Abstract
Background:
Antimicrobial resistance of Helicobacter pylori is the main reason for eradication failure. We have studied the feasibility of a commercial transport medium for cultural recovery and subsequent drug susceptibility testing.
Patients and Methods:
From March to December 2000, 79 consecutive gastric biopsies, positive in a rapid urease test, were transferred into a commercial transport medium and sent within 24 hours from the district hospital to the microbiological laboratory for culture and susceptibility testing. A commercial agar plate and an in-house Wilkins-Chalgren agar plate were used for culture. Susceptibility data were compared with data collected from 1992 to 2003 in the University Hospital of Zurich.
Results:
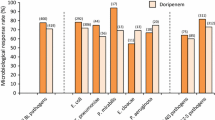
Cultural recovery and susceptibility testing of H. pylori was successful in 55 of 79 patients. In 17 cases cultural recovery failed because of technical problems (n = 14), long transport time (n = 1) and unknown reason (n = 2). Failure of susceptibility testing (n = 7) was mainly due to fungal overgrowth. Resistance to metronidazole and clarithromycin was found in 15 (27%) and in 12 patients (22%), respectively; resistance to amoxicillin was not observed. Five patients (9%) showed resistance both to metronidazole and to clarithromycin. Eradication therapy failed in all patients with macrolide resistance. Resistance rates were higher in females than in males; 30% vs 12% for clarithromycin and 33% vs 20% for metronidazole. Resistance to metronidazole was significantly lower in Swiss patients (15%) than in non-Swiss patients (39%).
Conclusion:
Antimicrobial resistance data can reliably be obtained by sending the biopsy specimen in a commercial transport medium to a microbiological laboratory. This is especially important after eradication failure. Resistance to metronidazole and clarithromycin is highly prevalent and more common in women and non-Swiss patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuen, B., Zbinden, R., Fried, M. et al. Cultural Recovery and Determination of Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Helicobacter pylori by Using Commercial Transport and Isolation Media. Infection 33, 77–81 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-005-4071-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-005-4071-y