Abstract
Purpose
Overexpression of HMGA2, known as small non-histone chromosomal protein, is associated with progression of various tumors, including colorectal cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a specific HMGA2 siRNA on apoptosis and cell cycle of HCT-116 (colorectal carcinoma) cells.
Methods
The cells were transfected with siRNAs using a transfection reagent. The cytotoxic effects of HMGA2 siRNA on colorectal carcinoma cells were determined using MTT assay. Relative HMGA2 mRNA and protein levels were measured by QRT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. Apoptosis was measured by a TUNEL test based on labeling of DNA strand breaks. We also evaluated caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 expression by QRTPCR to determine which pathway is involved in apoptosis. Cell cycle was assessed by FACS and cell cycle analysis using PI DNA staining.
Results
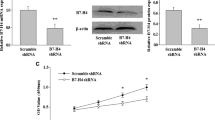
HMGA2 siRNA significantly reduced both mRNA and protein expression levels 48 h after transfection and dose-dependent manner in colorectal carcinoma cells. We also showed that the silencing of HMGA2 led to the induction of apoptosis through intrinsic pathway and cell cycle arrest in G2/M phases of interphase in HCT-116 cells in vitro.
Conclusions
These results propose that HMGA2 might play an important role in the progression of colorectal carcinoma and might be a potential therapeutic target for trigger apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in colorectal carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Lotfipour F, Hallaj-Nezhadi S, Valizadeh H, Dastmalchi S, Baradaran B, Jalali MB, Dobakhti F. Preparation of chitosan-plasmid DNA nanoparticles encoding interleukin-12 and their expression in CT-26 colon carcinoma cells. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2011;14(2):181–95.
Mohammadi A, Mansoori B, Aghapour M, Baradaran PC, Shajari N, Davudian S, Salehi S, Baradaran B. The herbal medicine Utrica dioica inhibits proliferation of colorectal cancer cell line by inducing apoptosis and arrest at the G2/M phase. Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer. 2016:1–9.
Valiyari S, Jahanban-Esfahlan R, Shahneh FZ, Yaripour S, Baradaran B, Delazar A. Cytotoxic and apoptotic activity of Scrophularia oxysepala in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Toxicol Environ Chem. 2013;95(7):1208–20.
Luwor R, Baradaran B, Taylor L, Iaria J, Nheu T, Amiry N, Hovens C, Wang B, Kaye A, Zhu H. Targeting Stat3 and Smad7 to restore TGF-β cytostatic regulation of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2013;32(19):2433–41.
Matzke M, Matzke AJ. RNAi extends its reach. Science. 2003;301(5636):1060–1.
Natarajan S, Hombach-Klonisch S, Dröge P, Klonisch T. HMGA2 inhibits apoptosis through interaction with ATR-CHK1 signaling complex in human cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2013;15(3):263–IN213.
Cleynen I, Van de Ven WJ. The HMGA proteins: a myriad of functions (Review). Int J Oncol. 2008;32(2):289–305.
Tessari MA, Gostissa M, Altamura S, Sgarra R, Rustighi A, Salvagno C, Caretti G, Imbriano C, Mantovani R, Del Sal G. Transcriptional activation of the cyclin A gene by the architectural transcription factor HMGA2. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(24):9104–16.
De Martino I, Visone R, Wierinckx A, Palmieri D, Ferraro A, Cappabianca P, Chiappetta G, Forzati F, Lombardi G, Colao A. HMGA proteins up-regulate CCNB2 gene in mouse and human pituitary adenomas. Cancer Res. 2009;69(5):1844–50.
Manfioletti G, Giancotti V, Bandiera A, Buratti E, Sautièere P, Cary P, Crane-Robinson C, Coles B, Goodwin G. cDNA cloning of the HML-C phosphoprotein, a nclear protein associated with neoplastic and undifferentiated phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19(24):6793–7.
Zhou X, Benson KF, Ashar HR, Chada K (1995) Mutation responsible for the mouse pygmy phenotype in the developmentally regulated factor HMGI-C.
