Abstract
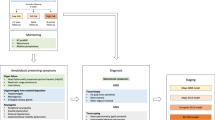
This manuscript summarizes the recommendations that emerged from the first Roundtable on Clinical Research in Immunoglobulin Light-chain Amyloidosis (AL), a meeting sponsored by the Amyloidosis Foundation (Clarkston, MI, USA) to develop a consensus of experts on a modern framework for clinical trial design and drug development in AL. Recent diagnostic and technical advances in AL, and updated consensus guidelines for assessing hematologic and organ responses, enable us to define study populations, appropriate end points, and other criteria for all phases of clinical research. This manuscript provides a framework for the design and conduct of systematic collaborative clinical research in AL to encourage more rapid testing of therapies and to expedite new drug development and approval.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merlini G, Palladini G . Amyloidosis: is a cure possible? Ann Oncol 2008; 19 (Suppl 4): iv63–iv66.
Kyle RA, Linos A, Beard CM, Linke RP, Gertz MA, O’Fallon WM et al. Incidence and natural history of primary systemic amyloidosis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 through 1989. Blood 1992; 79: 1817–1822.
Rajkumar SV, Gertz MA . Advances in the treatment of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2413–2415.
Lebovic D, Hoffman J, Levine BM, Hassoun H, Landau H, Goldsmith Y et al. Predictors of survival in patients with systemic light-chain amyloidosis and cardiac involvement initially ineligible for stem cell transplantation and treated with oral melphalan and dexamethasone. Br J Haematol 2008; 143: 369–373.
Palladini G, Kyle RA, Larson DR, Therneau TM, Merlini G, Gertz MA . Multicentre versus single centre approach to rare diseases: the model of systemic light chain amyloidosis. Amyloid 2005; 12: 120–126.
Wechalekar AD, Offer M, Gillmore JD, Hawkins PN, Lachmann HJ . Cardiac amyloidosis, a monoclonal gammopathy and a potentially misleading mutation. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2009; 6: 128–133.
Wechalekar A, Kastritis E, Merlini G, Hawkins PN, Dimopoulos MA, Russo P et al. European collaborative study of 153 patients with systemic AL amyloidosis with Mayo stage III disease. Haematologica 2011; 96 (Suppl 1): S158.
Merlini G, Bellotti V . Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 583–596.
Comenzo RL, Zhou P, Fleisher M, Clark B, Teruya-Feldstein J . Seeking confidence in the diagnosis of systemic AL (Ig light-chain) amyloidosis: patients can have both monoclonal gammopathies and hereditary amyloid proteins. Blood 2006; 107: 3489–3491.
Merlini G, Westermark P . The systemic amyloidoses: clearer understanding of the molecular mechanisms offers hope for more effective therapies. J Intern Med 2004; 255: 159–178.
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV . Monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance: a review. Immunol Rev 2003; 194: 112–139.
Arbustini E, Morbini P, Verga L, Concardi M, Porcu E, Pilotto A et al. Light and electron microscopy immunohistochemical characterization of amyloid deposits. Amyloid 1997; 4: 157–170.
Vrana JA, Gamez JD, Madden BJ, Theis JD, Bergen HR, Dogan A . Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood 2009; 114: 4957–4959.
Brambilla F, Lavatelli F, Di Silvestre D, Valentini V, Rossi R, Palladini G et al. Reliable typing of systemic amyloidoses through proteomic analysis of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Blood 2012; 119: 1844–1847.
Bryce AH, Ketterling RP, Gertz MA, Lacy M, Knudson RA, Zeldenrust S et al. Translocation t(11;14) and survival of patients with light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Haematologica 2009; 94: 380–386.
Bochtler T, Hegenbart U, Cremer FW, Heiss C, Benner A, Hose D et al. Evaluation of the cytogenetic aberration pattern in amyloid light chain amyloidosis as compared with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance reveals common pathways of karyotypic instability. Blood 2008; 111: 4700–4705.
Zhou P, Hoffman J, Landau H, Hassoun H, Iyer L, Comenzo RL . Clonal plasma cell pathophysiology and clinical features of disease are linked to clonal plasma cell expression of Cyclin D1 in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2012; 12: 49–58.
Lachmann HJ, Gallimore R, Gillmore JD, Carr-Smith HD, Bradwell AR, Pepys MB et al. Outcome in systemic AL amyloidosis in relation to changes in concentration of circulating free immunoglobulin light chains following chemotherapy. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 78–84.
