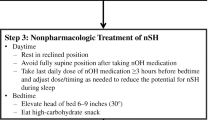
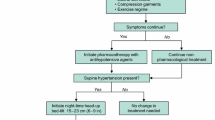
Abstract
The maintenance of blood pressure in the upright position requires intact autonomic cardiovascular reflexes. Diseases that affect the sympathetic innervation of the cardiovascular system result in a sustained fall in blood pressure upon standing (i.e., neurogenic orthostatic hypotension) that can impair the blood supply to the brain and other organs and cause considerable morbidity and mortality. Here we review treatment options for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and include an algorithm for its management that emphasizes the importance of non-pharmacologic measures and provides guidance on pharmacologic treatment options.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smit AA, Halliwill JR, Low PA, Wieling W. Pathophysiological basis of orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure. J Physiol. 1999;519(Pt 1):1–10.
Matzen S, Perko G, Groth S, Friedman DB, Secher NH. Blood volume distribution during head-up tilt induced central hypovolaemia in man. Clin Physiol. 1991;11(5):411–22.
Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res. 2011;21(2):69–72.
Lahrmann H, Cortelli P, Hilz M, Mathias CJ, Struhal W, Tassinari M. EFNS guidelines on the diagnosis and management of orthostatic hypotension. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(9):930–6.
Masaki KH, Schatz IJ, Burchfiel CM, Sharp DS, Chiu D, Foley D, et al. Orthostatic hypotension predicts mortality in elderly men: the Honolulu Heart Program. Circulation. 1998;98(21):2290–5.
Rose KM, Eigenbrodt ML, Biga RL, Couper DJ, Light KC, Sharrett AR, et al. Orthostatic hypotension predicts mortality in middle-aged adults: the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation. 2006;114(7):630–6.
Ganjehei L, Massumi A, Razavi M, Wilson JM. Orthostatic hypotension as a manifestation of vitamin B12 deficiency. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012;39(5):722–3.
Girard P, Lebrun C, Peyrade F, Brunetto JL, Chatel M. Orthostatic hypotension revealing vitamin B12 deficiency. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1998;154(4):342–4.
Moore A, Ryan J, Watts M, Pillay I, Clinch D, Lyons D. Orthostatic tolerance in older patients with vitamin B12 deficiency before and after vitamin B12 replacement. Clin Auton Res. 2004;14(2):67–71.
Graber JJ, Sherman FT, Kaufmann H, Kolodny EH, Sathe S. Vitamin B12-responsive severe leukoencephalopathy and autonomic dysfunction in a patient with “normal” serum B12 levels. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81(12):1369–71.
Vernino S. Autoimmune and paraneoplastic channelopathies. Neurotherapeutics. 2007;4(2):305–14.
Schroeder C, Vernino S, Birkenfeld AL, Tank J, Heusser K, Lipp A, et al. Plasma exchange for primary autoimmune autonomic failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(15):1585–90.
Metzler M, Duerr S, Granata R, Krismer F, Robertson D, Wenning GK. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. J Neurol. Epub 2012 Nov 20.
Robertson D. The pathophysiology and diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18(Suppl. 1):2–7.
Goldstein DS, Sharabi Y. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a pathophysiological approach. Circulation. 2009;119(1):139–46.
Kollensperger M, Geser F, Ndayisaba JP, Boesch S, Seppi K, Ostergaard K, et al. Presentation, diagnosis, and management of multiple system atrophy in Europe: final analysis of the European multiple system atrophy registry. Mov Disord. 2010;25(15):2604–12.
Wenning GK, Geser F, Krismer F, Seppi K, Duerr S, Boesch S, et al. The natural history of multiple system atrophy: a prospective European cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(3):264–74.
Kaufmann H, Biaggioni I. Autonomic failure in neurodegenerative disorders. Semin Neurol. 2003;23(4):351–63.
Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 1996;46(5):1470.
Senard JM, Rai S, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Brefel C, Rascol O, Rascol A, et al. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63(5):584–9.
Wood BH, Bilclough JA, Bowron A, Walker RW. Incidence and prediction of falls in Parkinson’s disease: a prospective multidisciplinary study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72(6):721–5.
Velseboer DC, de Haan RJ, Wieling W, Goldstein DS, de Bie RM. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011;17(10):724–9.
