Abstract
Purpose
Bone metabolism disorder is often associated with cardiovascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Sclerostin, a novel candidate protein, has been identified to be involved in the bone–vascular axis. The aims of the current investigation were to assess vessel sclerostin expression and its relationship with circulating sclerostin levels.
Methods
A cross-sectional observational study was conducted from January 2012 to December 2014. Thirty-two predialysis patients with CKD stage 5 who received arteriovenous fistula (AVF) operations were enrolled in this study. Radial arteries were collected and paraffin-embedded during the AVF operation, followed by immunohistochemical staining for sclerostin expression. In addition, serum sclerostin levels were measured by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
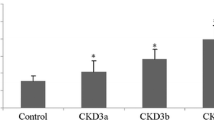
The prevalence of positive sclerostin staining in the radial arteries was 56.25%. Sclerostin expression was localized in the artery media layer. Serum sclerostin levels in patients with positive sclerostin expression were much higher than in those with negative expression (p = 0.018). Multivariate logistic regression analyses including potential confounders as age, gender, systolic blood pressure (BP), diastolic BP, serum sclerostin, corrected calcium (Ca), phosphate (P), Ca × P product, alkaline phosphatase, intact parathyroid hormone, and estimated glomerular filtration rate showed that only serum sclerostin levels were closely related to vessel sclerostin expression (p = 0.025). The area under the curve of serum sclerostin levels for predicting positive vessel sclerostin expression was 0.742 with 61.1% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity (p = 0.008). The cutoff point for vessel sclerostin expression of serum sclerostin was 1591.53 pg/mL.
Conclusions
Positive expression of sclerostin in the radial artery media layer was related to high serum sclerostin levels. Sclerostin may act as both a local and systemic regulator involved in vascular calcification.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russo D, Corrao S, Battaglia Y et al (2011) Progression of coronary artery calcification and cardiac events in patients with chronic renal disease not receiving dialysis. Kidney Int 80(1):112–118
Gauthier-Bastien A, Ung RV, Larivière R et al (2014) Vascular remodeling and media calcification increases arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Hypertens 36(3):173–180
Davies MR, Hruska KA (2001) Pathophysiological mechanisms of vascular calcification in end-stage renal disease. Pathophysiological mechanisms of vascular calcification in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 60(2):472–479
Demer LL, Tintut Y (2008) Vascular calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation 117(22):2938–2948
Gaudio A, Privitera F, Battaglia K et al (2012) Sclerostin levels associated with inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling and reduced bone turnover in type 2diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(10):3744–3750
Brandenburg VM, Kramann R, Koos R et al (2013) Relationship between sclerostin and cardiovascular calcification in hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol 14:219
Kramann R, Brandenburg VM, Schurgers LJ et al (2013) Novel insights into osteogenesis and matrix remodelling associated with calcific uraemic arteriolopathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:856–868
Zhu D, Mackenzie NC, Millán JL et al (2011) The appearance and modulation of osteocyte marker expression during calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19595
Qureshi AR, Olauson H, Witasp A et al (2015) Increased circulating sclerostin levels in end-stage renal disease predict biopsy-verified vascular medial calcification and coronary artery calcification. Kidney Int 88(6):1356–1364
Kanbay M, Siriopol D, Saglam M et al (2014) Serum sclerostin and adverse outcomes in nondialyzed chronic kidney disease patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(10):E1854–E1861
Morena M, Jaussent I, Dupuy AM et al (2015) Osteoprotegerin and sclerostin in chronic kidney disease prior to dialysis: potential partners in vascular calcifications. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(8):1345–1356
Pelletier S, Confavreux CB, Haesebaert J et al (2015) Serum sclerostin: the missing link in the bone-vessel cross-talk in hemodialysis patients? Osteoporos Int 26(8):2165–2174
Claes KJ, Viaene L, Heye S et al (2013) Sclerostin: another vascular calcification inhibitor? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(8):3221–3228
Balcı M, Kırkpantur A, Turkvatan A et al (2015) Sclerostin as a new key player in arteriovenous fistula calcification. Herz 40(2):289–297
Kirkpantur A, Balci M, Turkvatan A et al (2015) Serum sclerostin levels, arteriovenous fistula calcification and 2-years all-cause mortality in prevalent hemodialysis patients. Nefrologia 36(1):24–32
Delanaye P, Krzesinski JM, Warling X et al (2014) Clinical and biological determinants of sclerostin plasma concentration in hemodialysis patients. Nephron Clin Pract 128(1–2):127–134
Yang CY, Chang ZF, Chau YP et al (2015) Circulating Wnt/β-catenin signalling inhibitors and uraemic vascular calcifications. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(8):1356–1363
Evenepoel P, Goffin E, Meijers B et al (2015) Sclerostin serum levels and vascular calcification progression in prevalent renal transplant recipients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(12):4669–4676
Lee YT, Ng HY, Chiu TT et al (2016) Association of bone-derived biomarkers with vascular calcification in chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin Chim Acta 452:38–43
Jean G, Chazot C, Bresson E et al (2016) High serum sclerostin levels are associated with a better outcome in haemodialysis patients. Nephron 132(3):181–190
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH et al (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150(9):604–612
Drake MT, Srinivasan B, Mödder UI et al (2010) Effects of parathyroid hormone treatment on circulating sclerostin levels in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(11):5056–5062
Cejka D, Marculescu R, Kozakowski N et al (2014) Renal elimination of sclerostin increases with declining kidney function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(1):248–255
Kanbay M, Solak Y, Siriopol D et al (2016) Sclerostin, cardiovascular disease and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 48(12):2029–2042
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Youth Talent Programme of Changzhou Government Healthy Service (No. QN201402). The authors thank Zhong Xue for making substantial contributions to data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Yang, M., Li, M. et al. Radial artery sclerostin expression in chronic kidney disease stage 5 predialysis patients: a cross-sectional observational study. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1433–1437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1604-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1604-0