Abstract
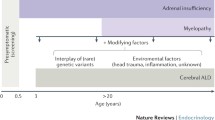
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a puzzling inborn error of metabolism with a strikingly heterogeneous clinical spectrum. All patients have mutations in the ABCD1 gene and accumulate very long chain fatty acids in all tissues. Virtually all male X-ALD patients develop adrenocortical insufficiency in childhood and progressive myelopathy and peripheral neuropathy in adulthood. A subset of male patients, however, develops a fatal cerebral demyelinating disease, cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy. Female patients also develop progressive myelopathy and peripheral neuropathy, but generally at a later age than males. They only very rarely develop adrenocortical insufficiency or cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy. This review proposes to simplify the classification of the clinical spectrum of X-ALD and reviews the largely unresolved pathophysiological mechanisms and the current treatment options.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Heubner O. Über diffuse Hirnsclerose. Charite Ann. 1897;22:298–310.
Haberfield W, Spieler F. Zur diffusen Hirn-Ruckenmarksklerose im Kindesalter. Dt Z Nervheilk. 1910;40:436–63.
Siemerling E, Creutzfeldt HG. Bronzekrankheit und sklerosierende Enzephalomyelitis. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr. 1923;68:217–44.
Schilder PF. Zur Frage der Encephalitis periaxialis diffusa (sogenannten diffusen Sklerose). Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatry. 1913;15:359–76.
Schilder PF. Die Encephalitis periaxialis diffusa (nebst Bemerkungen über die Apraxie des Lidschlusses). Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr. 1924;71:327–56.
Adams RD, Kubik CS. The morbid anatomy of the demyelinative disease. Am J Med. 1952;12(5):510–46.
Hoefnagel D, Brun A, Ingbar SH. Addison’s disease and diffuse cerebral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967;30(1):56–60.
Hoefnagel D, Van Den Noort S, Ingbar SH. Diffuse cerebral sclerosis with endocrine abnormalities in young males. Brain. 1962;85:553–68.
Fanconi A, Prader A, Isler W, Luethy F, Siebenmann R. Addison’s disease with cerebral sclerosis in childhood. A hereditary syndrome transmitted through chromosome X? Helv Paediatr Acta. 1963;18:480–501.
Blaw ME, Osterberg K, Kozak P, Nelson E. Sudanophilic leukodystrophy and adrenal cortical atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1964;11:626–31.
Crome L, Zapella M. Schilder’s Disease (Sudanophilic leucodystrophy) in five male members of one family. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963;26:431–8.
Blaw ME. Melanodermic type leukodystrophy (adreno-leukodystrophy). In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn CW, editors. Handbook of clinical neurology. New York: American Elsevier; 1970. p. 128–33.
Powers JM, Schaumburg HH. Adreno-leukodystrophy (sex-linked Schilder’s disease). A pathogenetic hypothesis based on ultrastructural lesions in adrenal cortex, peripheral nerve and testis. Am J Pathol. 1974;76(3):481–91.
Igarashi M, Schaumburg HH, Powers J, Kishmoto Y, Kolodny E, Suzuki K. Fatty acid abnormality in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurochem. 1976;26(4):851–60.
Penman RW. Addison’s disease in association with spastic paraplegia. Br Med J. 1960;1(5170):402.
Harris-Jones JN, Nixon PG. Familial Addison’s disease with spastic paraplegia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955;15(6):739–44. doi:10.1210/jcem-15-6-739.
Griffin JW, Goren E, Schaumburg H, Engel WK, Loriaux L. Adrenomyeloneuropathy: a probable variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. I. Clinical and endocrinologic aspects. Neurology. 1977;27(12):1107–13.
Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS, Spencer PS, Griffin JW, Prineas JW, et al. Adrenomyeloneuropathy: a probable variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. II. General pathologic, neuropathologic, and biochemical aspects. Neurology. 1977;27(12):1114–9.
Budka H, Sluga E, Heiss WD. Spastic paraplegia associated with Addison’s disease: adult variant of adreno-leukodystrophy. J Neurol. 1976;213(3):237–50.
Migeon BR, Moser HW, Moser AB, Axelman J, Sillence D, Norum RA. Adrenoleukodystrophy: evidence for X linkage, inactivation, and selection favoring the mutant allele in heterozygous cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981;78(8):5066–70.
Mosser J, Douar AM, Sarde CO, Kioschis P, Feil R, Moser H, et al. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature. 1993;361(6414):726–30. doi:10.1038/361726a0.