Thaisetthawatkul P, Boeve BF, Benarroch EE, Sandroni P, Ferman TJ, Petersen R, et al. Autonomic dysfunction in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology. 2004;62(10):1804–9.
Sonnesyn H, Nilsen DW, Rongve A, Nore S, Ballard C, Tysnes OB, et al. High prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in mild dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2009;28(4):307–13.
Freeman R. Clinical practice. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(6):615–24.
Freeman R. Autonomic peripheral neuropathy. Lancet. 2005;365(9466):1259–70.
Low PA. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18(Suppl. 1):8–13.
Poon IO, Braun U. High prevalence of orthostatic hypotension and its correlation with potentially causative medications among elderly veterans. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2005;30(2):173–8.
Barochiner J, Alfie J, Aparicio L, Rada M, Morales M, Cuffaro P, et al. Orthostatic hypotension in treated hypertensive patients. Rom J Intern Med. 2012;50(3):203–9.
Darowski A, Chambers SA, Chambers DJ. Antidepressants and falls in the elderly. Drugs Aging. 2009;26(5):381–94.
Mackin P. Cardiac side effects of psychiatric drugs. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2008;23(Suppl. 1):3–14.
Figueroa JJ, Basford JR, Low PA. Preventing and treating orthostatic hypotension: as easy as A, B, C. Cleve Clin J Med. 2010;77(5):298–306.
Podoleanu C, Maggi R, Brignole M, Croci F, Incze A, Solano A, et al. Lower limb and abdominal compression bandages prevent progressive orthostatic hypotension in elderly persons: a randomized single-blind controlled study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(7):1425–32.
Tutaj M, Marthol H, Berlin D, Brown CM, Axelrod FB, Hilz MJ. Effect of physical countermaneuvers on orthostatic hypotension in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol. 2006;253(1):65–72.
ten Harkel AD, van Lieshout JJ, Wieling W. Effects of leg muscle pumping and tensing on orthostatic arterial pressure: a study in normal subjects and patients with autonomic failure. Clin Sci (Lond). 1994;87(5):553–8.
Bouvette CM, McPhee BR, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Low PA. Role of physical countermaneuvers in the management of orthostatic hypotension: efficacy and biofeedback augmentation. Mayo Clin Proc. 1996;71(9):847–53.
Freeman R. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension. Semin Neurol. 2003;23(4):435–42.
Jordan J, Biaggioni I. Diagnosis and treatment of supine hypertension in autonomic failure patients with orthostatic hypotension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4(2):139–45.
Vagaonescu TD, Saadia D, Tuhrim S, Phillips RA, Kaufmann H. Hypertensive cardiovascular damage in patients with primary autonomic failure. Lancet. 2000;355(9205):725–6.
Kronenberg MW, Forman MB, Onrot J, Robertson D. Enhanced left ventricular contractility in autonomic failure: assessment using pressure–volume relations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(6):1334–42.
MacLean AR, Allen BV. Orthostatic hypotension and orthostatic tachycardia: treatment with the “head-up” bed. JAMA. 1940;115(25):2162–7.
ten Harkel AD, van Lieshout JJ, Wieling W. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension with sleeping in the head-up tilt position, alone and in combination with fludrocortisone. J Intern Med. 1992;232(2):139–45.
Fan CW, Gasparro D, Crowley V, Cunningham CJ. Acute haemodynamic response to sleeping head-up at 6 inches in older inpatients. Clin Auton Res. 2009;19(1):51–7.
Arnold AC, Biaggioni I. Management approaches to hypertension in autonomic failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21(5):481–5.
Shannon JR, Diedrich A, Biaggioni I, Tank J, Robertson RM, Robertson D, et al. Water drinking as a treatment for orthostatic syndromes. Am J Med. 2002;112(5):355–60.
Deguchi K, Ikeda K, Sasaki I, Shimamura M, Urai Y, Tsukaguchi M, et al. Effects of daily water drinking on orthostatic and postprandial hypotension in patients with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol. 2007;254(6):735–40.
Humm AM, Mason LM, Mathias CJ. Effects of water drinking on cardiovascular responses to supine exercise and on orthostatic hypotension after exercise in pure autonomic failure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(10):1160–4.
May M, Jordan J. The osmopressor response to water drinking. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300(1):R40–6.
Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Black BK, Rali A, Jordan J, Taneja I, et al. Sodium paradoxically reduces the gastropressor response in patients with orthostatic hypotension. Hypertension. 2006;48(2):329–34.
