Key Points
-
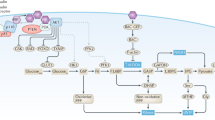
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signalling systems are ancient and involve regulation of physiology in ways beyond their well-known medically recognized roles concerning regulation of carbohydrate metabolism and growth.
-
There is substantial experimental and clinical evidence that cancer cells express insulin and IGF1 receptors, and that these receptors are important activators of the Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling networks in neoplastic tissue.
-
Population studies provide substantial direct and circumstantial evidence that cancer risk and cancer prognosis are influenced by IGF1 and insulin levels.
-
Preclinical evaluation of drug candidates that target IGF1 and/or insulin signalling has revealed antineoplastic activity.
-
At least 10 different drug candidates are being evaluated in clinical trials; early results have justified expansion of clinical trial programmes.
-
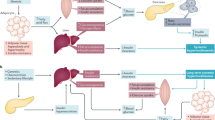
Energy metabolism is an important topic in cancer research. IGF1 and insulin might have roles, along with other regulators, in mediating effects of perturbations of whole organism energy balance (for example, dietary excess, caloric restriction and exercise) on cellular energy physiology.
Abstract
Insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are well known as key regulators of energy metabolism and growth. There is now considerable evidence that these hormones and the signal transduction networks they regulate have important roles in neoplasia. Epidermiological, clinical and laboratory research methods are being used to investigate novel cancer prevention and treatment strategies related to insulin and IGF signalling. Pharmacological strategies under study include the use of novel receptor-specific antibodies, receptor kinase inhibitors and AMP-activated protein kinase activators such as metformin. There is evidence that insulin and IGF signalling may also be relevant to dietary and lifestyle factors that influence cancer risk and cancer prognosis. Recent results are encouraging and have justified the expansion of many translational research programmes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steiner, D. F., Chan, S. J., Welsh, J. M. & Kwok, S. C. Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Annu. Rev. Genet. 19, 463–484 (1985).
De Meyts, P. Insulin and its receptor: structure, function and evolution. Bioessays 26, 1351–1362 (2004).
Dong, M. Q. et al. Quantitative mass spectrometry identifies insulin signaling targets in C. elegans. Science 317, 660–663 (2007).
Toyoshima, Y. et al. The role of insulin receptor signaling in zebrafish embryogenesis. Endocrinol. 7 Aug 2008 (doi:10.1210/en.2008-0329).
Shaw, R. J. et al. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science 310, 1642–1646 (2005). Genetic evidence from a knockout model that advances understanding of the mechanism of action of metformin.
Dowling, R. J., Zakikhani, M., Fantus, I. G., Pollak, M. & Sonenberg, N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67, 10804–10812 (2007).
Zakikhani, M., Dowling, R., Fantus, I. G., Sonenberg, N. & Pollak, M. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66, 10269–10273 (2006). This report provides evidence that metformin does not act as an 'insulin sensitizer' for neoplastic cells in vitro ; rather it reduces mitogenic activity of insulin by an AMPK-dependent mechanism.
Bowker, S. L., Majumdar, S. R., Veugelers, P. & Johnson, J. A. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care 29, 254–258 (2006).
Evans, J. M., Donnelly, L. A., Emslie-Smith, A. M., Alessi, D. R. & Morris, A. D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 330, 1304–1305 (2005). This population study provides hypothesis-generating evidence for an unexpected reduction of cancer risk associated with use of metformin among diabetic subjects.
Pollak, M. N., Schernhammer, E. S. & Hankinson, S. E. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 505–518 (2004).
Chitnis, M. M., Yuen, J. S. P., Protheroe, A. S., Pollak, M. & Macaulay, V. M. The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6364–6370 (2008).
Sachdev, D. & Yee, D. Disrupting insulin-like growth factor signaling as a potential cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 6, 1–12 (2007).
Kroemer, G. & Pouyssegur, J. Tumor cell metabolism: cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer Cell 13, 472–482 (2008).
DeBerardinis, R. J., Lum, J. J., Hatzivassiliou, G. & Thompson, C. B. The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell. Metab. 7, 11–20 (2008).
Shaw, R. J. Glucose metabolism and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 598–608 (2006).
Brogiolo, W. et al. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr. Biol. 11, 213–221 (2001).
Teleman, A. A., Hietakangas, V., Sayadian, A. C. & Cohen, S. M. Nutritional control of protein biosynthetic capacity by insulin via Myc in Drosophila. Cell. Metab. 7, 21–32 (2008).