Dispenzieri A, Kyle R, Merlini G, Miguel JS, Ludwig H, Hajek R et al. International Myeloma Working Group guidelines for serum-free light chain analysis in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Leukemia 2009; 23: 215–224.
Palladini G DA, Gertz MA, Kumar S, Wechalekar A, Hawkins PN, Schönland S et al. Validation of the criteria of response to treatment in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 1364a.
Tate JR, Mollee P, Dimeski G, Carter AC, Gill D . Analytical performance of serum free light-chain assay during monitoring of patients with monoclonal light-chain diseases. Clin Chim Acta 2007; 376: 30–36.
Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Lacy MQ, Burritt MF, Therneau TM et al. Serum cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide: a staging system for primary systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 3751–3757.
Palladini G, Barassi A, Klersy C, Pacciolla R, Milani P, Sarais G et al. The combination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) at presentation and changes in N-terminal natriuretic peptide type B (NT-proBNP) after chemotherapy best predicts survival in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 3426–3430.
Kristen AV, Giannitsis E, Lehrke S, Hegenbart U, Konstandin M, Lindenmaier D et al. Assessment of disease severity and outcome in patients with systemic light-chain amyloidosis by the high-sensitivity troponin T assay. Blood 116: 2455–2461.
Falk RH . Diagnosis and management of the cardiac amyloidoses. Circulation 2005; 112: 2047–2060.
Palladini G, Campana C, Klersy C, Balduini A, Vadacca G, Perfetti V et al. Serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide is a sensitive marker of myocardial dysfunction in AL amyloidosis. Circulation 2003; 107: 2440–2445.
Dispenzieri A, Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Therneau TM, Miller WL, Chandrasekaran K et al. Survival in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis and raised serum cardiac troponins. Lancet 2003; 361: 1787–1789.
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Colby C et al. Revised prognostic staging system for light chain amyloidosis incorporating cardiac biomarkers and serum free light chain measurements. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 989–995.
Wall JS, Kennel SJ, Stuckey AC, Long MJ, Townsend DW, Smith GT et al. Radioimmunodetection of amyloid deposits in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 2241–2244.
Bodin K, Ellmerich S, Kahan MC, Tennent GA, Loesch A, Gilbertson JA et al. Antibodies to human serum amyloid P component eliminate visceral amyloid deposits. Nature 2010; 468: 93–97.
Ward JE, Ren R, Toraldo G, Soohoo P, Guan J, O'Hara C et al. Doxycycline reduces fibril formation in a transgenic mouse model of AL amyloidosis. Blood 118: 6610–6617.
Kyle RA, Greipp PR . Primary systemic amyloidosis: comparison of melphalan and prednisone versus placebo. Blood 1978; 52: 818–827.
Comenzo RL, Vosburgh E, Falk RH, Sanchorawala V, Reisinger J, Dubrey S et al. Dose-intensive melphalan with blood stem-cell support for the treatment of AL (amyloid light-chain) amyloidosis: survival and responses in 25 patients. Blood 1998; 91: 3662–3670.
Gertz MA, Comenzo R, Falk RH, Fermand JP, Hazenberg BP, Hawkins PN et al. Definition of organ involvement and treatment response in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL): a consensus opinion from the 10th International Symposium on Amyloid and Amyloidosis, Tours, France, 18–22 April 2004. Am J Hematol 2005; 79: 319–328.
Gertz MA, Merlini G . Definition of organ involvement and response to treatment in AL amyloidosis: an updated consensus opinion. Amyloid 2010; 17: 48a.
Bellavia D, Pellikka PA, Al-Zahrani GB, Abraham TP, Dispenzieri A, Miyazaki C et al. Independent predictors of survival in primary systemic (Al) amyloidosis, including cardiac biomarkers and left ventricular strain imaging: an observational cohort study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010; 23: 643–652.
Dietrich S, Schonland SO, Benner A, Bochtler T, Kristen AV, Beimler J et al. Treatment with intravenous melphalan and dexamethasone is not able to overcome the poor prognosis of patients with newly diagnosed systemic light chain amyloidosis and severe cardiac involvement. Blood 2010; 116: 522–528.
Kastritis E, Wechalekar AD, Dimopoulos MA, Merlini G, Hawkins PN, Perfetti V et al. Bortezomib with or without dexamethasone in primary systemic (light chain) amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1031–1037.
Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Lacy MQ, Burritt MF, Therneau TM et al. Prognostication of survival using cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 1881–1887.
