Abstract
Introduction
Steroid myopathy is a well-known sign of endogenous Cushing’s syndrome as well as a side effect of glucocorticoid administration. The clinical finding of muscle weakness and the clinical inspection of the muscle size are the most commonly used diagnostic tools, sometimes in combination with needle electromyography, but there are no means to detect the myopathy before the appearance of clinical or electrodiagnostic signs. Until now, no guidelines have been produced for a disease-specific evaluation of muscle impairment in patients with Cushing’s syndrome.
Review
We reviewed the measurement properties and limitations of the following tools that are currently adopted in clinical research and routine care for diagnosis and monitoring of steroid myopathy: muscle strength assessment; needle biopsy; intramuscular and surface electromyography; laboratory assays; muscle mass assessments (through bioelectrical impedance analysis, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and computed tomography).
Conclusions
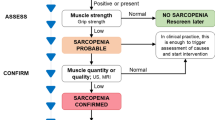
We suggest that the management of steroid myopathy patients in clinical research and practice would benefit from a multidisciplinary approach based on the combined assessment of muscle mass, strength, and performance. However, further studies are required to establish an operational definition of steroid myopathy and to identify population-specific criteria for diagnosis of the myopathic process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Minetto, F. Lanfranco, G. Motta, S. Allasia, E. Arvat, G. D’Antona, Steroid myopathy: some unresolved issues. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 34, 370–375 (2011)
O. Schakman, S. Kalista, C. Barbé, A. Loumaye, J.P. Thisse, Glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 45, 2163–2172 (2013)
R.M. Pereira, J. Freire de Carvalho, Glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. Joint Bone Spine 78, 41–44 (2011)
M.A. Minetto, A. Rainoldi, J.F. Jabre, The clinical use of macro and surface electromyography in diagnosis and follow-up of endocrine and drug-induced myopathies. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 30, 791–796 (2007)
A.A. Sapega, Muscle performance evaluation in orthopaedic practice. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 72, 1562–1574 (1990)
R.W. Bohannon, Measuring knee extensor muscle strength. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 80, 13–18 (2001)
N.A. Maffiuletti, Assessment of hip and knee muscle function in orthopaedic practice and research. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 92, 220–229 (2010)
A.W. Andrews, M.W. Thomas, R.W. Bohannon, Normative values for isometric muscle force measurements obtained with hand-held dynamometers. Phys. Ther. 76, 248–259 (1996)
R.W. Bohannon, Reference values for extremity muscle strength obtained by hand-held dynamometry from adults aged 20 to 79 years. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 78, 26–32 (1997)
A.A. Khaleeli, R.H. Edwards, K. Gohil, G. McPhail, M.J. Rennie, J. Round, E.J. Ross, Corticosteroid myopathy: a clinical and pathological study. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.). 8, 155–166 (1983)
A.A. Khaleeli, D.J. Betteridge, R.H. Edwards, J.M. Round, E.J. Ross, Effect of treatment of Cushing’s syndrome on skeletal muscle structure and function. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.). 19, 547–556 (1983)
S. Baudry, F. Lanfranco, R. Merletti, J. Duchateau, M.A. Minetto, Effects of short-term dexamethasone administration on corticospinal excitability. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 46, 695–701 (2014)
F. Kanda, S. Okuda, T. Matsushita, K. Takatani, K.I. Kimura, K. Chihara, Steroid myopathy: pathogenesis and effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I administration. Horm. Res. 56(Suppl 1), 24–28 (2001)
D. Dumitru. Myopathies. in Electrodiagnostic Medicine, ed. by D. Dumitru (Hanley & Belfus: Philadelphia, 1995), pp. 1031–1129
G. D’Antona, M.A. Pellegrino, R. Adami, R. Rossi, C.N. Carlizzi, M. Canepari, B. Saltin, R. Bottinelli, The effect of ageing and immobilization on structure and function of human skeletal muscle fibres. J. Physiol. 552, 499–511 (2003)