Benyoucef, S., Surinya, K. H., Hadaschik, D. & Siddle, K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem. J. 403, 603–613 (2007).
Belfiore, A. The role of insulin receptor isoforms and hybrid insulin/IGF-I receptors in human cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13, 671–686 (2007).
Eccles, S. A. et al. NVP-AUY922: a novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor active against xenograft tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Cancer Res. 68, 2850–2860 (2008).
Lang, S. A. et al. Targeting heat shock protein 90 in pancreatic cancer impairs insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling, disrupts an interleukin-6/signal-transducer and activator of transcription 3/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α autocrine loop, and reduces orthotopic tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 6459–6468 (2007).
Martins, A. S. et al. A pivotal role for heat shock protein 90 in Ewing sarcoma resistance to anti-insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor treatment: in vitro and in vivo study. Cancer Res. 68, 6260–6270 (2008).
De Souza, A. T. et al. M6P/IGF2R gene is mutated in human hepatocellular carcinomas with loss of heterozygosity. Nature Genet. 11, 447–449 (1995).
Hellawell, G. O. et al. Expression of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor is up-regulated in primary prostate cancer and commonly persists in metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 62, 2942–2950 (2002).
Cox, M. et al. Insulin receptor expression by human prostate cancers. Prostate 10 Sep 2008 (doi:10.1002/pros.20852).
Law, J. H. et al. Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-1/insulin receptor is present in all breast cancer subtypes and is related to poor survival. Cancer Res. (in the press).
Osborne, C. K., Bolan, G., Monaco, M. E. & Lippman, M. E. Hormone responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue culture: effect of insulin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 73, 4536–4540 (1976).
Frasca, F. et al. The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 114, 23–37 (2008).
Arcaro, A. et al. Novel role for insulin as an autocrine growth factor for malignant brain tumour cells. Biochem. J. 406, 57–66 (2007).
Ohsugi, M. et al. Reduced expression of the insulin receptor in mouse insulinoma (MIN6) cells reveals multiple roles of insulin signaling in gene expression, proliferation, insulin content, and secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 4992–5003 (2005).
Kaneda, A. et al. Enhanced sensitivity to IGF-II signaling links loss of imprinting of IGF2 to increased cell proliferation and tumor risk. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 20926–20931 (2007).
Zhang, L. et al. Gene expression profiles in normal and cancer cells. Science 276, 1268–1272 (1997). A demonstration that overexpression of IGF2 is a common event in colorectal cancer.
Firth, S. M. & Baxter, R. C. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 23, 824–854 (2002).
Buckbinder, L. et al. Induction of the growth inhibitor IGF-binding protein 3 by p53. Nature 377, 646–649 (1995).
Rozen, F., Yang, X., Huynh, H. T. & Pollak, M. Antiproliferative action of vitamin-D-related compounds and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 accumulation. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 89, 652–656 (1997).
Huynh, H. T., Yang, X. F. & Pollak, M. Estradiol and antiestrogens regulate a growth inhibitory insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 autocrine loop in human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 1016–1021 (1996).
Gucev, Z. S., Oh, Y., Kelley, K. M. & Rosenfeld, R. G. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 mediates retinoic acid and transforming growth factor β2-induced growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 56, 1545–1550 (1996).
So, A. et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 is a novel therapeutic target associated with breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6944–6954 (2008).
Mehrian-Shai, R. et al. Insulin growth factor-binding protein 2 is a candidate biomarker for PTEN status and PI3K/Akt pathway activation in glioblastoma and prostate cancer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 5563–5568 (2007).
Levitt, R. J., Georgescu, M. M. & Pollak, M. PTEN-induction in U251 glioma cells decreases the expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 1056–1061 (2005).
Perks, C. M., Vernon, E. G., Rosendahl, A. H., Tonge, D. & Holly, J. M. IGF-II and IGFBP-2 differentially regulate PTEN in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26, 5966–5972 (2007).
Holmes, K. M. et al. Integrin-linked kinase contributes to glioma progression in a glial-specific tumour mouse model. Proc. 99th Annu. Meet. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res., Abstr. 2909 (AACR, Philadelphia, 2008).
Zhu, W. et al. IGFBP-4 is an inhibitor of canonical Wnt signalling required for cardiogenesis. Nature 454, 345–349 (2008).
