Abstract
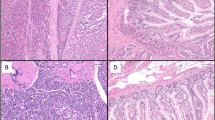
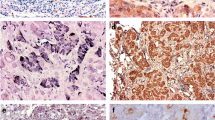
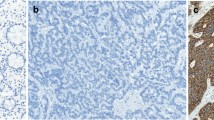
Somatostatin and its synthetic analogs act through five specific somatostatin receptors (sstr1–5), found on the cell membrane of various tumors, including endocrine ones. Dopamine—a known neurotransmitter—acts through five membranous dopamine receptors (D1R–D5R) which have recently been found to be expressed in endocrine tumors. We evaluated the immunohistochemical expression of the sstrs and D2R in a large series of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). A total of 22 (28.94%) well-differentiated NETs (WDNETs), 6 (7.89%) WDNETs of uncertain biology, 26 (34.21%) well-differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, and 22 (28.94%) poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas were studied. Overall, 76.31% of the tumors were positive for different types of sstrs with variable intensity of the membranous staining whereas 36.95% were positive for D2R alone. The sstr2A was the most frequently expressed, followed by sstr2B, sstr1, and sstr5. Co-expression of sstrs and D2R was seen in 88.23% of positive tumors. The high rates of sstr2A and sstr2B and in a lower extent of sstr5 expression are of great importance for more accurate imaging, staging and targeted therapy of the disease. The co-expression of sstrs and D2R in a significant number of the studied cases offers a potential therapeutic alternative for GEP-NETs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel YC. Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 1999;20:157–198.
Lamberts SW, Krenning EP, Reubi JC. The role of somatostatin and its analogs in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors. Endocr Rev. 1991;12:450–482. Review.
de Herder WW, Hofland LJ, van der Lely AJ et al. Somatostatin receptors in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2003;10:451–458.
Papotti M, Bongiovanni M, Volante M, et al. Expression of somatostatin receptors 1–5 in 81 cases of gastrointestinal and pancreatic tumors. A correlative immunohistochemical and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Virchows Arch 2002;440:461–475.
Reubi JC, Schaer JC, Waser B, et al. Expression and localization of somatostatin receptor SSTR1, SSTR2, and SSTR3 messenger RNAs in primary human tumors using in situ hybridization. Cancer Res 1994;54:3455–3459.
Reubi JC, Hacki WH, Lamberts SW. Hormone-producing gastrointestinal tumors contain a high density of somatostatin receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1987;65:1127–1134.
Corleto VD, Scopinaro F, Angeletti S et al. Somatostatin receptor localization of pancreatic endocrine tumors. World J Surg 1996;20:241–244.
Hofland LJ, Liu Q, Van Koetsveld PM et al. Immunohistochemical detection of somatostatin receptor subtypes sst1 and sst2A in human somatostatin receptor positive tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 775–780.
Ferone D, Arvigo M, Semino C et al. Somatostatin and dopamine receptor expression in lung carcinoma cells and effects of chimeric somatostatin-dopamine molecules on cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 289: E1044–E1050.
Florio T, Barbieri F, Spaziante R et al. Efficacy of a dopamine–somatostatin chimeric molecule, BIM-23A760, in the control of cell growth from primary cultures of human non-functioning pituitary adenomas: a multi-center study Endocr Relat Cancer; 2008;15:583–596
Rindi G, Klöppel G, Couvelard A et al. TNM staging of midgut and hindgut (neuro) endocrine tumors: a consensus proposal including a grading system. Virchows Arch. 2007; 451:757–762.
Klöppel G, Rindi G, Anlauf M et al. Site-specific biology and pathology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Virchows Arch. 2007;451(Suppl) 1:S9–S27.
Kaltsas GA, Besser GM, Grossman AB. The diagnosis and medical management of advanced neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Rev. 2004;458–511.