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Black BK, Ali Y, Farley M, Costa F, et al. The pressor response to water drinking in humans: a sympathetic reflex? Circulation. 2000;101(5):504–9.
Z’Graggen WJ, Hess CW, Humm AM. Acute fluid ingestion in the treatment of orthostatic intolerance—important implications for daily practice. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(11):1370–6.
Logan IC, Witham MD. Efficacy of treatments for orthostatic hypotension: a systematic review. Age Ageing. 2012;41(5):587–94.
Seppi K, Weintraub D, Coelho M, Perez-Lloret S, Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, et al. The movement disorder society evidence-based medicine review update: treatments for the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2011;26(Suppl. 3):S42–80.
Gibbons CH, Raj SR. A meta-analysis of pharmacologic treatments of orthostatic hypotension [abstract]. Clin Auton Res. 2012;22(5):231–2.
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Biaggioni I, Norman R, Black BK, Robertson D. Contrasting actions of pressor agents in severe autonomic failure. Am J Med. 1998;105(2):116–24.
Low PA, Gilden JL, Freeman R, Sheng KN, McElligott MA. Efficacy of midodrine vs placebo in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a randomized, double-blind multicenter study. Midodrine Study Group. JAMA. 1997;277(13):1046–51.
Jankovic J, Gilden JL, Hiner BC, Kaufmann H, Brown DC, Coghlan CH, et al. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study with midodrine. Am J Med. 1993;95(1):38–48.
Wright RA, Kaufmann HC, Perera R, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McElligott MA, Sheng KN, et al. A double-blind, dose-response study of midodrine in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Neurology. 1998;51(1):120–4.
Fouad-Tarazi FM, Okabe M, Goren H. Alpha sympathomimetic treatment of autonomic insufficiency with orthostatic hypotension. Am J Med. 1995;99(6):604–10.
Hoeldtke RD, Horvath GG, Bryner KD, Hobbs GR. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension with midodrine and octreotide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83(2):339–43.
Kaufmann H, Brannan T, Krakoff L, Yahr MD, Mandeli J. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension due to autonomic failure with a peripheral alpha-adrenergic agonist (midodrine). Neurology. 1988;38(6):951–6.
Steinbach K, Weidinger P. Effect of midodrin on orthostasis. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1973;85(38):621–4.
Zachariah PK, Bloedow DC, Moyer TP, Sheps SG, Schirger A, Fealey RD. Pharmacodynamics of midodrine, an antihypotensive agent. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986;39(5):586–91.
Schirger A, Sheps SG, Thomas JE, Fealey RD. Midodrine: a new agent in the management of idiopathic orthostatic hypotension and Shy-Drager syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56(7):429–33.
Cruz DN. Midodrine: a selective alpha-adrenergic agonist for orthostatic hypotension and dialysis hypotension. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000;1(4):835–40.
Pohl K, Kriech W. Therapy of orthostatic disorders of cardiovascular regulation: placebo controlled double-blind study with oxilofrine. Fortschr Med. 1991;109(33):685–8.
Freistuhler M, Passenberg P, Burger M. The Shy-Drager syndrome. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1992;117(30):1146–8.
Gemeinhardt S, Schardt F, Polzien P. Abnormalities of hypotonic orthostatic regulation: cardiovascular effects of dihydroergotamine, etilefrine and their combination [author’s transl]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1981;106(35):1095–9.
Broadley KJ. The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;125(3):363–75.
Robertson D, Hollister AS, Carey EL, Tung CS, Goldberg MR, Robertson RM. Increased vascular beta2-adrenoceptor responsiveness in autonomic dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984;3(3):850–6.
Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Brass LM, Broderick JP, Brott T, Feldmann E, et al. Phenylpropanolamine and the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(25):1826–32.
Mathias CJ. l-Dihydroxyphenylserine (Droxidopa) in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension: the European experience. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18(Suppl. 1):25–9.
Kaufmann H. l-Dihydroxyphenylserine (Droxidopa): a new therapy for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: the US experience. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18(Suppl. 1):19–24.
Man in ‘t Veld AJ, Boomsma F, van den Meiracker AH, Schalekamp MA. Effect of unnatural noradrenaline precursor on sympathetic control and orthostatic hypotension in dopamine-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Lancet. 1987;2(8569):1172–5.
