Abstract
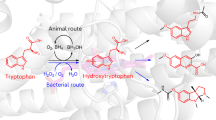
THE rat pineal gland contains large amounts of serotonin1 and the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase2 and aromatic 1-amino-acid decarboxylase3 which synthesize this indoleamine from tryptophan. We have reported that rat pineals in organ culture retain the ability to produce serotonin from its amino-acid precursors tryptophan and 5-hydroxytryptophan4. Most of the serotonin normally formed in the pineal is oxidized to 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid5 by the enzymes monoamine oxidase6 and aldehyde dehydrogenase. In addition, a portion of the indoleamine is N-acetylated7 and then converted to melatonin by hydroxyindole-O-methyl transferase8, an enzyme present in mammals only in the pineal gland9. By using isotopically labelled tryptophan as the substrate for our organ culture system, we have observed that such preparations can transform the serotonin produced to two end products: 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5HIAA) and melatonin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quay, W. B., Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1, 3 (1963).
Lovenberg, W., Jequier, E., and Sjoerdsma, A., Science, 155, 217 (1967).
Snyder, S. H., Axelrod, J., Fischer, J. E., and Wurtman, R. J., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 147, 371 (1965).
Shein, H., Wurtman, R. J., and Axelrod, J., Nature, 213, 730 (1967).
Quay, W. B., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 115, 710 (1964).
Wurtman, R. J., Axelrod, J., and Phillips, L. S., Science, 142, 1071 (1963).
Weissbach, H., Redfield, B. G., and Axelrod, J., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 43, 352 (1960).
Axelrod, J., and Weissbach, H., J. Biol. Chem., 236, 211 (1961).
Axelrod, J., MacLean, P. D., Albers, R. W., and Weissbach, H., in Regional Neurochemistry (edit. by Kety, S. S., and Elkes, J.), 307 (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1961).
Wurtman, R. J., Axelrod, J., and Fischer, J. E., Science, 143, 1325 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WURTMAN, R., LARIN, F., AXELROD, J. et al. Formation of Melatonin and 5-Hydroxyindole Acetic Acid from 14C-Tryptophan by Rat Pineal Glands in Organ Culture. Nature 217, 953–954 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/217953a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/217953a0
This article is cited by
-
Wie wirken Antidepressiva? Weil sie einen Serotoninmangel im Gehirn ausgleichen?
psychopraxis. neuropraxis (2023)
-
Melatonergic Receptors (Mt1/Mt2) as a Potential Additional Target of Novel Drugs for Depression
Neurochemical Research (2022)
-
Metabolomics for clinical use and research in chronic kidney disease
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2017)
-
Acyclovir inhibits rat liver tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase and induces a concomitant rise in brain serotonin and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid levels
Metabolic Brain Disease (2008)
-
Diurnal variation in norepinephrine-stimulated release of pineal serotonin in vitro
Journal of Neural Transmission (1989)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.