M.A. Weber, H. Krakowski-Roosen, L. Schröder, R. Kinscherf, M. Krix, A. Kopp-Schneider, M. Essig, P. Bachert, H.U. Kauczor, W. Hildebrandt, Morphology, metabolism, microcirculation, and strength of skeletal muscles in cancer-related cachexia. Acta Oncol. 48, 116–124 (2009)
M. Zamboni, A.P. Rossi, F. Corzato, C. Bambace, G. Mazzali, F. Fantin, Sarcopenia, cachexia and congestive heart failure in the elderly. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 13, 58–67 (2013)
S.D. Harridge, R. Bottinelli, M. Canepari, M.A. Pellegrino, C. Reggiani, M. Esbjörnsson, B. Saltin, Whole-muscle and single-fibre contractile properties and myosin heavy chain isoforms in humans. Pflug. Arch. 432, 913–920 (1996)
M.A. Minetto, R. Qaisar, V. Agoni, G. Motta, E. Longa, D. Miotti, M.A. Pellegrino, R. Bottinelli, Quantitative and qualitative adaptations of muscle fibers to glucocorticoids. Muscle Nerve 52, 631–639 (2015)
P. Hanson, A. Dive, J.M. Brucher, M. Bisteau, M. Dangoisse, T. Deltombe, Acute corticosteroid myopathy in intensive care patients. Muscle Nerve 20, 1371–1380 (1997)
M.A. Minetto, A. Botter, F. Lanfranco, M. Baldi, E. Ghigo, E. Arvat, Muscle fiber conduction slowing and decreased levels of circulating muscle proteins after short-term dexamethasone administration in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 1663–1671 (2010)
M.A. Minetto, F. Lanfranco, A. Botter, G. Motta, G. Mengozzi, R. Giordano, A. Picu, E. Ghigo, E. Arvat, Do muscle fiber conduction slowing and decreased levels of circulating muscle proteins represent sensitive markers of steroid myopathy? A pilot study in Cushing’s disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 164, 985–993 (2011)
P.J. Blijham, H.J. ter Laak, H.J. Schelhaas, B.G. van Engelen, D.F. Stegeman, M.J. Zwarts, Relation between muscle fiber conduction velocity and fiber size in neuromuscular disorders. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 100, 1837–1841 (2006)
M. Elia, A. Carter, S. Bacon, C.G. Winearls, R. Smith, Clinical usefulness of urinary 3-methylhistidine excretion in indicating muscle protein breakdown. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.). 282, 351–354 (1981)
N. Aranibar, J.D. Vassallo, J. Rathmacher, S. Stryker, Y. Zhang, J. Dai, E.B. Janovitz, D. Robertson, M. Reily, L. Lowe-Krentz, L. Lehman-McKeeman, Identification of 1- and 3-methylhistidine as biomarkers of skeletal muscle toxicity by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolic profiling. Anal. Biochem. 410, 84–91 (2011)
H.C. Lukaski, W.W. Bolonchuk, C.B. Hall, W.A. Siders, Validation of tetrapolar bioelectrical impedance method to assess human body composition. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 60, 1327–1332 (1986)
D.L. Kendler, J.L. Borges, R.A. Fielding, A. Itabashi, D. Krueger, K. Mulligan, B.M. Camargos, B. Sabowitz, C.H. Wu, E.W. Yu, J. Shepherd, The official positions of the international society for clinical densitometry: Indications of use and reporting of DXA for body composition. J. Clin. Densitom. 16, 496–507 (2013)
I. Janssen, S.B. Heymsfield, R.N. Baumgartner, R. Ross, Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985 89, 465–471 (2000)
G. Sergi, M. De Rui, N. Veronese, F. Bolzetta, L. Berton, S. Carraro, G. Bano, A. Coin, E. Manzato, E. Perissinotto, Assessing appendicular skeletal muscle mass with bioelectrical impedance analysis in free-living Caucasian older adults. Clin. Nutr. 34, 667–673 (2015)
R.N. Baumgartner, K.M. Koehler, D. Gallagher, L. Romero, S.B. Heymsfield, R.R. Ross, P.J. Garry, R.D. Lindeman, Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am. J. Epidemiol. 147, 755–763 (1998)
I. Janssen, S.B. Heymsfield, Z.M. Wang, R. Ross, Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18-88 yr. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 89, 81–88 (2000)
I. Janssen, R.N. Baumgartner, R. Ross, I.H. Rosenberg, R. Roubenoff, Skeletal muscle cutpoints associated with elevated physical disability risk in older men and women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 159, 413–421 (2004)
P.M. Cawthon, K.W. Peters, M.D. Shardell, R.R. McLean, T.T. Dam, A.M. Kenny, M.S. Fragala, T.B. Harris, D.P. Kiel, J.M. Guralnik, L. Ferrucci, S.B. Kritchevsky, M.T. Vassileva, S.A. Studenski, D.E. Alley, Cutpoints for low appendicular lean mass that identify older adults with clinically significant weakness. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 69, 567–575 (2014)