Mathias CJ, Bannister RB, Cortelli P, Heslop K, Polak JM, Raimbach S, et al. Clinical, autonomic and therapeutic observations in two siblings with postural hypotension and sympathetic failure due to an inability to synthesize noradrenaline from dopamine because of a deficiency of dopamine beta hydroxylase. Q J Med. 1990;75(278):617–33.
Robertson D, Goldberg MR, Onrot J, Hollister AS, Wiley R, Thompson JG Jr, et al. Isolated failure of autonomic noradrenergic neurotransmission: evidence for impaired beta-hydroxylation of dopamine. N Engl J Med. 1986;314(23):1494–7.
Garland EM, Raj SR, Demartinis N, Robertson D. Case report: marathon runner with severe autonomic failure. Lancet. 2005;366(Suppl. 1):S13.
Mathias CJ, Senard JM, Braune S, Watson L, Aragishi A, Keeling JE, et al. l-Threo-dihydroxyphenylserine (l-threo-DOPS; droxidopa) in the management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a multi-national, multi-center, dose-ranging study in multiple system atrophy and pure autonomic failure. Clin Auton Res. 2001;11(4):235–42.
Kaufmann H, Saadia D, Voustianiouk A, Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Yahr MD, et al. Norepinephrine precursor therapy in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Circulation. 2003;108(6):724–8.
Mathias CJ, Senard JM, Cortelli P. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to determine the efficacy and safety of droxidopa in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension associated with multiple system atrophy or Parkinson’s disease [abstract]. Clin Auton Res. 2007;17(272).
Kaufmann H, Freeman R, Biaggioni I, Low PA, Pedder S, Hewitt A, et al. Treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension with droxidopa: results from a multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group, induction design study [abstract]. Neurology. 2012;78(Suppl. 1):4–22.
Singer W, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McPhee BR, Hilz MJ, Bharucha AE, Low PA. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition: a novel approach in the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74(9):1294–8.
Singer W, Sandroni P, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Suarez GA, Klein CM, Hines S, et al. Pyridostigmine treatment trial in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(4):513–8.
Sandroni P, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Singer W, Low PA. Pyridostigmine for treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension [correction of hypertension]—a follow-up survey study. Clin Auton Res. 2005;15(1):51–3.
Shibao C, Okamoto LE, Gamboa A, Yu C, Diedrich A, Raj SR, et al. Comparative efficacy of yohimbine against pyridostigmine for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2010;56(5):847–51.
Grossman E, Rea RF, Hoffman A, Goldstein DS. Yohimbine increases sympathetic nerve activity and norepinephrine spillover in normal volunteers. Am J Physiol. 1991;260(1 Pt 2):R142–7.
Senard JM, Rascol O, Durrieu G, Tran MA, Berlan M, Rascol A, et al. Effects of yohimbine on plasma catecholamine levels in orthostatic hypotension related to Parkinson disease or multiple system atrophy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1993;16(1):70–6.
Sharabi Y, Eldadah B, Li ST, Dendi R, Pechnik S, Holmes C, et al. Neuropharmacologic distinction of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension syndromes. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006;29(3):97–105.
Kochar MS, Itskovitz HD. Treatment of idiopathic orthostatic hypotension (Shy-Drager syndrome) with indomethacin. Lancet. 1978;1(8072):1011–4.
Abate G, Polimeni RM, Cuccurullo F, Puddu P, Lenzi S. Effects of indomethacin on postural hypotension in Parkinsonism. Br Med J. 1979;2(6203):1466–8.
Watt SJ, Tooke JE, Perkins CM, Lee MR. The treatment of idiopathic orthostatic hypotension: a combined fludrocortisone and flurbiprofen regime. Q J Med. 1981;50(198):205–12.
Aellig WH. Direct effects of vasoactive substances on superficial human veins in vivo. Int Angiol. 1985;4(2):235–42.
Muth HH, Jansen W. Dihydroergot plus in the long-term therapy of orthostatic hypotonic dysregulation in older patients. Fortschr Med. 1980;98(40):1571–4.
Lang E. Orthostatic hypotension in the aged. Cardiology. 1976;61(Suppl. 1):225–35.
Thulesius O, Berlin E. Dihydroergotamine therapy in orthostatic hypotension due to psychotropic drugs. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1986;24(9):465–7.
