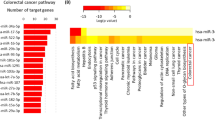
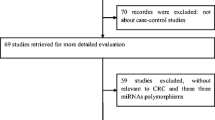
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate target gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Although recent studies have indicated that miR-146a is involved in the tumorigenesis of various types of malignancies, few studies have investigated its role in colorectal cancer. In the current study, we examined the expression of miR-146a in colorectal cancer tissue and adjacent normal controls using publicly available expression profiling data. We then conducted a population-based case-control study which included 554 colorectal cancer cases and 566 matched healthy controls to assess the association of a genetic variant (rs2910164) in miR-146a with colorectal cancer susceptibility. We observed decreased expression of miR-146a in rectal cancer tissue compared with adjacent normal controls (P < 0.001). Association between miR-146a rs2910164 polymorphism and risk of colorectal cancer was detected with effect modification by alcohol drinking status (P for interaction = 0.010). Among non-alcohol drinkers, individuals with CC/CG genotype had an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer compared with those carrying GG genotype (odds ratio (OR) = 1.63, 95 % confidence interval (CI): 1.07∼2.47). Our findings indicate an association between miR-146a dysregulation and colorectal cancer, and suggest that miR-146a may play a role in colorectal carcinogenesis. Further large population-based prospective studies as well as mechanistic investigations are warranted to validate our findings.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C, Ward EM. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19(8):1893–907.
Center MM, Jemal A, Ward E. International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(6):1688–94.
Huxley RR, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Clifton P, Czernichow S, Parr CL, Woodward M. The impact of dietary and lifestyle risk factors on risk of colorectal cancer: a quantitative overview of the epidemiological evidence. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(1):171–80.
Faber C, Kirchner T, Hlubek F. The impact of microRNAs on colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2009;454(4):359–67.
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 2008;299(4):425–36.
Li Y, Vandenboom 2nd TG, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S, Philip PA, et al. miR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70(4):1486–95.
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S, Mori M. Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(13):4277–84.
Scapoli L, Palmieri A, Lo Muzio L, Pezzetti F, Rubini C, Girardi A, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of oral carcinoma identifies new markers of tumor progression. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2010;23(4):1229–34.
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D, Ying SY. Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. RNA. 2008;14(3):417–24.
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil CK, Campisi J, Benz CC. Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27(42):5643–7.
Yao Q, Cao Z, Tu C, Zhao Y, Liu H, Zhang S. MicroRNA-146a acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting WASF2. Cancer Lett. 2013;335(1):219–24.
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR, de la Chapelle A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(20):7269–74.
Xu T, Zhu Y, Wei QK, Yuan Y, Zhou F, Ge YY, et al. A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene is associated with the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(11):2126–31.
Xu B, Feng NH, Li PC, Tao J, Wu D, Zhang ZD, et al. A functional polymorphism in pre-miR-146a gene is associated with prostate cancer risk and mature miR-146a expression in vivo. Prostate. 2010;70(5):467–72.
Zhou F, Zhu H, Luo D, Wang M, Dong X, Hong Y, et al. A functional polymorphism in pre-miR-146a is associated with susceptibility to gastric cancer in a Chinese population. DNA Cell Biol. 2012;31(7):1290–5.
Pizzini S, Bisognin A, Mandruzzato S, Biasiolo M, Facciolli A, Perilli L, et al. Impact of microRNAs on regulatory networks and pathways in human colorectal carcinogenesis and development of metastasis. BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):589.
Ahmed FE, Ahmed NC, Vos PW, Bonnerup C, Atkins JN, Casey M, et al. Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon cancer in stool: I. Proof of principle. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2013;10(3):93–113.
Hwang WL, Jiang JK, Yang SH, Huang TS, Lan HY, Teng HW, et al. MicroRNA-146a directs the symmetric division of snail-dominant colorectal cancer stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(3):268–80.
Zhong H, Wang HR, Yang S, Zhong JH, Wang T, Wang C, et al. Targeting Smad4 links microRNA-146a to the TGF-beta pathway during retinoid acid induction in acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line. Int J Hematol. 2010;92(1):129–35.