Heuson, J. C. & Legros, N. Influence of insulin deprivation on growth of the 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary carcinoma in rats subjected to alloxan diabetes and food restriction. Cancer Res. 32, 226–232 (1972).
Hede, K. Doctors seek to prevent breast cancer recurrence by lowering insulin levels. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 100, 530–532 (2008).
Pollak, M., Perdue, J. F., Margolese, R. G., Baer, K. & Richard, M. Presence of somatomedin receptors on primary human breast and colon carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 38, 223–230 (1987). This paper provides the initial description of IGF1 binding sites on human tumour specimens, and proposed the possibility of therapies that target IGF1 receptors.
Myal, Y., Shiu, R. P., Bhaumick, B. & Bala, M. Receptor binding and growth-promoting activity of insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer cells (T-47D) in culture. Cancer Res. 44, 5486–5490 (1984).
Sell, C. et al. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen is unable to transform mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11217–11221 (1993).
Majeed, N. et al. A germ line mutation that delays prostate cancer progression and prolongs survival in a murine prostate cancer model. Oncogene 24, 4736–4740 (2005).
Yang, X. F., Beamer, W., Huynh, H. T. & Pollak, M. Reduced growth of human breast cancer xenografts in hosts homozygous for the 'lit' mutation. Cancer Res. 56, 1509–1511 (1996). This is an early example of laboratory evidence for an influence of the host growth hormone–IGF1 axis on tumour growth in vivo.
Wu, Y. et al. Reduced circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels delay the onset of chemically and genetically induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 63, 4384–4388 (2003).
Pollak, M., Blouin, M. J., Zhang, J. C. & Kopchick, J. J. Reduced mammary gland carcinogenesis in transgenic mice expressing a growth hormone anatgonist. Br. J. Cancer 85, 428–430 (2001).
Creighton, C. J. et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I activates gene transcription programs strongly associated with poor breast cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 4078–4085 (2008).
Goya, M. et al. Growth inhibition of human prostate cancer cells in human adult bone implanted into nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice by a ligand-specific antibody to human insulin-like growth factors. Cancer Res. 64, 6252–6258 (2004).
Haluska, P. et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer Res. 66, 362–371 (2006).
Ji, Q. S. et al. A novel, potent, and selective insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor blocks insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in vitro and inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I receptor dependent tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 6, 2158–2167 (2007).
Rowinsky, E. K. et al. IMC-A12, a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 5549s–5555s (2007).
Cohen, B. D. et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751, 871. Clin.Cancer Res. 11, 2063–2073 (2005).
Venkateswaran, V. et al. Association of diet-induced hyperinsulinemia with accelerated growth of prostate cancer (LNCaP) xenografts. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 99, 1793–1800 (2007). This paper provides experimental evidence consistent with a stimulatory effect of a high-sucrose diet on prostate cancer proliferation, mediated by diet-induced hyperinsulinaemia.
Jenkins, P. J. Cancers associated with acromegaly. Neuroendocrinology 83, 218–223 (2006).
Shevah, O. & Laron, Z. Patients with congenital deficiency of IGF-I seem protected from the development of malignancies: a preliminary report. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 17, 54–57 (2007).
Schernhammer, E. S. et al. Body shape throughout life and correlations with IGFs and GH. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 14, 721–732 (2007).
Vatten, L. J., Nilsen, S. T., Odegard, R. A., Romundstad, P. R. & Austgulen, R. Insulin-like growth factor-I and leptin in umbilical cord plasma and infant birth size at term. Pediatrics 109, 1131–1135 (2002).
McCormack, V. A. et al. Fetal growth and subsequent risk of breast cancer: results from long term follow up of Swedish cohort. BMJ 326, 248 (2003).
Sandhu, M. S., Luben, R., Day, N. E. & Khaw, K. T. Self-reported birth weight and subsequent risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 11, 935–938 (2002).
Tibblin, G., Eriksson, M., Cnattingius, S. & Ekbom, A. High birthweight as a predictor of prostate cancer risk. Epidemiology 6, 423–424 (1995).
Gunnell, D. et al. Height, leg length, and cancer risk: a systematic review. Epidemiol. Rev. 23, 313–342 (2001).
Ahlgren, M., Melbye, M., Wohlfahrt, J. & Sorensen, T. I. Growth patterns and the risk of breast cancer in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 1619–1626 (2004).