Mannelli M, Pupilli C, Fabbri G, Musante R, De Feo ML, Franchi F, et al. Endogenous dopamine (DA) and DA2 receptors: a mechanism limiting excessive sympathetic-adrenal discharge in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988;66(3):626–31.
Magnifico F, Pierangeli G, Barletta G, Candela C, Bonavina G, Contin M, et al. The cardiovascular effects of metoclopramide in multiple system atrophy and pure autonomic failure. Clin Auton Res. 2001;11(3):163–8.
Destee A, Leys D, Delisse B, Warot P. Orthostatic hypotension due to diabetic autonomic neuropathy? Treatment with domperidone. Arch Neurol. 1987;44(1):11.
Schoffer KL, Henderson RD, O’Maley K, O’Sullivan JD. Nonpharmacological treatment, fludrocortisone, and domperidone for orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2007;22(11):1543–9.
Lopes de Faria SR, Zanella MT, Andriolo A, Ribeiro AB, Chacra AR. Peripheral dopaminergic blockade for the treatment of diabetic orthostatic hypotension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988;44(6):670–4.
Montastruc JL, Chamontin B, Senard JM, Rascol A. Domperidone in the management of orthostatic hypotension. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1985;8(2):191–2.
Lertxundi U, Peral J, Mora O, Domingo-Echaburu S, Martinez-Bengoechea MJ, Garcia-Monco JC. Antidopaminergic therapy for managing comorbidities in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(5):414–9.
Rossi M, Giorgi G. Domperidone and long QT syndrome. Curr Drug Saf. 2010;5(3):257–62.
van Noord C, Dieleman JP, van Herpen G, Verhamme K, Sturkenboom MC. Domperidone and ventricular arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death: a population-based case-control study in the Netherlands. Drug Saf. 2010;33(11):1003–14.
Johannes CB, Varas-Lorenzo C, McQuay LJ, Midkiff KD, Fife D. Risk of serious ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in a cohort of users of domperidone: a nested case-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19(9):881–8.
Schroeder C, Tank J, Boschmann M, Diedrich A, Sharma AM, Biaggioni I, et al. Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibition as a human model of orthostatic intolerance. Circulation. 2002;105(3):347–53.
Tank J, Schroeder C, Diedrich A, Szczech E, Haertter S, Sharma AM, et al. Selective impairment in sympathetic vasomotor control with norepinephrine transporter inhibition. Circulation. 2003;107(23):2949–54.
Shibao C, Raj SR, Gamboa A, Diedrich A, Choi L, Black BK, et al. Norepinephrine transporter blockade with atomoxetine induces hypertension in patients with impaired autonomic function. Hypertension. 2007;50(1):47–53.
Okamoto LE, Shibao C, Gamboa A, Choi L, Diedrich A, Raj SR, et al. Synergistic effect of norepinephrine transporter blockade and alpha-2 antagonism on blood pressure in autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2012;59(3):650–6.
Chobanian AV, Volicer L, Tifft CP, Gavras H, Liang CS, Faxon D. Mineralocorticoid-induced hypertension in patients with orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 1979;301(2):68–73.
Weber KT, Brilla CG. Pathological hypertrophy and cardiac interstitium: fibrosis and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Circulation. 1991;83(6):1849–65.
van Lieshout JJ, ten Harkel AD, Wieling W. Fludrocortisone and sleeping in the head-up position limit the postural decrease in cardiac output in autonomic failure. Clin Auton Res. 2000;10(1):35–42.
Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Axelrod FB, Kaufmann H. Developmental abnormalities, blood pressure variability and renal disease in Riley Day syndrome. J Hum Hypertens. 2013;27(1):51–5.
Biaggioni I, Robertson D, Krantz S, Jones M, Haile V. The anemia of primary autonomic failure and its reversal with recombinant erythropoietin. Ann Intern Med. 1994;121(3):181–6.
Winkler AS, Marsden J, Parton M, Watkins PJ, Chaudhuri KR. Erythropoietin deficiency and anaemia in multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord. 2001;16(2):233–9.
Winkler AS, Landau S, Watkins P, Chaudhuri KR. Observations on haematological and cardiovascular effects of erythropoietin treatment in multiple system atrophy with sympathetic failure. Clin Auton Res. 2002;12(3):203–6.
Rao SV, Stamler JS. Erythropoietin, anemia, and orthostatic hypotension: the evidence mounts. Clin Auton Res. 2002;12(3):141–3.