Dispenzieri A, Dingli D, Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Lacy MQ, Hayman S et al. Discordance between serum cardiac biomarker and immunoglobulin-free light-chain response in patients with immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis treated with immune modulatory drugs. Am J Hematol 85: 757–759.
Seldin DC, Anderson JJ, Sanchorawala V, Malek K, Wright DG, Quillen K et al. Improvement in quality of life of patients with AL amyloidosis treated with high-dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 1888–1893.
Dember LM, Sanchorawala V, Seldin DC, Wright DG, LaValley M, Berk JL et al. Effect of dose-intensive intravenous melphalan and autologous blood stem-cell transplantation on al amyloidosis-associated renal disease. Ann Intern Med 2001; 134 (9 Part 1): 746–753.
Palladini G, Lavatelli F, Russo P, Perlini S, Perfetti V, Bosoni T et al. Circulating amyloidogenic free light chains and serum N-terminal natriuretic peptide type B decrease simultaneously in association with improvement of survival in AL. Blood 2006; 107: 3854–3858.
Cibeira MT, Sanchorawala V, Seldin DC, Quillen K, Berk JL, Dember LM et al. Outcome of AL amyloidosis after high-dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation: long-term results in a series of 421 patients. Blood 2011; 118: 4346–4352.
Reece DE, Sanchorawala V, Hegenbart U, Merlini G, Palladini G, Fermand JP et al. Weekly and twice-weekly bortezomib in patients with systemic AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 1 dose-escalation study. Blood 2009; 114: 1489–1497.
Sanchorawala V, Skinner M, Quillen K, Finn KT, Doros G, Seldin DC . Long-term outcome of patients with AL amyloidosis treated with high-dose melphalan and stem-cell transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 3561–3563.
Sanchorawala V, Wright DG, Rosenzweig M, Finn KT, Fennessey S, Zeldis JB et al. Lenalidomide and dexamethasone in the treatment of AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 2 trial. Blood 2007; 109: 492–496.
Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Zeldenrust SR, Hayman SR, Kumar SK, Geyer SM et al. The activity of lenalidomide with or without dexamethasone in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis. Blood 2007; 109: 465–470.
Wechalekar AD, Goodman HJ, Lachmann HJ, Offer M, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD . Safety and efficacy of risk-adapted cyclophosphamide, thalidomide, and dexamethasone in systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood 2007; 109: 457–464.
Reece DE, Hegenbart U, Sanchorawala V, Merlini G, Palladini G, Blade J et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly and twice-weekly bortezomib in patients with relapsed systemic AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 1/2 study. Blood 2011; 118: 865–873.
Dhodapkar MV, Hussein MA, Rasmussen E, Solomon A, Larson RA, Crowley JJ et al. Clinical efficacy of high-dose dexamethasone with maintenance dexamethasone/alpha interferon in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis: results of United States Intergroup Trial Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S9628. Blood 2004; 104: 3520–3526.
Cohen AD, Zhou P, Chou J, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reich L, Hassoun H et al. Risk-adapted autologous stem cell transplantation with adjuvant dexamethasone ± thalidomide for systemic light-chain amyloidosis: results of a phase II trial. Br J Haematol 2007; 139: 224–233.
Landau H HH, Bello C, Hoover E, Jia X, Riedel ER, Nimer SD et al. Adjuvant bortezomib and dexamethasone following risk-adapted melphalan and stem cell transplant in systemic AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 2010; 17: 80a.
Acknowledgements
We thank the supporters of the Amyloidosis Foundation and the Foundation’s Board of Directors whose continued efforts and involvement made this first roundtable held in Boston in late 2010 a reality. We also thank S Frieda Pearce, PhD, for editing assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comenzo, R., Reece, D., Palladini, G. et al. Consensus guidelines for the conduct and reporting of clinical trials in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Leukemia 26, 2317–2325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.100
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prognostic value of native T1 and extracellular volume in patients with immunoglubin light-chain amyloidosis
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2024)
-
Risk factors, treatments and outcomes of patients with light chain amyloidosis who relapse after autologous stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
A comprehensive overview of AL amyloidosis disease characteristics accumulated over two decades at a single referral center in Korea
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
An observational, non-interventional study for the follow-up of patients with amyloidosis who received miridesap followed by dezamizumab in a phase 1 study
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
Early serum free light chain response after high-dose melphalan and stem cell transplantation predicts hematologic response in AL amyloidosis
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)