Abstract
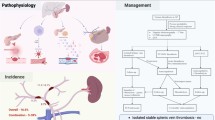
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in children, and has been reported as the most common malignancy associated with thromboembolism in the pediatric age group. Treatment with Escherichia coli asparaginase, concomitant steroids, presence of central venous lines, and thrombophilic abnormalities are established risk factors for thromboembolism. The incidence varies with age, co-morbidities and chemotherapy regimens but the risk is highest during the induction and intensification phases. Treatment is necessary in majority of children to prevent serious sequelae. Mortality from thromboembolic events in any location is 2 to 4 % and the risk of recurrence is 7 to 10 %, further enhanced in the setting of malignancy. Randomized trials of venous thromboembolism (VTE) management in pediatric patients with ALL are lacking due to the low overall incidence, resulting in considerable variation in practice. The objective of this article is to review current knowledge on the treatment and prevention of thrombosis associated with pediatric ALL.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew M, David M, Adams M, Ali K, Anderson R, Barnard D, et al. Venous thromboembolic complications (VTE) in children: First analyses of the Canadian Registry of VTE. Blood. 1994;83:1251–7.
van Ommen CH, Heijboer H, Büller HR, Hirasing RA, Heijmans HS, Peters M. Venous thromboembolism in childhood: A prospective two-year registry in The Netherlands. J Pediatr. 2001;139:676–81.
Monagle P, Adams M, Mahoney M, Ali K, Barnard D, Bernstein M, et al. Outcome of pediatric thromboembolic disease: A report from the Canadian Childhood Thrombophilia Registry. Pediatr Res. 2000;47:763–6.
Athale UH, Chan AK. Thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Part I. Epidemiology of thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Thromb Res. 2003;111:125–31.
Shapiro AD, Clarke SL, Christian JM, Odom LF, Hathaway WE. Thrombosis in children receiving L-asparaginase. Determining patients at risk. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;15:400–5.
Mitchell L, Hoogendoorn H, Giles AR, Vegh P, Andrew M. Increased endogenous thrombin generation in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Risk of thrombotic complications in L’Asparaginase-induced antithrombin III deficiency. Blood. 1994;83:386–91.
Nowak-Gottl U, Junker R, Kreuz W, von Eckardstein A, Kosch A, Nohe N, et al. Risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in children with combined prothrombotic risk factors. Blood. 2001;97:858–62.
Caruso V, Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, Storti S, Mariani G, de Gaetano G, et al. Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients. Blood. 2006;108:2216–22.
Uszynski M, Osinska M, Zekanowska E, Ziolkowska E. Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Is there any subgroup of children without elevated thrombin generation? A preliminary study utilizing measurements of thrombin-antithrombin III complexes. Med Sci Monit. 2000;6:108–11.
Sutherland DE, Weitz IC, Liebman HA. Thromboembolic complications of cancer: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Hematol. 2003;72:43–52.
Athale UH, Chan AK. Thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Part II. Pathogenesis of thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Effects of the disease and therapy. Thromb Res. 2003;111:199–212.
Nowak-Gottl U, Wermes C, Junker R, Koch HG, Schobess R, Fleischhack G, et al. Prospective evaluation of the thrombotic risk in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia carrying the MTHFR TT 677 genotype, the prothrombin G20210A variant, and further prothrombotic risk factors. Blood. 1999;93:1595–9.
Mitchell LG, Andrew M, Hanna K, Abshire T, Halton J, Anderson R, et al. A prospective cohort study determining the prevalence of thrombotic events in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and a central venous line who are treated with L-asparaginase: Results of the Prophylactic Antithrombin Replacement in Kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Asparaginase (PARKAA) Study. Cancer. 2003;97:508–16.
Athale UH, Siciliano SA, Crowther M, Barr RD, Chan AK. Thromboembolism in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated on Dana-Farber Cancer Institute protocols: Effect of age and risk stratification of disease. Br J Haematol. 2005;129:803–10.
Mitchell L, Lambers M, Flege S, Kenet G, Li-Thiao-Te V, Holzhauer S, et al. Validation of a predictive model for identifying an increased risk for thromboembolism in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of a multicenter cohort study. Blood. 2010;115:4999–5004.
Al-Aridi C, Abboud MR, Saab R, Eid D, Jeha S, Chan AK, et al. Thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated at a tertiary care center in Lebanon: Revisiting the role of predictive models. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2011;28:676–81.
Monagle P, Chan AK, Goldenberg NA, Ichord RN, Journeycake JM, Nowak-Gottl U, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children: Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141:e737S–801.
Sutor AH, Chan AK, Massicotte P. Low-molecular-weight heparin in pediatric patients. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2004;30:31–9.
Wermes C, von Depka Prondzinski M, Lichtinghagen R, Barthels M, Welte K, Sykora KW. Clinical relevance of genetic risk factors for thrombosis in paediatric oncology patients with central venous catheters. Eur J Pediatr. 1999;158:S143–6.
Albisetti M. Thrombolytic therapy in children. Thromb Res. 2006;118:95–105.
Wang M, Hays T, Balasa V, Bagatell R, Gruppo R, Grabowski EF, et al. Low-dose tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2003;25:379–86.
Yee DL, Chan AK, Williams S, Goldenberg NA, Massicotte MP, Raffini LJ. Varied opinions on thrombolysis for venous thromboembolism in infants and children: Findings from a survey of pediatric hematology-oncology specialists. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53:960–6.
Manco-Johnson MJ, Nuss R, Hays T, Krupski W, Drose J, Manco-Johnson ML. Combined thrombolytic and anticoagulant therapy for venous thrombosis in children. J Pediatr. 2000;136:446–53.
Williams MD. Thrombolysis in children. Br J Haematol. 2010;148:26–36.
