Abstract
Background and aim
Primary prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is an important strategy to reduce morbidity and mortality in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Efficacy and safety of alternating rifaximin and norfloxacin as primary prophylaxis is questionable.
Methods
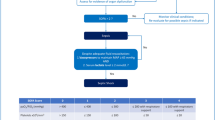
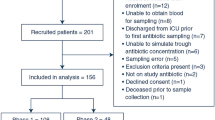
Three hundred thirty-four cirrhotic patients with high SAAG (≥1.1) ascites, protein level in ascitic fluid less than 1.5 g/dL with advanced liver disease (Child-Pugh score >9 points with serum bilirubin level >3 mg/dL) or renal impairment (serum creatinine level >1.2 mg/dL, blood urea nitrogen level >25 mg/dL, or serum sodium level <130 mEq/L) were included in an open-label, randomized study aimed at comparing alternating use of norfloxacin and rifaximin vs. norfloxacin or rifaximin alone as primary prophylaxis for SBP. Both intention-to-treat and per-protocol efficacy analyses were done after 6 months of treatment by assessment of ascitic fluid neutrophil count. Safety analysis was done for all intention-to-treat populations.
Results
Alternating norfloxacin and rifaximin showed superior prophylaxis by intention-to-treat (74.7 vs. 56.4 % vs. 68.3 %, p < 0.048). Pairwise analysis showed that alternating regimen had lower probability to develop SBP when compared to a norfloxacin-based regimen in intention-to-treat (p = 0.016) and per protocol analysis (p = 0.039). There was no difference among the studied groups regarding the incidence and severity of adverse events reported.
Conclusions
Alternating norfloxacin- and rifaximin-based primary prophylaxis for SBP showed higher efficacy with the same safety profile when compared with monotherapy of norfloxacin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalambokis GN, Mouzaki A, Rodi M, Tsianos EV. Rifaximin for the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:1700–1702
Koulaouzidis A. Diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an update on leucocyte esterase reagent strips. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:1091–1094
Biecker E. Diagnosis and therapy of ascites in liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:1237–1248
Fernandez J, Navasa M, Gomez J, Colmenero J, Vila J, Arroyo V, et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: epidemiological changes with invasive procedures and norfloxacin prophylaxis. Hepatology 2002;35:140–148
Koo HL, DuPont HL. Rifaximin: a unique gastrointestinal-selective antibiotic for enteric diseases. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2010;26:17–25
Vlachogiannakos J, Saveriadis AS, Viazis N, Theodoropoulos I, Foudoulis K, Manolakopoulos S, et al. Intestinal decontamination improves liver haemodynamics in patients with alcohol-related decompensated cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009;29:992–999
Vlachogiannakos J, Viazis N, Vasianopoulou P, Vafiadis I, Karamanolis DG, Ladas SD. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:450–455
Richardson L. Alternating antibiotics render resistant bacteria beatable. PLoS Biol 2015;13:e1002105
Fagiuoli S, Colli A, Bruno R, Burra P, Craxi A, Gaeta GB, et al. Management of infections in cirrhotic patients: report of a consensus conference. Dig Liver Dis 2014;46:204–212
Angeli P, Gines P, Wong F, Bernardi M, Boyer TD, Gerbes A, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut 2015;64:531–537
Arroyo V, Gines P, Gerbes AL, Dudley FJ, Gentilini P, Laffi G, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology 1996;23:164–176
Salerno F, Gerbes A, Gines P, Wong F, Arroyo V. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Gut 2007;56:1310–1318
Sigal SH, Stanca CM, Fernandez J, Arroyo V, Navasa M. Restricted use of albumin for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gut 2007;56:597–599
Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, Aldeguer X, Planas R, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med 1999;341:403–409
Hsieh WJ, Lin HC, Hwang SJ, Hou MC, Lee FY, Chang FY, et al. The effect of ciprofloxacin in the prevention of bacterial infection in patients with cirrhosis after upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:962–966
Narahara Y, Kanazawa H, Sakamoto C, Maruyama H, Yokosuka O, Mochida S, et al. The efficacy and safety of terlipressin and albumin in patients with type 1 hepatorenal syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, explorative study. J Gastroenterol 2012;47:313–320
Uriz J, Gines P, Cardenas A, Sort P, Jimenez W, Salmeron JM, et al. Terlipressin plus albumin infusion: an effective and safe therapy of hepatorenal syndrome. J Hepatol 2000;33:43–48
Fernandez J, Navasa M, Planas R, Montoliu S, Monfort D, Soriano G, et al. Primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis delays hepatorenal syndrome and improves survival in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007;133:818–824
Runyon BA. Low-protein-concentration ascitic fluid is predisposed to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology 1986;91:1343–1346
Guarner C, Sola R, Soriano G, Andreu M, Novella MT, Vila MC, et al. Risk of a first community-acquired spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotics with low ascitic fluid protein levels. Gastroenterology 1999;117:414–419
Llach J, Rimola A, Navasa M, Gines P, Salmeron JM, Gines A, et al. Incidence and predictive factors of first episode of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis with ascites: relevance of ascitic fluid protein concentration. Hepatology 1992;16:724–747
