Abstract
Background
Intragastric balloons have been used since 1985 to treat obesity, but an evidence-based systematic review had not been previously performed. The objective of this study is to determine the safety, efficacy, and effectiveness of the most widely used balloon, BioEnterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB®), to treat obesity.
Methods
Systematic literature review of Medline, Embase, and other information sources from inception to March 2006. The quality of selected studies was assessed. Meta-analysis of weighted mean difference was made using the inverse variance method.
Results
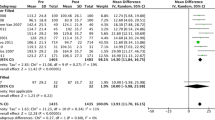
We pooled 15 articles (3,608 patients) to estimate BIBs® effectiveness. The estimates for weight lost at balloon removal for BIB® were the following: 14.7 kg, 12.2% of initial weight, 5.7 kg/m2, and 32.1% of excess weight. However, data were scant after balloon removal. Yet, efficacy at balloon removal was estimated with a meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials (75 patients) that compared balloon versus placebo, indicating the balloon group lost more weight than the placebo group. These differences in weight lost were 6.7 kg, 1.5% of initial weight, 3.2 kg/m2, and 17.6% of excess weight. Regarding BIB® safety, the majority of complications were mild and the early removal rate was 4.2%.
Conclusion
The use of the BIB®, within a multidisciplinary weight management program, is a short-term effective treatment to lose weight, but it is not yet possible to verify its capacity to maintain the weight lost over a long period of time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandes M, Atallah AN, Soares BGO, et al. Baloes Intragástricos para pessoas com obesidade. Cochrane Library. Oxford: Update Software Ltd.; 2006.
National Institutes of Health, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, North American Association for the Study of Obesity. Practical Guide to the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. NIH Publication no. 00-4084. Bethesda: NIH; 2000. p. 94.
Meshkinpour H, Hsu D, Farivar S. Effect of gastric bubble as a weight reduction device: a controlled, crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:589–92.
Schapiro M, Benjamin S, Blackburn G, et al. Obesity and the gastric balloon: a comprehensive workshop. Tarpon Springs, Florida, March 19–21, 1987. Gastrointest Endosc. 1987;33:323–7.
Allison C. Intragastric balloons: a temporary treatment for obesity. Issues in emerging health technologies, no. 79. Canadian Coordinating Office for Health Technology Assessment, Ottawa; 2006.
Forestieri P, De Palma GD, Formato A, et al. Heliosphere(R) bag in the treatment of severe obesity: preliminary experience. Obes Surg. 2006;16:635–7.
Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 4.2.6. In: The Cochrane Library. Issue 4, ed. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.; 2006.
Jadad AR. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12.
Khan KS, Riet G, Glanville J, et al. Undertaking systematic reviews of research on effectiveness. CRD’s guidance for those carrying out or commissioning reviews. no. 4. York: NHS Center for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2001.
Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine. Quality filters [On line]. Web of the centre for evidence-based medicine, 23-10-2006. http://www.cebm.net/levels_of_evidence.asp.
Schwartz D. Métodos estadísticos para médicos y biólogos. Barcelona: Editorial Herder; 1991. p. 385.
Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, et al. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta-analyses can provide accurate results. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59:7–10.
Angrisani L, Lorenzo M, Borrelli V, et al. Is bariatric surgery necessary after intragastric balloon treatment. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1135–7.
Busetto L, Segato G, De Luca M, et al. Preoperative weight loss by intragastric balloon in super-obese patients treated with laparoscopic gastric banding: a case-control study. Obes Surg. 2004;14:671–6.
Busetto L, Enzi G, Inelmen EM, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in morbid obesity: effects of intragastric balloon. Chest. 2005;128:618–23.
Doldi SB, Micheletto G, Perrini MN, et al. Intragastric balloon: another option for treatment of obesity and morbid obesity. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:294–7.
Francica G, Giardiello C, Iodice G, et al. Ultrasound as the imaging method of choice for monitoring the intragastric balloon in obese patients: normal findings, pitfalls and diagnosis of complications. Obes Surg. 2004;14:833–7.
Galloro G, De Palma GD, Catanzano C, et al. Preliminary endoscopic technical report of a new silicone intragastric balloon in the treatment of morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 1999;9:68–71.
Mathus-Vliegen EM, Tytgat GN. Gastro-oesophageal reflux in obese subjects: influence of overweight, weight loss and chronic gastric balloon distension. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:1246–52.