Rogalla P, Drechsler K, Frey G, Hennig Y, Helmke B, Bonk U, Bullerdiek J. HMGI-C expression patterns in human tissues. Implications for the genesis of frequent mesenchymal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1996;149(3):775.
Guang-meng X, Hai-na Z, Xiao-feng T, Mei S, Xue-dong F. Effect of HMGA2 shRNA on the cell proliferation and invasion of human colorectal cancer SW480 cells in vitro. CHEMICAL RESEARCH IN CHINESE UNIVERSITES. 2012;28(2):264–8.
Belge G, Meyer A, Klemke M, Burchardt K, Stern C, Wosniok W, Loeschke S, Bullerdiek J. Upregulation of HMGA2 in thyroid carcinomas: a novel molecular marker to distinguish between benign and malignant follicular neoplasias. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2008;47(1):56–63.
Rogalla P, Drechsler K, Kazmierczak B, Rippe V, Bonk U, Bullerdiek J. Expression of HMGI-C, a member of the high mobility group protein family, in a subset of breast cancers: relationship to histologic grade. Mol Carcinog. 1997;19(3):153–6.
Langelotz C, Schmid P, Jakob C, Heider U, Wernecke K, Possinger K, Sezer O. Expression of high-mobility-group-protein HMGI-C mRNA in the peripheral blood is an independent poor prognostic indicator for survival in metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;88(9):1406–10.
Di Cello F, Hillion J, Hristov A, Wood LJ, Mukherjee M, Schuldenfrei A, Kowalski J, Bhattacharya R, Ashfaq R, Resar LM. HMGA2 participates in transformation in human lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(5):743–50.
Abe N, Watanabe T, Suzuki Y, Matsumoto N, Masaki T, Mori T, Sugiyama M, Chiappetta G, Fusco A, Atomi Y. An increased high-mobility group A2 expression level is associated with malignant phenotype in pancreatic exocrine tissue. Br J Cancer. 2003;89(11):2104–9.
Hristov AC, Cope L, Reyes MD, Singh M, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Maitra A, Resar L. HMGA2 protein expression correlates with lymph node metastasis and increased tumor grade in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2009;22(1):43–9.
Miyazawa J, Mitoro A, Kawashiri S, Chada KK, Imai K. Expression of mesenchyme-specific gene HMGA2 in squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity. Cancer Res. 2004;64(6):2024–9.
Malek A, Bakhidze E, Noske A, Sers C, Aigner A, Schäfer R, Tchernitsa O. HMGA2 gene is a promising target for ovarian cancer silencing therapy. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(2):348–56.
Park S-M, Shell S, Radjabi AR, Schickel R, Feig C, Boyerinas B, Dinulescu DM, Lengyel E, Peter ME. Let-7 prevents early cancer progression by suppressing expression of the embryonic gene HMGA2. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(21):2585–90.
Yang G, Zhang L, Bo J, Hou K, Cai X, Chen Y, Li H, Liu D, Huang Y. Overexpression of HMGA2 in bladder cancer and its association with clinicopathologic features and prognosis: HMGA2 as a prognostic marker of bladder cancer. European Journal of Surgical Oncology (EJSO). 2011;37(3):265–71.
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Mori M. Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(8):2334–40.
Huang M-L, Chen C-C, Chang L-C. Gene expressions of HMGI-C and HMGI (Y) are associated with stage and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Color Dis. 2009;24(11):1281–6.
Wang X, Liu X, Li AY-J, Chen L, Lai L, Lin HH, Hu S, Yao L, Peng J, Loera S. Overexpression of HMGA2 promotes metastasis and impacts survival of colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2570–80.
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Goldar S, Shanehbandi D, Mohammadnejad L, Baghbani E, Kazemi T, Kachalaki S, Baradaran B (2016) Silencing of high mobility group isoform IC (HMGI-C) enhances paclitaxel chemosensitivity in breast adenocarcinoma cells (MDA-MB-468).
Karami H, Baradaran B, Esfahani A, Estiar MA, Naghavi-Behzad M, Sakhinia M, Sakhinia E. siRNA-Mediated silencing of survivin inhibits proliferation and enhances etoposidechemosensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7719–24.