Diorio, C. et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I, IGF-binding protein-3, and mammographic breast density. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 14, 1065–1073 (2005).
Byrne, C. et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and mammographic density. Cancer Res. 60, 3744–3748 (2000).
Diorio, C., Brisson, J., Berube, S. & Pollak, M. Genetic polymorphisms involved in insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway in relation to mammographic breast density and IGF levels. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17, 880–888 (2008).
Tamimi, R. M. et al. Common genetic variation in IGF1, IGFBP-1, and IGFBP-3 in relation to mammographic density: a cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer Res. 9, R18, (2007).
Adams, T. D. et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 753–761 (2007).
Sjostrom, L. et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 741–752 (2007).
de la Torre, N. G. et al. Effects of weight loss after bariatric surgery for morbid obesity on vascular endothelial growth factor-A, adipocytokines, and insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 19 Aug 2008 (doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1370).
Ma, J. et al. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, and IGF-binding protein-3. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 91, 620–625 (1999).
Giovannucci, E. et al. A prospective study of plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 9, 345–349 (2000).
Palmqvist, R. et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study in northern Sweden. Gut 50, 642–646 (2002).
Chan, J. M. et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279, 563–566 (1998). This was the first prospective population study to investigate the relationship between circulating IGF1 levels and cancer risk; the finding led to a renewed interest in IGF1 physiology in the context of neoplasia and stimulated both epidemiological and laboratory research.
Chan, J. M. et. al. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 as predictors of advanced-stage prostate cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 94, 1099–1106 (2002).
Harman, S. M., Metter, E. J., Blackman, M. R., Landis, P. K. & Carter, H. B. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-II, IGF-binding protein-3, and prostate-specific antigen as predictors of clinical prostate cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 4258–4265 (2000).
Stattin, P. et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 92, 1910–1917 (2000).
Schernhammer, E. S., Holly, J. M., Hunter, D. J., Pollak, M. N. & Hankinson, S. E. Insulin-like growth factor-I, its binding proteins (IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3), and growth hormone and breast cancer risk in The Nurses Health Study II. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 13, 583–592 (2006).
Kurmasheva, R. T. & Houghton, P. J. IGF-I mediated survival pathways in normal and malignant cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1766, 1–22 (2006).
Miller, A. B. Commentary: implications of the frequent occurrence of occult carcinoma of the prostate. Int. J. Epidemiol. 36, 282–284 (2007).
Cheng, I. et al. Common genetic variation in IGF1 and prostate cancer risk in the Multiethnic Cohort. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 98, 123–134 (2006).
Johansson, M. et al. Implications for prostate cancer of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) genetic variation and circulating IGF-I levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 4820–4826 (2007).
Reeves, S. G. et al. IGF1 is a modifier of disease risk in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 123, 1339–1343 (2008).
Suh, Y. et al. Functionally significant insulin-like growth factor I receptor mutations in centenarians. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3438–3442 (2008).
Ma, J. et al. Prediagnostic body-mass index, plasma C-peptide concentration, and prostate cancer-specific mortality in men with prostate cancer: a long-term survival analysis. Lancet Oncol. 9, 1039–1047 (2008). This paper provides direct evidence for a relationship between plasma c-peptide levels, which reflect insulin secretion, and prostate cancer-specific death in men with this disease.
Goodwin, P. J. et al. Fasting insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 42–51 (2002). This report provides early evidence for a relationship between high-fasting insulin levels and risk of relapse in breast cancer, a finding since confirmed by reference 94 and additional studies.
Freedland, S. J., Giovannucci, E. & Platz, E. A. Are findings from studies of obesity and prostate cancer really in conflict? Cancer Causes Control 17, 5–9 (2006).
Giovannucci, E. Metabolic syndrome, hyperinsulinemia, and colon cancer: a review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 86, s836–s842 (2007).
Pollak, M. et al. Insulin resistance, estimated by serum c-peptide level, is associated with reduced event-free survival for postmenopausal women in the NCIC MA14 adjuvant breast cancer trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 24 (June 20 Suppl.), 524 (2006).
Wolpin, B. M. et al. Insulin, the insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. (in the press).
Fuchs, C. S. et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like binding protein-3 and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from intergroup trial N9741. Clin. Cancer Res. (in the press).
Calle, E. E., Rodriguez, C., Walker-Thurmond, K. & Thun, M. J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U. S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1625–1638 (2003).