Mosser J, Lutz Y, Stoeckel ME, Sarde CO, Kretz C, Douar AM, et al. The gene responsible for adrenoleukodystrophy encodes a peroxisomal membrane protein. Hum Mol Genet. 1994;3(2):265–71.
Moser HW, Smith KD, Watkins PA, Powers J, Moser AB. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. In: Scriver CR, Sly WS, Childs B, Beaudet AL, Valle D, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, editors. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2001. p. 3257–301.
van Geel BM, Bezman L, Loes DJ, Moser HW, Raymond GV. Evolution of phenotypes in adult male patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(2):186–94.
Engelen M, Kemp S, de Visser M, van Geel BM, Wanders RJ, Aubourg P, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): clinical presentation and guidelines for diagnosis, follow-up and management. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7:51. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-51. This review is especially useful to clinicians.
Dubey P, Raymond GV, Moser AB, Kharkar S, Bezman L, Moser HW. Adrenal insufficiency in asymptomatic adrenoleukodystrophy patients identified by very long-chain fatty acid screening. J Pediatr. 2005;146(4):528–32. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.10.067.
Assies J, Gooren LJ, Van Geel B, Barth PG. Signs of testicular insufficiency in adrenomyeloneuropathy and neurologically asymptomatic X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: a retrospective study. Int J Androl. 1997;20(5):315–21.
van Geel BM, Koelman JH, Barth PG, de Visser Ongerboer BW. Peripheral nerve abnormalities in adrenomyeloneuropathy: a clinical and electrodiagnostic study. Neurology. 1996;46(1):112–8.
Horn MA, Nilsen KB, Jorum E, Mellgren SI, Tallaksen CM. Small nerve fiber involvement is frequent in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurology. 2014;82(19):1678–83. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000415.
Raymond GV, Seidman R, Monteith TS, Kolodny E, Sathe S, Mahmood A, et al. Head trauma can initiate the onset of adreno-leukodystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 2010;290(1–2):70–4. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.11.005.
Kemp S, Berger J, Aubourg P. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical, metabolic, genetic and pathophysiological aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(9):1465–74. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.03.012.
Van der Knaap MS, Valk J. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. In: Heilmann U, editor. Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders. Berlin: Springer; 2005. p. 176–90.
Engelen M, Barbier M, Dijkstra IM, Schur R, de Bie RM, Verhamme C, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in women: a cross-sectional cohort study. Brain. 2014;137(3):693–706. doi:10.1093/brain/awt361. This is a large prospective cohort study that systematically describes the phenotype of women with X-ALD.
El-Deiry SS, Naidu S, Blevins LS, Ladenson PW. Assessment of adrenal function in women heterozygous for adrenoleukodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(3):856–60. doi:10.1210/jcem.82.3.3802.
Jangouk P, Zackowski KM, Naidu S, Raymond GV. Adrenoleukodystrophy in female heterozygotes: underrecognized and undertreated. Mol Genet Metab. 2012;105(2):180–5. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.11.001.
Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS, Suzuki K, Richardson Jr EP. Adrenoleukodystrophy. A clinical and pathological study of 17 cases. Arch Neurol. 1975;32(9):577–91.
Musolino PL, Rapalino O, Caruso P, Caviness VS, Eichler FS. Hypoperfusion predicts lesion progression in cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Brain. 2012;135(9):2676–83. doi:10.1093/brain/aws206.
Phillips JP, Lockman LA, Shapiro EG, Blazar BR, Loes DJ, Moser HW, et al. CSF findings in adrenoleukodystrophy: correlation between measures of cytokines, IgG production, and disease severity. Pediatr Neurol. 1994;10(4):289–94.
Schaumburg HH, Richardson EP, Johnson PC, Cohen RB, Powers JM, Raine CS. Schilder’s disease. Sex-linked recessive transmission with specific adrenal changes. Arch Neurol. 1972;27(5):458–60.
Hoftberger R, Kunze M, Weinhofer I, Aboul-Enein F, Voigtlander T, Oezen I, et al. Distribution and cellular localization of adrenoleukodystrophy protein in human tissues: implications for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurobiol Dis. 2007;28(2):165–74. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.07.007.
Moser HW, Moser AB, Frayer KK, Chen W, Schulman JD, O’Neill BP, et al. Adrenoleukodystrophy: increased plasma content of saturated very long chain fatty acids. Neurology. 1981;31(10):1241–9.