Zheng TS, Hunot S, Kuida K, Momoi T, Srinivasan A, Nicholson DW, Lazebnik Y, Flavell RA. Deficiency in caspase-9 or caspase-3 induces compensatory caspase activation. Nat Med. 2000;6(11):1241–7.
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Shirjang S, Baradaran B (2016) HMGI-C suppressing induces P53/caspase9 axis to regulate apoptosis in breast adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Cycle (just-accepted):00–00
Cuddihy AR, O’Connell MJ. Cell-cycle responses to DNA damage in G2. Int Rev Cytol. 2003;222:99–140.
Chiappetta G, Ferraro A, Vuttariello E, Monaco M, Galdiero F, De Simone V, Califano D, Pallante P, Botti G, Pezzullo L. HMGA2 mRNA expression correlates with the malignant phenotype in human thyroid neoplasias. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44(7):1015–21.
Gattas GJ, Quade BJ, Nowak RA, Morton CC. HMGIC expression in human adult and fetal tissues and in uterine leiomyomata. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 1999;25(4):316–22.
Hebert C, Norris K, Scheper MA, Nikitakis N, Sauk JJ. High mobility group A2 is a target for miRNA-98 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2007;6(1).
Mahajan A, Liu Z, Gellert L, Zou X, Yang G, Lee P, Yang X, Wei J-J. HMGA2: a biomarker significantly overexpressed in high-grade ovarian serous carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2010;23(5):673–81.
Meyer B, Loeschke S, Schultze A, Weigel T, Sandkamp M, Goldmann T, Vollmer E, Bullerdiek J. HMGA2 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2007;46(7):503–11.
Wu J, Liu Z, Shao C, Gong Y, Hernando E, Lee P, Narita M, Muller W, Liu J, Wei J-J. HMGA2 overexpression-induced ovarian surface epithelial transformation is mediated through regulation of EMT genes. Cancer Res. 2011;71(2):349–59.
Montazami N, Kheirandish M, Majidi J, Yousefi M, Yousefi B, Mohamadnejad L, Shanebandi D, Estiar M, Khaze V, Mansoori B. siRNA-mediated silencing of MDR1 reverses the resistance to oxaliplatin in SW480/OxR colon cancer cells. Cellular and molecular biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France). 2015;61(2):98.
Devi G. siRNA-based approaches in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13(9):819–29.
Yang M, Mattes J. Discovery, biology and therapeutic potential of RNA interference, microRNA and antagomirs. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117(1):94–104.
Shan G. RNA interference as a gene knockdown technique. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(8):1243–51.
Kachalaki S, Baradaran B, Majidi J, Yousefi M, Shanehbandi D, Mohammadinejad S, Mansoori B. Reversal of chemoresistance with small interference RNA (siRNA) in etoposide resistant acute myeloid leukemia cells (HL-60). Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2015;75:100–4.
Mansoori B, Shotorbani SS, Baradaran B. RNA interference and its role in cancer therapy. Advanced pharmaceutical bulletin. 2014;4(4).
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Shir Jang S, Baradaran B. Mechanisms of immune system activation in mammalians by small interfering RNA (siRNA. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology. 2015:1–8.
Musavi Shenas SMH, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Salehi S, Kaffash B, Talebi B, Babaloo Z, Shanehbandi D, Baradaran B. SiRNA-mediated silencing of snail-1 induces apoptosis and alters micro RNA expression in human urinary bladder cancer cell line. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016:1–6.
Brantl S. Antisense-RNA regulation and RNA interference. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Structure and Expression. 2002;1575(1):15–25.
Aoki Y, Cioca D, Oidaira H, Kamiya J, Kiyosawa K. RNA interference may be more potent than antisense RNA in human cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003;30(1–2):96–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmailzadeh, S., Mansoori, B., Mohammadi, A. et al. siRNA-Mediated Silencing of HMGA2 Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Colorectal Carcinoma. J Gastrointest Canc 48, 156–163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-016-9871-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-016-9871-z