Abstract
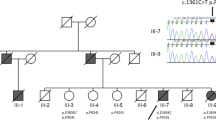
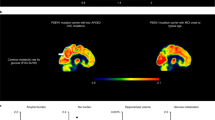
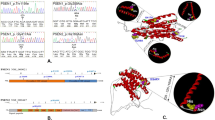
We describe a novel variant of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a Finnish pedigree with 17 affected individuals of both sexes in three generations. The disease is characterized by progressive dementia which is, in most cases, preceded by spastic paraparesis. Neuropathological investigations revealed numerous, distinct, large, round and eosinophilic plaques as well as neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid angiopathy throughout the cerebral cortex. The predominant plaques resembled cotton wool balls and were immunoreactive for Aβ but lacked a con-gophilic dense core or marked plaque-related neuritic pathology. Molecular genetic analysis revealed that the disease was caused by a deletion of exon 9 (Δ9) of the presenilin 1 (PSI) gene from the mRNA: unlike previous examples of the Δ9 variant, the deletion was not caused by a splice acceptor site mutation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goate, A.M. et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature 349, 704–706 (1991)
Sherrington, R. et al. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature 375, 754–760 (1995).
Levy-Lahad, E. et al. Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer's disease locus. Science 269, 973–977 (1995).
Hardy, J., d, the presenilins and Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci: 20, 154–159(1997).
Hutton, M. & Hardy, J. The presenilins and Alzheimer's disease. Human Mol. Genet. 6, 1639–1646 (1997).
Perez-Tur, J. et al. A mutation in Alzheimer's disease destroying a splice acceptor site in the presenilin 1 gene. Neuroreport 7, 204–207 (1995).
Kwok, J.B.J. et al. Two novel (M233T and R278T) presenilin 1 mutations in early onset Alzheimer's disease and preliminary evidence for association of presenilin 1 mutations with a novel phenotype. Neuroreport 8, 1537–1542 (1997).
Sato, S. et al. Splicing mutation of presenilin 1 gene for early onset, familial Alzheimer's disease. Human Mutation (in the press).
Mehta, N.M. et al. Increased Aβ42(43) from cell lines expressing presenilin 1 mutations. Annals Neurol. (in the press).
Hutton, M. et al. Complete analysis of the presenilin 1 gene in families with early onset Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 7, 801–805 (1996).
Ploughman, L.M. & Boehnke, M. Estimating the power of a proposed linkage study for a complex genetic trait. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 44, 543–551 (1989).
Thinakaran, G. et al. Endoproteolysis of presenilin 1 and accumulation of processed derivatives in vivo. Neuron 17, 181–190 (1996).
Levitan, D. et al. Assessment of normal and mutant human presenilin function in Caenorhabditis elegans . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93, 14940–14944 (1996).
Baumeister, R. et al. Proteolytic cleavage of the Alzheimer's disease associated presenilin 1 is not required for its function in Caenorhabditis elegans notch signaling. Genes Func. 1, 149–159. (1997).
Clarke, R.F. et al. The structure of the presenilin-1 (SI 82) gene and identification of six novel mutations in early onset AD families. Nature Genet. 11, 219–222 (1995).
Haltia, M. et al. Chromosome 14 encoded Alzheimer's disease: genetic and clinico-pathological description. Ann. Neurol. 36, 362–367 (1994).
Lowe, J., Lennox, G. & Leigh, P.N. Disorders of movement and system degenerations. In Graham D.I., Lantos P.L. (Eds.): Greenfield's Neuropathology, sixth edition. Arnold, London 1997, pp. 281–366
Mullan, M. et al. Clinical features of early onset, familial Alzheimer's disease linked to chromosome 14. Neuropsychiatric Genet. 60, 44–52 (1995).
Ishii, K. et al. Increased Aβ42(43)-plaque deposition in early onset familial Alzheimer's disease brains with the deletion of exon 9 and the missense point mutation (H163R) in the PS-1 gene. Neurosci. Letts. 228, 17–20 (1997).
Dickson, D.W. The pathogenesis of senile plaques. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 321–339 (1997).
Schmidt, M L. Lee, V.M.-Y., Forman, M., Chiu, T.-S. & Trojanowski, J.Q. Monoclonal antibodies to a 100-kd protein reveal abundant Aβ-negative plaques throughout gray matter of Alzheimer's disease brains. Am. J. Pathol. 151, 69–80 (1997).
Probst, A., Langui, D. & Ulrich, J. Alzheimer's disease: a description of the structural lesions. Brain Pathol. 1, 229–239 (1991).
Mann, D.M.A. et al. Amyloid-(protein (Aβ) deposition in chromosome 14 linked Alzheimer's disease: predominance of Aβ42(43). Ann. Neurol. 40, 149–156 (1996).
Castano, E.M. et al. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease β-protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 141, 782–789 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crook, R., Verkkoniemi, A., Perez-Tur, J. et al. A variant of Alzheimer's disease with spastic paraparesis and unusual plaques due to deletion of exon 9 of presenilin 1. Nat Med 4, 452–455 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0498-452
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0498-452
This article is cited by
-
Transformation of non-neuritic into neuritic plaques during AD progression drives cortical spread of tau pathology via regenerative failure
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2023)
-
Long-read sequencing revealing intragenic deletions in exome-negative spastic paraplegias
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Neuritic Plaques — Gateways to Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Chronic effects of blast injury on the microvasculature in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease related Aβ amyloidosis
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
Progressive cognitive impairment and familial spastic paraparesis due to PRESENILIN 1 mutation: anatomoclinical characterization
Journal of Neurology (2022)