Lopez, T. & Hanahan, D. Elevated levels of IGF-1 receptor convey invasive and metastatic capability in a mouse model of pancreatic islet tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 1, 339–353 (2002).
Plymate, S. R. et al. An antibody targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor enhances the castration-induced response in androgen-dependent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 6429–6439 (2007).
Pollak, M. N. et al. NCIC-CTG MA14 trial: Tamoxifen (tam) vs. tam + octreotide (oct) for adjuvant treatment of stage I or II postmenopausal breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 532 (2008).
Divisova, J. et al. The growth hormone receptor antagonist pegvisomant blocks both mammary gland development and MCF-7 breast cancer xenograft growth. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 98, 315–327 (2006).
Lacy, M. Q. et al. Phase I, Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the anti-insulin like growth factor type 1 receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 3196–3203 (2008).
Haluska, P. et al. Phase I dose escalation study of the anti insulin-like growth factor-I receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 5834–5840 (2007).
De Bono, J. S. et al. Potential applications for circulating tumor cells expressing the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 3611–3616 (2007).
Karp, D. D. et al. High activity of the anti-IGF-IR antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in squamous NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 8015 (2008). This abstract updated the latest results of a phase II clinical trial study of a combination of an IGF1R-specific antibody with chemotherapy in the treatment of squamous lung cancer; the data contributed to the justification of large phase III clinical trial studies currently underway.
Gualberto, A. et al. Characterization of NSCLC patients responding to anti-IGF-IR therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 8000 (2008).
Olmos, D. et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and preliminary activity of the anti-IGF-IR antibody CP-751, 871 in patients with sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 10501 (2008).
Yin, D., et al. Population pharmacokinetics of CP-751,871, a monoclonal antibody against IGF-I receptor, in patients with multiple myeloma or solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 2524 (2008).
Tolcher, A. W. et al. A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of AMG 479, a fully human monoclonal antibody against insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF-1R), in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 25 (Jun 20 Suppl.), 3002 (2007).
Sarantopoulos, J. et al. A phase IB study of AMG 479, a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) antibody, in combination with panitumumab (P) or gemcitabine (G). J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 3583 (2008).
Moreau, P. et al. Phase I study of AVE1642 anti IGF-1R monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced multiple myeloma. Proceedings of ASH, abstract 1166 (2007).
Tolcher, A. W. et al. A phase I study of AVE1642, a humanized monoclonal antibody IGF-1R antagonist, in patients with advanced solid tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 3582 (2008).
Higano, C. S. et al. A phase I, first in man study of weekly IMC-A12, a fully human insulin like growth factor-I receptor IgG1 monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 25 (Jun 20 Suppl.), 3505 (2007).
Rothenberg, M. L. et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of the anti-IGF-IR recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (Mab) IMC-A12, administered every other week to patients with advanced solid tumors. Proc. AACR NCI EORTC Int. Conf. Mol. Targets Cancer Therapeut., abstract C84 (2007).
Higano, C. et al. A phase I study of the recombinant human IgG1 anti-IGF-IR monoclonal antibody (Mab) IMC-A12, administered on a weekly basis to patients with advanced solid tumors: interim analysis. Proc. AACR NCI EORTC Int. Conf. Mol. Targets Cancer Therapeut., abstract B19 (2007).
Hidalgo, M. et al. A phase I sudy of MK-0646, a humanized monoclonal antibody against the insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 in advanced solid tumor patients in a q2 wk schedule. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 3520 (2008).
Atzori, F. et al. A phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of weekly MK-0646, an insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 3519 (2008).
Rodon, J. et al. A phase I study of q3W R1507, a human monoclonal antibody IGF-1R antagonist in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 3590 (2007).
del Rincon, J. P. et al. Growth hormone regulation of p85α expression and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in adipose tissue: mechanism for growth hormone-mediated insulin resistance. Diabetes 56, 1638–1646 (2007).
Zimmermann, K., et al. Balancing oral exposure with Cyp3A4 inhibition in benzimidazole-based IGF-IR inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 4075–4080 (2008).
Mulvihill, M. J. et al. Novel 2-phenylquinolin-7-yl-derived imidazo[1,5-a]pyrazines as potent insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 1359–1375 (2008).
Hofmann, F. & Garcia-Echeverria, C. Blocking the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a strategy for targeting cancer. Drug Discov. Today 10, 1041–1047 (2005).
