origin. J Hum Hypertens 1997; 11: 571–576.
Hwang SJ, Ballantyne CM, Sharrett AR, Smith LC, Davis CE, Gotto Jr AM et al. Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease cases: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 1997; 96: 4219–4225.
Ferri C, Desideri M, Valenti M, Bellini C, Pasin M, Santucci A et al. Early upregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules in obese hypertensive men. Hypertension 1999; 34: 568–573.
Demerath E, Towne B, Blangero J, Siervogel RM . The relationship of soluble ICAM-1, VCAM-1, P-selectin and E-selectin to cardiovascular disease risk factors in healthy men and women. Ann Human Biol 2001; 28: 664–678.
Rohde LE, Hennekens CH, Ridker PM . Cross-sectional study of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and cardiovascular risk factors in apparently healthy men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19: 1595–1599.
DeSouza CA, Dengel DR, Macko RF, Cox K, Seals DR . Elevated levels of circulating cell adhesion molecules in uncomplicated essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: 1335–1341.
Ponthieux A, Herbeth B, Droesch S, Haddy N, Lambert D, Visvikis S . Biological determinants of serum ICAM-1, E-selectin, P-selectin and L-selectin levels in healthy subjects: the Stanislas study. Atherosclerosis 2004; 172: 299–308.
Cappuccio FP, Cook DG, Atkinson RW, Strazzullo P . Prevalence, detection, and management of cardiovascular risk factors in different ethnic groups in south London. Heart 1997; 78: 555–563.
Cappuccio FP, Cook DG, Atkinson RW, Wicks PD . The Wandsworth Heart & Stroke Study. A population-based survey of cardiovascular risk factors in different ethnic groups. Methods and baseline findings. Nutr Metab Cacrdiovasc Dis 1998; 8: 371–385.
National Institutes of Health. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute in cooperation with the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Rockville, MD. Publication No. 98-4083 1998.
Vega GL . Obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Minerva Endocrinol 2004; 29: 47–54.
Barnes PJ, Karin M . Mechanisms of disease: nuclear factor-κB – a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 1066–1071.
Dandona P, AlJada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Hamouda W, Assian E et al. Insulin inhibits intranuclear nuclear factor κB and stimulates IκB in mononuclear cells in obese subjects: evidence for an anti-inflammatory effect? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 3257–3265.
Miller MA, Kerry SM, Dong Y, Strazzullo P, Cappuccio FP . Association between the Thr715Pro P-selectin gene polymorphism and soluble P-selectin levels in a multiethnic population in South London. Thromb Haemost 2004; 5: 1060–1065.
Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A, Mohanty P, Garg R . Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation 2005; 111: 1448–1454.
Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Abdo T, Devjit T, Chaudhuri A et al. Increase in intranuclear nuclear factor κB and decrease in inhibitor κB in mononuclear cells after a mixed meal: evidence for a proinflammatory effect. Am J Clinical Nutrition 2004; 79: 682–690.
Ito H, Ohshima A, Inoue M, Ohto N, Nakasuga K, Kaji Y et al. Weight reduction decreases soluble cellular adhesion molecules in obese women. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2002; 29: 399–404.
Chia MC . The role of adhesion molecules in atherosclerosis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 1998; 35: 573–602.
Furie B, Furie BC . Role of platelet P-selectin and microparticle PSGL-1 in thrombus formation. Trends Mol Med 2004; 4: 171–178.
Winkler G, Lakatos P, Salamon F, Nagy Z, Speer G, Kovacs M et al. Elevated serum TNF-alpha level as a link between endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance in normotensive obese patients. Diabet Med 1999; 16: 207–211.
Arcaro G, Zamboni M, Rossi L, Turcato E, Covi G, Armellini F et al. Body fat distribution predicts the degree of endothelial dysfunction in uncomplicated obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23: 936–942.
Dandona P, Weinstock R, Thusu K, Abdel-Rahman E, Aljada A, Wadden T . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in sera of obese patients: fall with weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 2907–2910.
Hanusch-Enserer U, Cauza E, Spak M, Endler G, Dunky A, Tura A et al. Improvement of insulin resistance and early atherosclerosis in patients after gastric banding. Obes Res 2004; 12: 284–291.
Acknowledgements
A list of the WHSS Group is given elsewhere.14 The study has received support from the former Wandsworth and South Thames Regional Health Authorities, NHS R&D Directorate, British Heart Foundation, former British Diabetic Association and The Stroke Association. This study was supported by the British Heart Foundation (Project Grant PG/2001023). There are no conflicts of interest or any disclaimers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M., Cappuccio, F. Cellular adhesion molecules and their relationship with measures of obesity and metabolic syndrome in a multiethnic population. Int J Obes 30, 1176–1182 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803264
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803264
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of circulating adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis
Inflammation Research (2024)
-
Association between serum cell adhesion molecules with hs-CRP, uric acid and VEGF genetic polymorphisms in subjects with metabolic syndrome
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity, Body Mass Index, and Circulating Levels of Cellular Adhesion Molecules
Lung (2020)
-
Chemokine gene polymorphisms association with increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Tatar ethnic group, Russia
Molecular Biology Reports (2019)
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 in patients with severe osteoarthritis of the hip
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift (2019)