Singh I, Moser HW, Moser AB, Kishimoto Y. Adrenoleukodystrophy: impaired oxidation of long chain fatty acids in cultured skin fibroblasts an adrenal cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981;102(4):1223–9.
Singh I, Moser AE, Moser HW, Kishimoto Y. Adrenoleukodystrophy: impaired oxidation of very long chain fatty acids in white blood cells, cultured skin fibroblasts, and amniocytes. Pediatr Res. 1984;18(3):286–90. doi:10.1203/00006450-198403000-00016.
Kemp S, Valianpour F, Mooyer PA, Kulik W, Wanders RJ. Method for measurement of peroxisomal very-long-chain fatty acid beta-oxidation in human skin fibroblasts using stable-isotope-labeled tetracosanoic acid. Clin Chem. 2004;50(10):1824–6. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.038539.
Kemp S, Mooyer PA, Bolhuis PA, van Geel BM, Mandel JL, Barth PG, et al. ALDP expression in fibroblasts of patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1996;19(5):667–74.
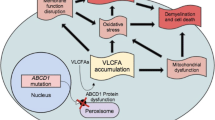
Wiesinger C, Kunze M, Regelsberger G, Forss-Petter S, Berger J. Impaired very long-chain acyl-CoA beta-oxidation in human X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy fibroblasts is a direct consequence of ABCD1 transporter dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(26):19269–79. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.445445.
Tsuji S, Sano T, Ariga T, Miyatake T. Increased synthesis of hexacosanoic acid (C23:0) by cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) and adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN). J Biochem. 1981;90(4):1233–6.
Kishimoto Y, Moser HW, Kawamura N, Platt M, Pallante SL, Fenselau C. Adrenoleukodystrophy: evidence that abnormal very long chain fatty acids of brain cholesterol esters are of exogenous origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980;96(1):69–76.
Kemp S, Valianpour F, Denis S, Ofman R, Sanders RJ, Mooyer P, et al. Elongation of very long-chain fatty acids is enhanced in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Mol Genet Metab. 2005;84(2):144–51. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.09.015.
Ofman R, Dijkstra IM, van Roermund CW, Burger N, Turkenburg M, van Cruchten A, et al. The role of ELOVL1 in very long-chain fatty acid homeostasis and X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. EMBO Mol Med. 2010;2(3):90–7. doi:10.1002/emmm.201000061.
Engelen M, Schackmann MJ, Ofman R, Sanders RJ, Dijkstra IM, Houten SM, et al. Bezafibrate lowers very long-chain fatty acids in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy fibroblasts by inhibiting fatty acid elongation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2012;35(6):1137–45. doi:10.1007/s10545-012-9471-4.
Engelen M, Tran L, Ofman R, Brennecke J, Moser AB, Dijkstra IM, et al. Bezafibrate for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41013. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041013.
Kemp S, Theodoulou FL, Wanders RJ. Mammalian peroxisomal ABC transporters: from endogenous substrates to pathology and clinical significance. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164(7):1753–66. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01435.x.
Powers JM, Schaumburg HH, Johnson AB, Raine CS. A correlative study of the adrenal cortex in adreno-leukodystrophy—evidence for a fatal intoxication with very long chain saturated fatty acids. Investig Cell Pathol. 1980;3(4):353–76.
Powers JM, Moser HW, Moser AB, Ma CK, Elias SB, Norum RA. Pathologic findings in adrenoleukodystrophy heterozygotes. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987;111(2):151–3.
Powers JM, DeCiero DP, Ito M, Moser AB, Moser HW. Adrenomyeloneuropathy: a neuropathologic review featuring its noninflammatory myelopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000;59(2):89–102.
Powers JM, DeCiero DP, Cox C, Richfield EK, Ito M, Moser AB, et al. The dorsal root ganglia in adrenomyeloneuropathy: neuronal atrophy and abnormal mitochondria. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2001;60(5):493–501.
Whitcomb RW, Linehan WM, Knazek RA. Effects of long-chain, saturated fatty acids on membrane microviscosity and adrenocorticotropin responsiveness of human adrenocortical cells in vitro. J Clin Investig. 1988;81(1):185–8. doi:10.1172/JCI113292.
Hein S, Schonfeld P, Kahlert S, Reiser G. Toxic effects of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy-associated, very long chain fatty acids on glial cells and neurons from rat hippocampus in culture. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17(12):1750–61. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn066.