M.V. Narici, N. Maffulli, Sarcopenia: characteristics, mechanisms and functional significance. Br. Med. Bull. 95, 139–159 (2010)
D. Gallagher, M. Visser, R.E. De Meersman, D. Sepúlveda, R.N. Baumgartner, R.N. Pierson, T. Harris, S.B. Heymsfield, Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: effects of age, gender, and ethnicity. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 83, 229–239 (1997)
W.K. Mitchell, J. Williams, P. Atherton, M. Larvin, J. Lund, M. Narici, Sarcopenia, dynapenia, and the impact of advancing age on human skeletal muscle size and strength; a quantitative review. Front. Physiol. 3, 260 (2012)
J.R. Moon, Body composition in athletes and sports nutrition: an examination of the bioimpedance analysis technique. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 67(Suppl 1), S54–S59 (2013)
S.A. Kemink, J.T. Frijns, A.R. Hermus, G.F. Pieters, A.G. Smals, W.D. van Marken Lichtenbelt, Body composition determined by six different methods in women bilaterally adrenalectomized for treatment of Cushing’s disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 3991–3999 (1999)
M. Pirlich, H. Biering, H. Gerl, M. Ventz, B. Schmidt, S. Ertl, H. Lochs, Loss of body cell mass in Cushing’s syndrome: effect of treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 1078–1084 (2002)
B.S. Miller, K.M. Ignatoski, S. Daignault, C. Lindland, P.G. Gauger, G.M. Doherty, S.C. Wang; University of Michigan Analytical Morphomics Group, A quantitative tool to assess degree of sarcopenia objectively in patients with hypercortisolism. Surgery 150, 1178–1185 (2011)
S. Lovitt, F.A. Marden, B. Gundogdu, M.L. Ostrowski, MRI in myopathy. Neurol. Clin. 22, 509–538 (2004)
E. Zoico, F. Corzato, C. Bambace, A.P. Rossi, R. Micciolo, S. Cinti, T.B. Harris, M. Zamboni, Myosteatosis and myofibrosis: relationship with aging, inflammation and insulin resistance. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 57, 411–416 (2013)
I.M. Arts, S. Pillen, H.J. Schelhaas, S. Overeem, M.J. Zwarts, Normal values for quantitative muscle ultrasonography in adults. Muscle Nerve 41, 32–41 (2010)
M.S. Cartwright, S. Demar, L.P. Griffin, N. Balakrishnan, J.M. Harris, F.O. Walker, Validity and reliability of nerve and muscle ultrasound. Muscle Nerve 47, 515–521 (2013)
S. Pillen, I.M. Arts, M.J. Zwarts, Muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disorders. Muscle Nerve 37, 679–693 (2008)
M.D. de Boer, O.R. Seynnes, P.E. di Prampero, R. Pisot, I.B. Mekjavić, G. Biolo, M.V. Narici, Effect of 5 weeks horizontal bed rest on human muscle thickness and architecture of weight bearing and non-weight bearing muscles. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 104, 401–407 (2008)
R.A. Atkinson, U. Srinivas-Shankar, S.A. Roberts, M.J. Connolly, J.E. Adams, J.A. Oldham, F.C. Wu, O.R. Seynnes, C.E. Stewart, C.N. Maganaris, M.V. Narici, Effects of testosterone on skeletal muscle architecture in intermediate-frail and frail elderly men. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 65, 1215–1219 (2010)
M.A. Minetto, C. Caresio, T. Menapace, A. Hajdarevic, A. Marchini, F. Molinari, N.A. Maffiuletti, Ultrasound-based detection of low muscle mass for diagnosis of sarcopenia in older adults. PM. R. 8, 453–462 (2016)
A.J. Cruz-Jentoft, J.P. Baeyens, J.M. Bauer, Y. Boirie, T. Cederholm, F. Landi, F.C. Martin, J.P. Michel, Y. Rolland, S.M. Schneider, E. Topinková, M. Vandewoude, M. Zamboni, European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People, Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing 39, 412–423 (2010)
S.A. Studenski, K.W. Peters, D.E. Alley, P.M. Cawthon, R.R. McLean, T.B. Harris, L. Ferrucci, J.M. Guralnik, M.S. Fragala, A.M. Kenny, D.P. Kiel, S.B. Kritchevsky, M.D. Shardell, T.T. Dam, M.T. Vassileva, The FNIH sarcopenia project: rationale, study description, recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 69, 547–558 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minetto, M.A., D’Angelo, V., Arvat, E. et al. Diagnostic work-up in steroid myopathy. Endocrine 60, 219–223 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1472-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1472-5