Elhasid R, Lanir N, Sharon R, Weyl Ben Arush M, Levin C, Postovsky S, et al. Prophylactic therapy with enoxaparin during L-asparaginase treatment in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2001;12:367–70.
Hutten BA, Prins MH, Gent M, Ginsberg J, Tijssen JG, Buller HR. Incidence of recurrent thromboembolic and bleeding complications among patients with venous thromboembolism in relation to both malignancy and achieved international normalized ratio: A retrospective analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3078–83.
Prandoni P, Lensing AW, Piccioli A, Bernardi E, Simioni P, Girolami B, et al. Recurrent venous thromboembolism and bleeding complications during anticoagulant treatment in patients with cancer and venous thrombosis. Blood. 2002;100:3484–8.
Meyer G, Marjanovic Z, Valcke J, Lorcerie B, Gruel Y, Solal-Celigny P, et al. Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin for the secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer: A randomized controlled study. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1729–35.
Lee AY, Levine MN, Baker RI, Bowden C, Kakkar AK, Prins M, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus a coumarin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:146–53.
Massicotte P, Leaker M, Marzinotto V, Adams M, Freedom R, Williams W, et al. Enhanced thrombin regulation during warfarin therapy in children compared to adults. Thromb Haemost. 1998;80:570–4.
Payne JH, Vora AJ. Thrombosis and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2007;138:430–45.
Yang JY, Williams S, Brandao LR, Chan AK. Neonatal and childhood right atrial thrombosis: Recognition and a risk-stratified treatment approach. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2010;21:301–7.
Sebire G, Tabarki B, Saunders DE, Leroy I, Liesner R, Saint-Martin C, et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in children: Risk factors, presentation, diagnosis and outcome. Brain. 2005;128:477–89.
Barnes C, Newall F, Furmedge J, Mackay M, Monagle P. Cerebral sinus venous thrombosis in children. J Paediatr Child Health. 2004;40:53–5.
deVeber G, Andrew M, Adams C, Bjornson B, Booth F, Buckley DJ, et al. Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:417–23.
deVeber G, Monagle P, Chan A, MacGregor D, Curtis R, Lee S, et al. Prothrombotic disorders in infants and children with cerebral thromboembolism. Arch Neurol. 1998;55:1539–43.
Kenet G, Kirkham F, Niederstadt T, Heinecke A, Saunders D, Stoll M, et al. Risk factors for recurrent venous thromboembolism in the European collaborative paediatric database on cerebral venous thrombosis: A multicentre cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:595–603.
Ferro JM, Canhao P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: Results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 2004;35:664–70.
Godfrey AL, Higgins JN, Beer PA, Craig JI, Vassiliou GS. In situ thrombolysis for cerebral venous thrombosis complicating anti-leukemic therapy. Leuk Res. 2011;35:1127–9.
Santoro N, Giordano P, Del Vecchio GC, Guido G, Rizzari C, Varotto S, et al. Ischemic stroke in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A retrospective study. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2005;27:153–7.
Abbott LS, Deevska M, Fernandez CV, Dix D, Price VE, Wang H, et al. The impact of prophylactic fresh-frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate on the incidence of central nervous system thrombosis and hemorrhage in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia receiving asparaginase. Blood. 2009;114:5146–51.
Tosetto A, Balduini CL, Cattaneo M, De Candia E, Mariani G, Molinari AC, et al. Management of bleeding and of invasive procedures in patients with platelet disorders and/or thrombocytopenia: guidelines of the Italian Society for Haemostasis and Thrombosis (SISET). Thromb Res. 2009;124:e13–8.
Saccullo G, Malato A, Raso S, Santoro M, Zammit V, Casuccio A, et al. Cancer patients requiring interruption of long-term warfarin because of surgery or chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia: The use of fixed sub-therapeutic doses of low-molecular weight heparin. Am J Hematol. 2012;87:388–91.
Smith S, Dawson S, Hennessey R, Andrew M. Maintenance of the patency of indwelling central venous catheters: Is heparin necessary? Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1991;13:141–3.
Randolph AG, Cook DJ, Gonzales CA, Andrew M. Benefit of heparin in peripheral venous and arterial catheters: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 1998;316:969–75.
Dillon PW, Jones GR, Bagnall-Reeb HA, Buckley JD, Wiener ES, Haase GM. Prophylactic urokinase in the management of long-term venous access devices in children: A Children’s Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2718–23.
Ruud E, Holmstrom H, De Lange C, Hogstad EM, Wesenberg F. Low-dose warfarin for the prevention of central line-associated thromboses in children with malignancies—a randomized, controlled study. Acta Paediatr. 2006;95:1053–9.
Massicotte P, Julian JA, Gent M, Shields K, Marzinotto V, Szechtman B, et al. An open-label randomized controlled trial of low molecular weight heparin for the prevention of central venous line-related thrombotic complications in children: The PROTEKT trial. Thromb Res. 2003;109:101–8.
Raffini L, Thornburg C. Testing children for inherited thrombophilia: More questions than answers. Br J Haematol. 2009;147:277–88.
Goldenberg NA. Long-term outcomes of venous thrombosis in children. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005;12:370–6.
Kearon C. Long-term management of patients after venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2004;110:I10–8.
Corapcioglu F, Uysal KM, Silistreli E, Unal N, Oren H, Acikel U. Catheter-associated recurrent intracardiac thrombosis and factor V Leiden mutation in a child with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Turk J Pediatr. 2005;47:279–82.
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Zia is the recipient of the National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF) Clinical Fellowship award.
Role of Funding Source
Funding was through NHF/Baxter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zia, A.N., Chitlur, M. Management of Thrombotic Complications in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Indian J Pediatr 80, 853–862 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1158-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1158-9