Galino J, Ruiz M, Fourcade S, Schluter A, Lopez-Erauskin J, Guilera C, et al. Oxidative damage compromises energy metabolism in the axonal degeneration mouse model of X-adrenoleukodystrophy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(8):2095–107. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3877.
Powers JM, Pei Z, Heinzer AK, Deering R, Moser AB, Moser HW, et al. Adreno-leukodystrophy: oxidative stress of mice and men. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64(12):1067–79.
Lopez-Erauskin J, Galino J, Bianchi P, Fourcade S, Andreu AL, Ferrer I, et al. Oxidative stress modulates mitochondrial failure and cyclophilin D function in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Brain. 2012;135(12):3584–98. doi:10.1093/brain/aws292.
Fourcade S, Lopez-Erauskin J, Galino J, Duval C, Naudi A, Jove M, et al. Early oxidative damage underlying neurodegeneration in X-adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17(12):1762–73. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn085.
Pujol A, Hindelang C, Callizot N, Bartsch U, Schachner M, Mandel JL. Late onset neurological phenotype of the X-ALD gene inactivation in mice: a mouse model for adrenomyeloneuropathy. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11(5):499–505.
Eichler FS, Ren JQ, Cossoy M, Rietsch AM, Nagpal S, Moser AB, et al. Is microglial apoptosis an early pathogenic change in cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy? Ann Neurol. 2008;63(6):729–42. doi:10.1002/ana.21391.
Lu JF, Lawler AM, Watkins PA, Powers JM, Moser AB, Moser HW, et al. A mouse model for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(17):9366–71.
Forss-Petter S, Werner H, Berger J, Lassmann H, Molzer B, Schwab MH, et al. Targeted inactivation of the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene in mice. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50(5):829–43.
Kobayashi T, Shinnoh N, Kondo A, Yamada T. Adrenoleukodystrophy protein-deficient mice represent abnormality of very long chain fatty acid metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;232(3):631–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6340.
Pujol A, Ferrer I, Camps C, Metzger E, Hindelang C, Callizot N, et al. Functional overlap between ABCD1 (ALD) and ABCD2 (ALDR) transporters: a therapeutic target for X-adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(23):2997–3006. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh323.
Kemp S, Pujol A, Waterham HR, van Geel BM, Boehm CD, Raymond GV, et al. ABCD1 mutations and the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutation database: role in diagnosis and clinical correlations. Hum Mutat. 2001;18(6):499–515. doi:10.1002/humu.1227.
Asheuer M, Bieche I, Laurendeau I, Moser A, Hainque B, Vidaud M, et al. Decreased expression of ABCD4 and BG1 genes early in the pathogenesis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(10):1293–303. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi140.
Miller WP, Rothman SM, Nascene D, Kivisto T, DeFor TE, Ziegler RS, et al. Outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy: the largest single-institution cohort report. Blood. 2011;118(7):1971–8. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-01-329235.
Loes DJ, Hite S, Moser H, Stillman AE, Shapiro E, Lockman L, et al. Adrenoleukodystrophy: a scoring method for brain MR observations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994;15(9):1761–6.
Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, Veres G, Schmidt M, Kutschera I, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Science. 2009;326(5954):818–23. doi:10.1126/science.1171242.
Aubourg P, Adamsbaum C, Lavallard-Rousseau MC, Rocchiccioli F, Cartier N, Jambaque I, et al. A two-year trial of oleic and erucic acids (“Lorenzo’s oil”) as treatment for adrenomyeloneuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(11):745–52. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309093291101.
van Geel BM, Assies J, Haverkort EB, Koelman JH, Verbeeten Jr B, Wanders RJ, et al. Progression of abnormalities in adrenomyeloneuropathy and neurologically asymptomatic X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy despite treatment with “Lorenzo’s oil”. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(3):290–9.
Horn MA, Erichsen MM, Wolff AS, Mansson JE, Husebye ES, Tallaksen CM, et al. Screening for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy among adult men with Addison’s disease. Clin Endocrinol. 2013;79(3):316–20. doi:10.1111/cen.12159.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Marc Engelen, Stephan Kemp and Bwee-Tien Poll-The declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Demyelinating Disorders
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelen, M., Kemp, S. & Poll-The, BT. X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 14, 486 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-014-0486-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-014-0486-0