Vasilcanu, R. et al. Picropodophyllin induces downregulation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: potential mechanistic involvement of Mdm2 and b-arrestin1. Oncogene 27, 1629–1638 (2008).
D'Ercole, A. J. & Ye, P. Expanding the mind: IGF-I and brain development. Endocrinol. 7 Aug 2008 (doi:10.1210/en.2008-0820).
Zhang, H., Pelzer, A. M., Kiang, D. T. & Yee, D. Down-regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to insulin. Cancer Res. 67, 391–397 (2007).
Hardie, D. G. Neither LKB1 nor AMPK are the direct targets of metformin. Gastroenterology 131, 973 (2006).
Algire, C., Zakikhani, M., Blouin, M.-J., Shuai, J. H. & Pollak, M. Metformin attenuates the stimulatory effect of a high energy diet on in vivo H59 carcinoma growth. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 15, 833–839 (2008). The in vivo model described in this paper suggests that antineoplastic activity of metformin might be confined to metabolically-defined subsets of individuals.
Rattan, R., Giri, S., Singh, A. K. & Singh, I. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-b-D-ribofuranoside inhibits cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 39582–39593 (2005).
Cool, B. et al. Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell. Metab. 3, 403–416 (2006).
Blagosklonny, M. V. & Campisi, J. Cancer and aging: more puzzles, more promises? Cell Cycle 7, 2615–2618 (2008).
Gotlieb, W. H. et al. In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 110, 246–250 (2008).
Huang, X. et al. Important role of the LKB1–AMPK pathway in suppressing tumourigenesis in PTEN deficient mice. Biochem. J. 412, 211–221 (2008).
Ben Sahra, I. et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene 27, 3576–3586 (2008).
Anisimov, V. N. et al. Effect of metformin on life span and on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Exp. Gerontol. 40, 685–693 (2005).
Phoenix, K. N., Vumbaca, F. & Claffey, K. P. Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation promotes the angiogenic phenotype in the ERα negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 7 Feb 2008 (doi:10.1007/s10549-008-9916-5).
Buzzai, M. et al. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67, 6745–6752 (2007).
Liang, J. et al. The energy sensing LKB1–AMPK pathway regulates p27kip1 phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or apoptosis. Nature Cell Biol. 9, 218–224 (2007).
Borger, D. R., Gavrilescu, L. C., Bucur, M. C., Ivan, M. & Decaprio, J. A. AMP-activated protein kinase is essential for survival in chronic hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 370, 230–234 (2008).
Anisimov, V. N. et al. Metformin slows down aging and extends life span of female SHR mice. Cell Cycle 7, 2769–2773 (2008).
Jiralerspong, S. et al. The effects of metformin on pathologic complete response rates in diabetic breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant systemic therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (May 20 Suppl.), 528 (2008).
Wan, X., Harkavy, B., Shen, N., Grohar, P. & Helman, L. J. Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26, 1932–1940 (2007).
O'Reilly, K. E. et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 66, 1500–1508 (2006). This reference shows that rapamycin activates the Akt pathway by a mechanism not originally anticipated that might be dependent on IGF1 signalling, providing a rationale for combination therapies involving rapamycin analogues and IGF1 and/or insulin receptor-targeting agents.
Lu, Y., Zi, X., Zhao, Y., Mascarenhas, D. & Pollak, M. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). J. Natl Cancer Inst. 93, 1852–1857 (2001). This paper provided early evidence for IGF1R-mediated resistance to other targeted therapies. It led to other reports that extended the findings, and contributed to the rationale for clinical trials now under way that co-target the IGF1R with other receptors, including members of the EGF receptor family.
Guix, M. et al. Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer cells is mediated by loss of IGF-binding proteins. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 2609–2619 (2008).
Buck, E. et al. Feedback mechanisms promote cooperativity for small molecule inhibitors of epidermal and insulin-like growth factor receptors. Cancer Res. 68, 8322–8332 (2008).
Lisztwan, J., Pornon, A., Chen, B., Chen, S. & Evans, D. B. The aromatase inhibitor letrozole and inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor I receptor synergistically induce apoptosis in in vitro models of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 10, R56 (2008).
Kopchick, J. J., Parkinson, C., Stevens, E. C. & Trainer, P. J. Growth hormone receptor antagonists: discovery, development, and use in patients with acromegaly. Endocr. Rev. 23, 623–646 (2002).
