Abstract
Objective
To analyze the association between the clinical presentation, clinical course, management and outcome in intussusception with emphasis on safety of saline hydrostatic reduction.
Methods
This retrospective study included 375 patients of intussusception diagnosed between March 2007 to February 2017. Symptoms at presentation, mode of reduction of intussusception and associated complications were recorded.
Results
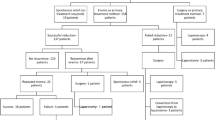
336 (89.6%) patients were aged below 3 years. Classical triad of abdominal pain, vomiting and red stools was present in 111 (29.6%) patients. While 64 (17.1 %) patients had spontaneous resolution, hydrostatic reduction and surgery cured 283 (75.5 %) and 28 (7.4 %) patients, respectively; overall recurrence rate was 13.1%. Among the patients who underwent operative reduction, blood in stools was present in 15 (53.6%) patients.
Conclusions
Hydrostatic reduction of intussusception is effective irrespective of duration of symptoms and number of recurrences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ein SH, Stephens CA. Intussusception: 354 cases in 10 years. J Pediatr Surg. 1971;6:16–27.
Bines JE, Ivanoff B, Justice F, Mulholland K. Clinical case definition for the diagnosis of acute intussusception. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39:511–8.
Gierup J, Jorulf H, Livaditis A. Management of intussusception in infants and children: A survey based on 288 consecutive cases. Pediatrics. 1972;50:535–46.
Daneman A, Navarro O. Intussusception. Part 2: An update on the evolution of management. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34:97–108.
Schuh S, Wesson DE. Intussusception in children 2 years of age or older. CMAJ. 1987;136:269–72.
Yap shiyi E, Ganapathy S. Intussusception in children presenting to the emergency department: An Asian Perspective. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2017;33:409–13.
Beasley SW. The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of intussusception: Where best practice reduces the need for surgery. J Paediatr Child Health. 2017;53:1118–22.
Justice FA, Auldist AW, Bines JE. Intussusception: Trends in clinical presentation and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:842–6.
Yalcin S, Ciftci AO, Karaagaoglu E, Tanyel FC, Senocak ME. Presenting clinical features and outcome in intussusception. Indian J Pediatr. 2009;76:401–5.
Kornecki A, Daneman A, Navarro O, Connolly B, Manson D, Alton DJ. Spontaneous reduction of intussusception: clinical spectrum, management and outcome. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30:58–63.
Fallon SC, Lopez ME, Zhang W, Brandt ML, Wesson DE, Lee TC, et al. Risk factors for surgery in pediatric intussusception in the era of pneumatic reduction. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48:1032–6.
Eklöf O, Reiter S. Recurrent intussusception. Analysis of a series treated with hydrostatic reduction. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1978;19:250–8.
Hsu WL, Lee HC, Yeung CY, Chan WT, Jiang CB, Sheu JC, et al. Recurrent intussusception: When should surgical intervention be performed? Pediatr Neonatol. 2012;53: 300–3.
Sandler AD, Ein SH, Connolly B, Daneman A, Filler RM. Unsuccessful air-enema reduction of intussusception: is a second attempt worthwhile? Pediatr Surg Int. 1999;15:214–6.
Ein SH. Recurrent intussusception in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1975;10:751–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, N.M., Joseph, J., Philip, R.R. et al. Intussusception: Single Center Experience of 10 Years. Indian Pediatr 56, 29–32 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1462-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1462-1