Hoeldtke RD, Streeten DH. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension with erythropoietin. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(9):611–5.
Perera R, Isola L, Kaufmann H. Effect of recombinant erythropoietin on anemia and orthostatic hypotension in primary autonomic failure. Clin Auton Res. 1995;5(4):211–3.
Winkler AS, Landau S, Watkins PJ. Erythropoietin treatment of postural hypotension in anemic type 1 diabetic patients with autonomic neuropathy: a case study of four patients. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(6):1121–3.
Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, Egrie JC, Nissenson AR, Okamoto DM, et al. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(9):584–90.
Albillos A, Rossi I, Iborra J, Lledo JL, Calleja JL, Barrios C, et al. Octreotide prevents postprandial splanchnic hyperemia in patients with portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 1994;21(1):88–94.
Hoeldtke RD, Bryner KD, Hoeldtke ME, Hobbs G. Treatment of autonomic neuropathy, postural tachycardia and orthostatic syncope with octreotide LAR. Clin Auton Res. 2007;17(6):334–40.
Bordet R, Benhadjali J, Destee A, Belabbas A, Libersa C. Octreotide effects on orthostatic hypotension in patients with multiple system atrophy: a controlled study of acute administration. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1995;18(1):83–9.
Lamarre-Cliche M, Cusson J. Octreotide for orthostatic hypotension. Can J Clin Pharmacol. 1999;6(4):213–5.
Smith GD, Alam M, Watson LP, Mathias CJ. Effect of the somatostatin analogue, octreotide, on exercise-induced hypotension in human subjects with chronic sympathetic failure. Clin Sci (Lond). 1995;89(4):367–73.
Kaufmann H, Oribe E, Miller M, Knott P, Wiltshire-Clement M, Yahr MD. Hypotension-induced vasopressin release distinguishes between pure autonomic failure and multiple system atrophy with autonomic failure. Neurology. 1992;42(3 Pt 1):590–3.
Ozawa T, Oyanagi K, Tanaka H, Horikawa Y, Takahashi H, Morita T, et al. Suprachiasmatic nucleus in a patient with multiple system atrophy with abnormal circadian rhythm of arginine-vasopressin secretion into plasma. J Neurol Sci. 1998;154(1):116–21.
Manning M, Sawyer WH. Design, synthesis and some uses of receptor-specific agonists and antagonists of vasopressin and oxytocin. J Recept Res. 1993;13(1–4):195–214.
Suchowersky O, Furtado S, Rohs G. Beneficial effect of intranasal desmopressin for nocturnal polyuria in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 1995;10(3):337–40.
Mathias CJ, Fosbraey P, da Costa DF, Thornley A, Bannister R. The effect of desmopressin on nocturnal polyuria, overnight weight loss, and morning postural hypotension in patients with autonomic failure. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293(6543):353–4.
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Pohar B, Paranjape SY, Robertson D, Robertson RM, et al. Contrasting effects of vasodilators on blood pressure and sodium balance in the hypertension of autonomic failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(1):35–42.
Shibao C, Gamboa A, Abraham R, Raj SR, Diedrich A, Black B, et al. Clonidine for the treatment of supine hypertension and pressure natriuresis in autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2006;47(3):522–6.
Shannon J, Jordan J, Costa F, Robertson RM, Biaggioni I. The hypertension of autonomic failure and its treatment. Hypertension. 1997;30(5):1062–7.
Polinsky RJ, Samaras GM, Kopin IJ. Sympathetic neural prosthesis for managing orthostatic hypotension. Lancet. 1983;1(8330):901–4.
Goldstein DS, Sewell L, Holmes C, Pechnik S, Diedrich A, Robertson D. Temporary elimination of orthostatic hypotension by norepinephrine infusion. Clin Auton Res. 2012;22(6):303–6.
Sato T, Kawada T, Shishido T, Sugimachi M, Alexander J Jr, Sunagawa K. Novel therapeutic strategy against central baroreflex failure: a bionic baroreflex system. Circulation. 1999;100(3):299–304.
Acknowledgments
HK is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Chelsea Therapeutics International, Ltd. and has received grant support from the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, and the Dysautonomia Foundation. JJ and CS have no disclosures. No funding was received for this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeder, C., Jordan, J. & Kaufmann, H. Management of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension in Patients with Autonomic Failure. Drugs 73, 1267–1279 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-013-0097-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-013-0097-0