Volante M, Brizzi MP, Faggiano A. Somatostatin receptor type 2A immunohistochemistry in neuroendocrine tumors: a proposal of scoring system correlated with somatostatin receptor scintigraphy. Mod Pathol. 2007 Nov; 20(11):1172–1182.
Srirajaskanthan R, Watkins J, Marelli L et al. Expression of somatostatin and dopamine 2 receptors in neuroendocrine tumours and the potential role for new biotherapies. Neuroendocrinology. 2009;89:308–314.
Papotti M, Croce S, Bello M, et al. Expression of somatostatin receptor 2,3 and 5 in biopsy and surgical specimens of human lung tumors. Correlation with preoperative octreotide scintigraphy. Virchows Arch 2001;439:787–797.
Taniyama Y, Suzuki T, Mikami Y et al. Systemic distribution of somatostatin receptor subtypes in human: an immunohistochemical study. Endocr J. 2005;52:605–611.
Schultz S, Schultz S, Schmitt J, et al. Immunocytochemical detection of somatostatin receptors SST1, SST2A, SST2B and SST3 in paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissue using subtype-specific antibodies. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:2047–2052.
Papotti M, Croce S, Macri L et al. Correlative immunohistochemical and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis of somatostatin receptor type 2 in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Diagn Mol Pathol 2000;9:47–55.
Solcia E, Kloppel G & Sobin LH 2000 Histological typing of endocrine tumours. In World Health Organization International Histological Classification of Tumour, ed. 2 Berlin: Springer. pp. 61–68.
De Lellis R, Lloyd RV, Heitz PU & Eng C 2004 Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Endocrine Organs (World Health Organization Classification of Tumours). Lyon: IARC Press.
Rindi G, Kloppel G, Alhman H et al TNM staging of foregut (neuro)endocrine tumours: a consensus proposal including a grading system. Virchows Arch 2006;449:395–401.
Rindi G, Kloppel G, Coulevard At et al TNM staging of midgut and hindgut (neuro) endocrine tumors: a consensus proposal including a grading system.) Virchows Arch.2007 Oct;451(4):757–762
Lemmer K, Ahnert-Hilger G, Höpfner M et al. Expression of dopamine receptors and transporter in neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumor cells. Life Sci. 2002;71:667–678.
O'Toole D, Saveanu A, Couvelard A et al. The analysis of quantitative expression of somatostatin and dopamine expression in gastro-entero-pancreatic tumours opens new therapeutic strategies. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;155:849–857.
Thodou E, Kontogeorgos G, Theodossiou D et al. Mapping of somatostatin receptor types in GH or/and PRL producing pituitary adenomas. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:274–279.
Papotti M, Kumar U, Volante M et al. Immunohistochemical detection of somatostatin receptor types 1–5 in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2001;54:641–649.
Reubi JC. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr Rev 2003; 24:389–427.
Oda Y, Tanaka Y, Naruse T, et al. Expression of somatostatin receptor and effects of somatostatin analog on pancreatic endocrine tumors. Surg Today 2002;36:690–694.
Weckbecker G, Briner U, Lewis I. SOM230: A new somatostatin peptidomimetic with potent inhibitory effects on the growth hormone/insulin-like Growth Factor-I axis in rats, primates and dogs. Endocrinology 2002;143:4123–4130.
Hofland LJ and Lamberts SW: The Pathophysiological Consequences of Somatostatin Receptor Internalization and Resistance Endocr Rev 2003;24:28–47.
Rocheville M, Lange DC, Kumar U et al. Receptors for dopamine and somatostatin: formation of hetero-oligomers with enhanced functional activity. Science. 2000; 288:154–157
Kwekkeboom DJ, Kam BL, van Essen M et al: Somatostatin receptor-based imaging and therapy of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;29:17: R53–R73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diakatou, E., Kaltsas, G., Tzivras, M. et al. Somatostatin and Dopamine Receptor Profile of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: An Immunohistochemical Study. Endocr Pathol 22, 24–30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-011-9149-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-011-9149-8