Krakamp B, Leidig P, Gehmlich D, et al. Der Magenvolumen-Reduzierungsballon zur Gewichtsreduktion: Welche Berechtigung hat diese umstrittene Methode? Zentralbl Chir. 1997;122:349–56.
Rydzewska G, Milewski J. Balony dozoladkowe-nowa nadzieja w leczeniu otylosci? Pol Merkuriusz Lek. 2004;17 Suppl 1:114–6.
Bonazzi P, Petrelli MD, Lorenzini I, et al. Gastric emptying and intragastric balloon in obese patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2005;9:15–21.
Alfalah H, Philippe B, Ghazal F, et al. Intragastric balloon for preoperative weight reduction in candidates for laparoscopic gastric bypass with massive obesity. Obes Surg. 2006;16:147–50.
Al Momen A, El Mogy I. Intragastric balloon for obesity: a retrospective evaluation of tolerance and efficacy. Obes Surg. 2005;15:101–5.
Carbonelli MG, Fusco MA, Cannistra F, et al. Body composition modification in obese patients treated with intragastric balloon. Acta Diabetol. 2003;40 Suppl 1:S261–2.
Evans JD, Scott MH. Intragastric balloon in the treatment of patients with morbid obesity. Br J Surg. 2001;88:1245–8.
Genco A, Bruni T, Doldi SB, et al. BioEnterics intragastric balloon: the italian experience with 2,515 patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1161–4.
Herve J, Wahlen CH, Schaeken A, et al. What becomes of patients one year after the intragastric balloon has been removed? Obes Surg. 2005;15:864–70.
Hodson RM, Zacharoulis D, Goutzamani E, et al. Management of obesity with the new intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2001;11:327–9.
Loffredo A, Cappuccio M, De Luca M, et al. Three years experience with the new intragastric balloon, and a preoperative test for success with restrictive surgery. Obes Surg. 2001;11:3.
Mion F, Napoleon B, Roman S, et al. Effects of intragastric balloon on gastric emptying and plasma ghrelin levels in non-morbid obese patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15:510–6.
Roman S, Napoleon B, Mion F, et al. Intragastric balloon for “non-morbid” obesity: a retrospective evaluation of tolerance and efficacy. Obes Surg. 2004;14:539–44.
Sallet JA, Marchesini JB, Paiva DS, et al. Brazilian multicenter study of the intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2004;14:991–8.
Sánchez B, Espinós J, Turró J, et al. Tratamiento y seguimiento nutricional en pacientes con balón intragástrico. Revista Española de Nutrición Comunitaria. 2005;11:152–5.
Totté E, Hendrickx L, Pauwels M, et al. Weight reduction by means of intragastric device: experience with the bioenterics intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2001;11:519–23.
Weiner R, Gutberlet H, Bockhorn H. Preparation of extremely obese patients for laparoscopic gastric banding by gastric-balloon therapy. Obes Surg. 1999;9:261–4.
Genco A, Cipriano M, Bacci V, et al. BioEnterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB): a short-term, double-blind, randomised, controlled, crossover study on weight reduction in morbidly obese patients. Int J Obes. 2006;30:129–33.
Mathus-Vliegen EM, Tytgat GN. Intragastric balloon for treatment-resistant obesity: safety, tolerance, and efficacy of 1-year balloon treatment followed by a 1-year balloon-free follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:19–27.
Maggard MA, Shugarman LR, Suttorp M, et al. Meta-analysis: surgical treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:547–59.
Goldstein DJ. Beneficial health effects of modest weight loss. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1992;16:397–415.
Li Z, Maglione M, Tu W, et al. Meta-analysis: pharmacologic treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:532–46.
McTigue KM, Hess R, Ziouras J. Obesity in older adults: a systematic review of the evidence for diagnosis and treatment. Obesity. 2006;14:1485–97.
Tosetti C, Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V, et al. Gastric emptying of solids in morbid obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996;20:200–5.
Geliebter A, Melton PM, McCray RS, et al. Clinical trial of silicone-rubber gastric balloon to treat obesity. Int J Obes. 1991;15:259–66.
Acknowledgment
We thank David Peck for his structural review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imaz, I., Martínez-Cervell, C., García-Álvarez, E.E. et al. Safety and Effectiveness of the Intragastric Balloon for Obesity. A Meta-Analysis. OBES SURG 18, 841–846 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9331-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9331-8