Gaedcke J, Grade M, Camps J, Sokilde R, Kaczkowski B, Schetter AJ, et al. The rectal cancer microRNAome—microRNA expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(18):4919–30.
Zheng S, Chen K, Liu X, Ma X, Yu H, Yao K, et al. Cluster randomization trial of sequence mass screening for colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003;46(1):51–8.
Chen K, Jin M, Zhu Y, Jiang Q, Yu W, Ma X, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of the uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 and colorectal cancer risk in relation to cigarette smoking and alcohol drinking in a Chinese population. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21(6):1036–41.
Hou Z, Xie L, Yu L, Qian X, Liu B. MicroRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med Oncol. 2012;29(2):886–92.
Papaconstantinou IG, Manta A, Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Lykoudis PM, Polymeneas G, et al. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas. 2013;42(1):67–71.
Rong M, He R, Dang Y, Chen G. Expression and clinicopathological significance of miR-146a in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Ups J Med Sci. 2014;119(1):19–24.
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I, Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G, Voros D. Expression of microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c, miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic significance. Mol Carcinog. 2013;52(4):297–303.
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS, Meyers C, et al. Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 2008;3(7):e2557.
Zhang H, Luo XQ, Zhang P, Huang LB, Zheng YS, Wu J, et al. MicroRNA patterns associated with clinical prognostic parameters and CNS relapse prediction in pediatric acute leukemia. PLoS One. 2009;4(11):e7826.
Jeon HS, Lee YH, Lee SY, Jang JA, Choi YY, Yoo SS, et al. A common polymorphism in pre-microRNA-146a is associated with lung cancer risk in a Korean population. Gene. 2014;534(1):66–71.
George GP, Gangwar R, Mandal RK, Sankhwar SN, Mittal RD. Genetic variation in microRNA genes and prostate cancer risk in North Indian population. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(3):1609–15.
Mittal RD, Gangwar R, George GP, Mittal T, Kapoor R. Investigative role of pre-microRNAs in bladder cancer patients: a case-control study in North India. DNA Cell Biol. 2011;30(6):401–6.
Srivastava K, Srivastava A, Mittal B. Common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs and risk of gallbladder cancer in North Indian population. J Hum Genet. 2010;55(8):495–9.
Chu YH, Tzeng SL, Lin CW, Chien MH, Chen MK, Yang SF. Impacts of microRNA gene polymorphisms on the susceptibility of environmental factors leading to carcinogenesis in oral cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39777.
Shimizu N, Nagata C, Shimizu H, Kametani M, Takeyama N, Ohnuma T, et al. Height, weight, and alcohol consumption in relation to the risk of colorectal cancer in Japan: a prospective study. Br J Cancer. 2003;88(7):1038–43.
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Bienertova-Vasku J, Sachlova M, Redova M, Vasku A, et al. Evaluation of SNPs in miR-196-a2, miR-27a and miR-146a as risk factors of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(22):2827–31.
Min KT, Kim JW, Jeon YJ, Jang MJ, Chong SY, Oh D, et al. Association of the miR-146aC>G, 149C>T, 196a2C>T, and 499A>G polymorphisms with colorectal cancer in the Korean population. Mol Carcinog. 2012;51 Suppl 1:E65–73.
Chae YS, Kim JG, Lee SJ, Kang BW, Lee YJ, Park JY, et al. A miR-146a polymorphism (rs2910164) predicts risk of and survival from colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(8):3233–9.
Ma L, Zhu L, Gu D, Chu H, Tong N, Chen J, et al. A genetic variant in miR-146a modifies colorectal cancer susceptibility in a Chinese population. Arch Toxicol. 2013;87(5):825–33.
Hu X, Li L, Shang M, Zhou J, Song X, Lu X, et al. Association between microRNA genetic variants and susceptibility to colorectal cancer in Chinese population. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(3):2151–6.
Lv M, Dong W, Li L, Zhang L, Su X, Wang L, et al. Association between genetic variants in pre-miRNA and colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(8):1405–10.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 81072356 and No. 81373087).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 2,535 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Y., Li, Y., Jing, F. et al. Association of a genetic variant in microRNA-146a with risk of colorectal cancer: a population-based case-control study. Tumor Biol. 35, 6961–6967 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1916-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1916-y