Cosaceanu, D. et al. Ionizing radiation activates IGF-1R triggering a cytoprotective signaling by interfering with Ku-DNA binding and by modulating Ku86 expression via a p38 kinase-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26, 2423–2434 (2007).
Burtrum, D., Pytowski, B. & Ludwig, D. Abrogation of PTEN does not confer resistance to anti-IGF-IR targeted therapy in IGF responsive tumor cells. Proc. 98th Annu. Meet. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res., Abstr. 425 (AACR, Philadelphia, 2007).
Jee, S. H. et al. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA 293, 194–202 (2005).
Kling, J. Inhaled insulin's last gasp? Nature Biotechnol. 26, 479–480 (2008).
Bouatia-Naji, N. et al. A polymorphism within the G6PC2 gene is associated with fasting plasma glucose levels. Science 320, 1085–1088 (2008).
Folsom, A. R. et al. Variation in TCF7L2 and increased risk of colon cancer: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Care 31, 905–909 (2008).
Smith, M. R., Lee, H. & Nathan, D. M. Insulin sensitivity during combined androgen blockade for prostate cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 1305–1308 (2006). This paper provides solid clinical evidence for hyperinsulinaemia as a consequence of androgen deprivation.
Locke, J. A. et al. Androgen levels increase by intratumoral de novo steroidogenesis during progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68, 6407–6415 (2008).
Warburg, O. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 124, 269–270 (1956).
Christofk, H. R. et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 452, 230–233 (2008).
Moore, T. et al. Dietary energy balance modulates signaling through the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways in multiple epithelial tissues. Cancer Prev. Res. 1, 65–76, (2008).
Jiang, W., Zhu, Z. & Thompson, H. J. Dietary energy restriction modulates the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase, Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin in mammary carcinomas, mammary gland, and liver. Cancer Res. 68, 5492–5499 (2008). This paper extends prior efforts to clarify the mechanisms underlying the protective effect of dietary energy restriction on neoplastic growth, documenting changes in gene expression within tumours as a function of host diet.
Kritchevsky, D. & Klurfeld, D. M. Influence of caloric intake on experimental carcinogenesis: a review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 206, 55–68 (1986).
Patel, A. C., Nunez, N. P., Perkins, S. N., Barrett, J. C. & Hursting, S. D. Effects of energy balance on cancer in genetically altered mice. J. Nutr. 134, 3394S–3398S, (2004).
Carling, D. LKB1: a sweet side to Peutz-Jeghers syndrome? Trends Mol. Med. 12, 144–147 (2006).
Hardie, D. G. AMPK and Raptor: matching cell growth to energy supply. Mol. Cell 30, 263–265 (2008).
Gwinn, D. M. et al. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol. Cell 30, 214–226 (2008).
Kahn, B. B., Alquier, T., Carling, D. & Hardie, D. G. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell. Metab. 1, 15–25 (2005).
Anisimov, V. N. et al. Metformin decelerates aging and development of mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 139, 721–723 (2005).
Morton, G. J., Cummings, D. E., Baskin, D. G., Barsh, G. S. & Schwartz, M. W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443, 289–295 (2006).
Inagaki, T. et al. Inhibition of growth hormone signaling by the fasting-induced hormone FGF21. Cell. Metab. 8, 77–83 (2008).
Giovannucci, E. et al. C. Nutritional predictors of insulin-like growth factor I and their relationships to cancer in men. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12, 84–89 (2003).
Bernstein, L. et al. Lifetime recreational exercise activity and breast cancer risk among black women and white women. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 97, 1671–1679 (2005).
Zhu, Z. et al. Effect of nonmotorized wheel running on mammary carcinogenesis: circulating biomarkers, cellular processes, and molecular mechanisms in rats. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17, 1920–1929 (2008).
Narkar, V. A. et al. AMPK and PPARγ agonists are exercise mimetics. Cell 134, 405–415 (2008).
Global action against cancer. (World Health Organization Press, Geneva, 2005).
Marques-Vidal, P., Madeleine, G., Romain, S., Gabriel, A. & Bovet, P. Secular trends in height and weight among children and adolescents of the Seychelles, 1956–2006 BMC. Public Health 8, 166 (2008).
Cardoso, H. F. Secular changes in body height and weight of Portuguese boys over one century. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 20, 270–277 (2008).
