Abstract
Background
Adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein (A-FABP) is an intracellular lipid transporter that mediates metabolically triggered inflammation, and it is associated with insulin resistance, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular risk.
Aims
The aim of this study was to evaluate A-FABP behavior in elderly people, and especially its association with liver steatosis at abdominal ultrasound.
Method
Cross-sectional study of two cohort of individuals with and without steatosis, with assessment of several clinical and laboratory variables. Prospective evaluation of liver steatosis remodeling after six years of follow-up. One hundred and fifty-six subjects aged over 65 years were enrolled.
Results
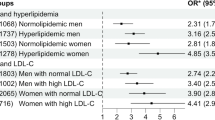
Serum A-FABP positively correlated with body fat percentage, total cholesterol, serum triglycerides and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Unlike expected, high A-FABP levels were associated with absence of liver steatosis, while there was no evidence of association with steatosis grade changes after 6 years of follow-up.
Conclusion
Among individuals aging more than 65 years included in the study, A-FABP was inversely associated with liver steatosis. It can be argued, that still uncovered mechanisms modify A-FABP behavior in elderly people, especially its association with multifactorial diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furuhashi M, Ishimura S, Ota H et al (2011) Lipid chaperones and metabolic inflammation. Int J Inflam 2011:642612
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature Dic 444(7121):860–867
Baar RA, Dingfelder CS, Smith LA et al (2005) Investigation of in vivo fatty acid metabolism in AFABP/aP2(-/-) mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab Gen 288:E187–E193
Elmasri H, Karaaslan C, Teper Y et al (2009) Fatty acid binding protein 4 is a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation in endothelial cells. FASEB J 23:3865–3873
Fu Y, Luo N, Lopes-Virella MF (2000) Oxidized LDL induces the expression of ALBP/aP2 mRNA and protein in human THP-1 macrophages. J Lipid Res Dic 41:2017–2023
Wang XQ, Yang K, He YS et al (2011) Receptor mediated elevation in FABP4 levels by advanced glycation end products induces cholesterol and triacylglycerol accumulation in THP-1 macrophages. Lipids 46:479–486
Fu Y, Luo N, Lopes-Virella MF et al (2002) The adipocyte lipid binding protein (ALBP/aP2) gene facilitates foam cell formation in human THP-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis 165:259–269
Makowski L, Brittingham KC, Reynolds JM et al (2005) The fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, coordinates macrophage cholesterol trafficking and inflammatory activity. Macrophage expression of aP2 impacts peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and Ikappa B kinase activities. J Biol Chem 280:12888–12895
Hui X, Li H, Zhou Z et al (2010) Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein modulates inflammatory responses in macrophages through a positive feedback loop involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases and activator protein-1. J BiolChem 2(285):10273–10280
Stejskal D, Karpisek M (2006) Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in a Caucasian population: a new marker of metabolic syndrome? Eur J Clin Invest 36:621–625
Kim Y-C, Cho Y-K, Lee W-Y et al (2011) Serum adipocyte-specific fatty acid-binding protein is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in apparently healthy subjects. J Nutr Biochem 22:289–292
Tuncman G, Erbay E, Hom X et al (2006) A genetic variant at the fatty acid-binding protein aP2 locus reduces the risk for hypertriglyceridemia, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6970–6975
Furuhashi M, Tuncman G, Görgün CZ et al (2007) Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2. Nature 447(7147):959–965
Makowski L, Boord JB, Maeda K et al (2001) Lack of macrophage fatty-acid-binding protein aP2 protects mice deficient in apolipoprotein E against atherosclerosis. Nat Med 7:699–705
Makowski L, Hotamisligil GS (2004) Fatty acid binding proteins–the evolutionary crossroads of inflammatory and metabolic responses. J Nutr 134:2464S–2468S
Byrne CD, Olufadi R, Bruce KD et al (2009) Metabolic disturbances in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Sci 116:539–564
Bianchi G, Rossi V, Muscari A et al (2008) Physical activity is negatively associated with the metabolic syndrome in the elderly. QJM 101:713–721
Muscari A, Giannoni C, Pierpaoli L et al (2010) Chronic endurance exercise training prevents aging-related cognitive decline in healthy older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 25:1055–1064
Washburn RA, Smith KW, Jette AM et al (1993) The Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (PASE): development and evaluation. J ClinEpidemiol 46:153–162
Durnin JV, Womersley J (1974) Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr 32:77–97
Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009 Gen 32 Suppl 1:S62–67
Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001 285:2486–97
Leite NC, Salles GF, Araujo ALE et al (2009) Prevalence and associated factors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Liver Int Gen 29:113–119
Doi M, Miyoshi T, Hirohata S et al (2011) Association of increased plasma adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein with coronary artery disease in non-elderly men. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:44
Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Silbershatz H (1997) Blood pressure and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality rates in the elderly. Am Heart J 134:758–763
Cabré A, Lázaro I, Girona J et al (2008) Plasma fatty acid binding protein 4 is associated with atherogenic dyslipidemia in diabetes. J Lipid Res 49:1746–1751
Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Park CY et al (2009) The association of serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein with coronary artery disease in Korean adults. Eur J Endocrinol 160:165–172
Jin J, Peng D, Yuan S et al (2010) Serum adipocyte fatty acid binding proteins and adiponectin in patients with coronary artery disease: the significance of A-FABP/adiponectin ratio. Clin ChimActa 411(21–22):1761–1765
Hsu B-G, Chen Y-C, Lee R-P et al (2010) Fasting serum level of fatty-acid-binding protein 4 positively correlates with metabolic syndrome in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ J 74:327–331
Morley JE (2012) Undernutrition in older adults. Fam Pract 29(suppl 1):i89–i93
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical contributions of Raffaela Chianese and Franca Ferri. The study was supported by grants from Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Bologna and Regione Emilia Romagna, Piani per la Salute.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masetti, M., Bianchi, G., Gianotti, G. et al. Adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res 26, 241–247 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0156-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0156-0