Abstract
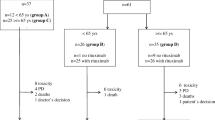
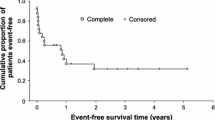
Background A systemic and intraventricular polychemotherapy regimen (the Bonn protocol) without radiotherapy resulted in durable responses in 75% of patients <60 years with primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL), but was complicated by a high rate of Ommaya reservoir infections. Here, the efficacy and toxicity of this regimen without intraventricular treatment was evaluated in PCNSL. Patients and methods From August 2003 to November 2005, 18 patients with PCNSL <60 years (median age, 53 years) were treated in a phase II trial with a high-dose methotrexate (MTX; cycles 1, 2, 4 and 5) and cytarabine (Ara-C; cycles 3 and 6) based systemic therapy including dexamethasone, vinca-alkaloids, ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide. Results Study accrual was prematurely stopped in November 2005 due to a high rate of early relapses. Seventeen of 18 patients were assessable for response: nine (53%) achieved complete response (CR), two (12%) complete response/unconfirmed (CRu) and two (12%) partial response (PR); four (24%) showed progressive disease (PD). One treatment was stopped due to toxicity. Median follow-up was 23 months, median response duration was only 10 months in responding patients, and median time to treatment failure (TTF) was 8 months in the whole group. Median overall survival (OS) has not been reached. Systemic toxicity was mainly hematologic. Conclusions In PCNSL patients <60 years, polychemotherapy without intraventricular treatment results in a high response rate, but is associated with early relapses in the majority of cases. This is in contrast to the results achieved with the same protocol but with intraventricular treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States (2005) Statistical report: primary brain tumors in the United States. Chicago, IL
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J et al (2000) Lymphoma classification—from controversy to consensus: the REAL and WHO Classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Ann Oncol 11(Suppl 1):3–10. doi:10.1023/A:1008383406103
Pels H, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Glasmacher A et al (2003) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: results of a pilot and phase II study of systemic and intraventricular chemotherapy with deferred radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 21:4489–4495. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.04.056
Ferreri AJ, Reni M, Pasini F et al (2002) A multicenter study of treatment of primary CNS lymphoma. Neurology 58:1513–1520
Khan RB, Shi W, Thaler HT et al (2002) Is intrathecal methotrexate necessary in the treatment of primary CNS lymphoma? J Neurooncol 58:175–178. doi:10.1023/A:1016077907952
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H et al (1994) A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 84:1361–1392
Gatter KCWR (2001) Diffuse large cell lymphoma. IARC Press, Lyon, France
Abrey LE, Batchelor TT, Ferreri AJ et al (2005) Report of an international workshop to standardize baseline evaluation and response criteria for primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23:5034–5043. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.13.524
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr et al (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
World Health Organization (1979) WHO handbook for reporting results of cancer treatment. In: WHO offset publication no 48. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, pp 14–21
Ferreri AJ, Blay JY, Reni M et al (2003) Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 21:266–272. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.09.139
Abrey LE, Ben-Porat L, Panageas KS et al (2006) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J Clin Oncol 24:5711–5715. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2941
Kaplan ELMP (1958) Non parametric estimations from complete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:163–179. doi:10.2307/2281868
Soussain C, Hoang-Xuan K, Levy V (2004) Results of intensive chemotherapy followed by hematopoietic stem-cell rescue in 22 patients with refractory or recurrent primary CNS lymphoma or intraocular lymphoma. Bull Cancer 91:189–192
Batchelor T, Carson K, O’Neill A et al (2003) Treatment of primary CNS lymphoma with methotrexate and deferred radiotherapy: a report of NABTT 96-07. J Clin Oncol 21:1044–1049. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.03.036
Herrlinger U, Kuker W, Uhl M et al (2005) NOA-03 trial of high-dose methotrexate in primary central nervous system lymphoma: final report. Ann Neurol 57:843–847. doi:10.1002/ana.20495
Guha-Thakurta N, Damek D, Pollack C et al (1999) Intravenous methotrexate as initial treatment for primary central nervous system lymphoma: response to therapy and quality of life of patients. J Neurooncol 43:259–268. doi:10.1023/A:1006210703827
Hoang-Xuan K, Taillandier L, Chinot O et al (2003) Chemotherapy alone as initial treatment for primary CNS lymphoma in patients older than 60 years: a multicenter phase II study (26952) of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group. J Clin Oncol 21:2726–2731. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.11.036
DeAngelis LM, Seiferheld W, Schold SC et al (2002) Combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study 93-10. J Clin Oncol 20:4643–4648. doi:10.1200/JCO.2002.11.013
O’Brien P, Roos D, Pratt G et al (2000) Phase II multicenter study of brief single-agent methotrexate followed by irradiation in primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 18:519–526
Abrey LE, Yahalom J, DeAngelis LM (2000) Treatment for primary CNS lymphoma: the next step. J Clin Oncol 18:3144–3150
Bessell EM, Lopez-Guillermo A, Villa S et al (2002) Importance of radiotherapy in the outcome of patients with primary CNS lymphoma: an analysis of the CHOD/BVAM regimen followed by two different radiotherapy treatments. J Clin Oncol 20:231–236. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.1.231
Poortmans PM, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Haaxma-Reiche H et al (2003) High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy followed by consolidating radiotherapy in non-AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lymphoma Group Phase II Trial 20962. J Clin Oncol 21:4483–4488. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.03.108
Batchelor T (2005) Neuro-oncology update: 2005. Curr Opin Neurol 18:631. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000189873.92362.dc
Batchelor T, Loeffler JS (2006) Primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 24:1281–1288. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.8819
Harder H, Holtel H, Bromberg JE et al (2004) Cognitive status and quality of life after treatment for primary CNS lymphoma. Neurology 62:544–547
Fisher B, Seiferheld W, Schultz C et al (2005) Secondary analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group study (RTOG) 9310: an intergroup phase II combined modality treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neurooncol 74:201–205. doi:10.1007/s11060-004-6596-9
O’Brien PC, Roos DE, Pratt G et al (2006) Combined-modality therapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma: long-term data from a phase II multicenter study (Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:408–413. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.07.958
Correa DD, DeAngelis LM, Shi W et al (2004) Cognitive functions in survivors of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurology 62:548–555
Fliessbach K, Helmstaedter C, Urbach H et al (2005) Neuropsychological outcome after chemotherapy for primary CNS lymphoma: a prospective study. Neurology 64:1184–1188
Neuwelt EA, Guastadisegni PE, Varallyay P et al (2005) Imaging changes and cognitive outcome in primary CNS lymphoma after enhanced chemotherapy delivery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:258–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Pels and A. Juergens contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pels, H., Juergens, A., Glasmacher, A. et al. Early relapses in primary CNS lymphoma after response to polychemotherapy without intraventricular treatment: results of a phase II study. J Neurooncol 91, 299–305 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9712-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9712-4