Turcotte, E., Leblanc, M., Carpentier, A. & Benard, F. Optimization of whole-body positron emission tomography imaging by using delayed 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose injection following I. V. Insulin in diabetic patients. Mol. Imaging Biol. 8, 348–354 (2006).
Shang Y et al. Antixenograft tumor activity of a humanized anti-insulin-like growth factor-I receptor monoclonal antibody is associated with decreased AKT activation and glucose uptake. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 2599–2608 (2008).
Cornelissen, B., McLarty, K., Kersemans, V. & Reilly, R. M. The level of insulin growth factor-1 receptor expression is directly correlated with the tumor uptake of 111In-IGF-1(E3R) in vivo and the clonogenic survival of breast cancer cells exposed in vitro to trastuzumab (Herceptin). Nucl. Med. Biol. 35, 645–653 (2008).
Raju, T. N. A mysterious something: the discovery of insulin and the 1923 Nobel Prize for Frederick G. Banting (1891–1941) and John J. R. Macleod(1876–1935). Acta Paediatr. 95, 1155–1156 (2006).
Elias, J. J. Effect of insulin and cortisol on organ cultures of adult mouse mammary gland. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 101, 500–502 (1959).
Heuson, J. C., Coune, A. & Heimann, R. Cell proliferation induced by insulin in organ culture of rat mammary carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 45, 351–360 (1967).
Salmon, W. D. & Daughaday, W. H. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulated sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 49, 825–836 (1957).
Jansen, M. et al. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor. Nature 306, 609–611 (1983).
Dull, T. J., Gray, A., Hayflick, J. S. & Ullrich, A. Insulin-like growth factor II precursor gene organization in relation to insulin gene family. Nature 310, 777–781 (1984).
Ullrich, A., Dull, T. J., Gray, A., Brosius, J. & Sures, I. Genetic variation in the human insulin gene. Science 209, 612–615 (1980).
Bell, G. I. et al. Sequence of the human insulin gene. Nature 284, 26–32 (1980).
Ullrich, A. et al. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 5, 2503–2512 (1986).
Ullrich, A., et al. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature 313, 756–761 (1985). Gave initial evidence for homology between the insulin and IGF1 receptors and characterized oncogenes. This key finding led to study of relationships between signalling systems controlling metabolism and those controlling proliferation.
Arteaga, C. L. et al. Blockade of the type l somatomedin receptor inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic mice. J. Clin. Invest. 84, 1418–1423 (1989). This report provided the first evidence that an IGF1R-specific antibody could reduce tumour growth rate in an animal model.
Samani, A. A., Yakar, S., LeRoith, D. & Brodt, P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr. Rev. 28, 20–47 (2007).
Pandini, G., et al. Functional responses and in vivo anti-tumour activity of h7C10: a humanised monoclonal antibody with neutralising activity against the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor and insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptors. Eur. J. Cancer 43, 1318–1327 (2007).
Osborne, R. Commercial interest waxes for IGF-1 blockers. Nature Biotechnol. 26, 719–720 (2008).
Calle, E. & Kaaks, R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 579–591 (2004).
Hursting, S. D. et al. Energy balance and carcinogenesis: underlying pathways and targets for intervention. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 7, 484–491 (2007).
Acknowledgements
I thank L. Lui for valuable assistance in manuscript preparation, and students and colleagues for useful discussions. I apologize to those whose work could not be cited due to space constraints. The author has received research support from the National Cancer Institute of Canada, the Canadian Breast Cancer Research Alliance, the Prostate Cancer Foundation (Santa Monica, California, USA), the Prostate Cancer Foundation of Canada, and the National Cancer Institute (Washington, DC, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollak, M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 8, 915–928 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2536
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2536
This article is cited by
-
Pregnancy associated plasma protein-A2 (PAPP-A2) and stanniocalcin-2 (STC2) but not PAPP-A are associated with circulating total IGF-1 in a human adult population
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Body composition and cancer survival: a narrative review
British Journal of Cancer (2024)
-
Association between hypertension grades and cancer mortality among Japanese men and women
Cancer Causes & Control (2024)
-
Akkermansia muciniphila and its membrane protein ameliorates intestinal inflammatory stress and promotes epithelial wound healing via CREBH and miR-143/145
Journal of Biomedical Science (2023)
-
Circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and brain health: Evidence from 369,711 participants in the UK Biobank
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2023)