Andreu M, Sola R, Sitges-Serra A, Alia C, Gallen M, Vila MC, et al. Risk factors for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Gastroenterology 1993;104:1133–1138
Follo A, Llovet JM, Navasa M, Planas R, Forns X, Francitorra A, et al. Renal impairment after spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: incidence, clinical course, predictive factors and prognosis. Hepatology 1994;20:1495–1501
Gines A, Escorsell A, Gines P, Salo J, Jimenez W, Inglada L, et al. Incidence, predictive factors, and prognosis of the hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis with ascites. Gastroenterology 1993;105:229–236
Bataller R, Gines P, Guevara M, Arroyo V. Hepatorenal syndrome. Semin Liver Dis 1997;17:233–247
Angeli P, Wong F, Watson H, Gines P, Investigators C. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: results of a patient population survey. Hepatology 2006;44:1535–1542
Rimola A, Garcia-Tsao G, Navasa M, Piddock LJ, Planas R, Bernard B, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a consensus document. International Ascites Club. J Hepatol 2000;32:142–153
Runyon BA. Practice Guidelines Committee AASLD. Management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004;39:841–856
Moore KP, Wong F, Gines P, Bernardi M, Ochs A, Salerno F, et al. The management of ascites in cirrhosis: report on the consensus conference of the International Ascites Club. Hepatology 2003;38:258–266
Moore KP, Aithal GP. Guidelines on the management of ascites in cirrhosis. Gut 2006;55(Suppl 6):vi1–12
Riggio O, Angeloni S. Ascitic fluid analysis for diagnosis and monitoring of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J Gastroenterol 2009;15:3845–3850
Runyon BA. A pill a day can improve survival in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1029–1031
Sandhu BS, Sanyal AJ. Management of ascites in cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis 2005;9:715–732, viii
Dupeyron C, Mangeney N, Sedrati L, Campillo B, Fouet P, Leluan G. Rapid emergence of quinolone resistance in cirrhotic patients treated with norfloxacin to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1994;38:340–344
Hanouneh MA, Hanouneh IA, Hashash JG, Law R, Esfeh JM, Lopez R, et al. The role of rifaximin in the primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2012;46:709–715
DuPont HL, Jiang ZD. Influence of rifaximin treatment on the susceptibility of intestinal gram-negative flora and enterococci. Clin Microbiol Infect 2004;10:1009–1011
DuPont HL, Jiang ZD, Okhuysen PC, Ericsson CD, de la Cabada FJ, Ke S, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of rifaximin to prevent travelers’ diarrhea. Ann Intern Med 2005;142:805–812
Darkoh C, Lichtenberger LM, Ajami N, Dial EJ, Jiang ZD, DuPont HL. Bile acids improve the antimicrobial effect of rifaximin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2010;54:3618–3624
Mostafa T, Badra G, Abdallah M. The efficacy and the immunomodulatory effect of rifaximin in prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic Egyptian patients. Turk J Gastroenterol 2015;26:163–169
Rasaratnam B, Kaye D, Jennings G, Dudley F, Chin-Dusting J. The effect of selective intestinal decontamination on the hyperdynamic circulatory state in cirrhosis. A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2003;139:186–193
Albillos A, de la Hera A, Gonzalez M, Moya JL, Calleja JL, Monserrat J, et al. Increased lipopolysaccharide binding protein in cirrhotic patients with marked immune and hemodynamic derangement. Hepatology 2003;37:208–217
Ruiz-del-Arbol L, Monescillo A, Arocena C, Valer P, Gines P, Moreira V, et al. Circulatory function and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2005;42:439–447
Acknowledgements
We thank all staff members of inpatient and outpatient departments in all sharing centers for their help in collection of our data.
Author contribution statement
M. Assem initiated the collaborative project, designed the trial, implemented the trial for the all countries, and drafted and revised the paper. M. Elsabaawy monitored data collection in Egypt, and revised the draft paper. M. Abdelrashed monitored data collection in Saudi Arabia, and drafted the paper. S. Elemam implemented the trial in Saudi Arabia and analyzed the data. Both S. Khodeer and W. Hamed analysed the data and drafted the paper. A. Abdelaziz monitored data collection for the whole trial especially for laboratory results and analyzed the data. G. El-Azab wrote the statistical analysis plan, designed data collection tools, monitored data collection for the whole trial, analyzed the data, and drafted and revised the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
All participating centers shared in the fund.
Conflict of interest
M. Assem, M. Elsabaawy, M. Abdelrashed, S. Elemam, S. Khodeer, W. Hamed, A. Abdelaziz, G. El-Azab declare no competing interests, either financial or non-financial.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee at each participating center and written informed consent was obtained from patients before entering the study. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assem, M., Elsabaawy, M., Abdelrashed, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of alternating norfloxacin and rifaximin as primary prophylaxis for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic ascites: a prospective randomized open-label comparative multicenter study. Hepatol Int 10, 377–385 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9688-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9688-z