Abstract
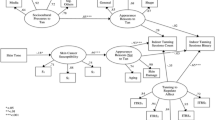
UV exposure via sunbathing and utilization of sun lamps and tanning beds are considered important risk factors for the development of skin cancer. Psychosocial models of UV exposure are often based on theories of health behavior, but theory from the body image field can be useful as well. The current study examines models that prospectively predict sunbathing and indoor tanning behaviors using constructs and interrelationships derived from the tripartite theory of body image, theory of reasoned action, health belief model, revised protection motivation theory, and a proposed integration of several health behavior models. The results generally support a model in which intentions mediate the relationship between appearance attitudes and tanning behaviors, appearance reasons to tan and intentions mediate the relationship between sociocultural influences and tanning behaviors, and appearance reasons not to tan and intentions mediate the role of perceived threat on behaviors. The implications of these findings are considered.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kuhl & J. Beckman (Eds.), Action-control: From cognition to behavior (pp. 11–39). Heidelberg, Germany: Springer.
Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
American Cancer Society. (2007). Cancer facts and figures. Atlanta, GA: Author.
Arbuckle, J. L. (1996). Full information estimation in the presence of incomplete data. In G. A. Marcoulides & R. E. Schumacker (Eds.), Advanced structural equation modeling (pp. 243–277). Mahweh, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2005). Amos 6.0 user’s guide. Spring House, PA: Amos Development Corporation.
Bollen, K., & Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: A structural equation perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 110, 305–314.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1987). Single sample cross-validation indices of covariance structures. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 24, 445–455.
Cafri, G., Thompson, J. K., & Jacobsen, P. (2006a). Appearance reasons for tanning mediate the relationship between media influence and UV exposure and protection. Archives of Dermatology, 142, 1067–1069.
Cafri, G., Thompson, J. K., Roehrig, M., Rojas, A., Sperry, S., Jacobsen, P., et al. (2008). Appearance motives to tan and not tan: Evidence for validity and reliability of a new scale. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 35, 209–220.
Cafri, G., Thompson, J. K., Roehrig, M., van den Berg, P., Jacobsen, P. B., & Stark, S. (2006b). An investigation of appearance motives for tanning: The development and evaluation of the physical appearance reasons for tanning scale (PARTS) and its relation to sunbathing and indoor tanning intentions. Body Image, 3, 199–209.
Cafri, G., Yamamiya, Y., Brannick, M., & Thompson, J. K. (2005). The impact of thin-ideal internalization on body dissatisfaction: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 12, 421–433.
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., & Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological Methods, 1, 16–29.
Davis, K. J., Cokkinides, V. E., Weinstock, M. A., O’Connell, M. C., & Wingo, P. A. (2002). Summer sunburn and sun exposure among US youths ages 11 to 18: National prevalence and associated factors. Pediatrics, 110(2), 7–35.
Demko, C. A., Borawski, E. A., Debanne, S. M., Cooper, K. D., & Stange, K. C. (2003). Use of indoor tanning facilities by white adolescents in the United States. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, 157, 854–860.
Fishbein, M. (2000). The role of theory in HIV prevention. Aids Care, 12, 273–278.
Fitzpatrick, T. B. (1988). The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Archives of Dermatology, 124, 869–871.
Glanz, K., & Mayer, J. A. (2005). Reducing ultraviolet radiation exposure to prevent skin cancer: Methodology and measurement. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 29, 131–142.
Goldsmith, M. F. (1987). Paler is better, say skin cancer fighters. Journal of the American Medical Association, 257, 893–894.
Hillhouse, J. J., Adler, C. M., Drinnon, J., & Turrisi, R. (1997). Application of Azjen’s theory of planned behavior to predict sunbathing, tanning salon use, and sunscreen use intentions and behaviors. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 20, 365–378.
Hillhouse, J. J., Stair, A. W., & Adler, C. M. (1996). Predictors of sunbathing and sunscreen use in college undergraduates. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 19, 543–560.
Hillhouse, J. J., & Turrisi, R. (2002). An examination of the efficacy of an appearance-focused intervention to reduce UV exposure. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 25, 395–409.
Hillhouse, J., Turrisi, R., Holwiski, F., & McVeigh, S. (1999). An examination of psychological variables relevant to artificial tanning tendencies. Journal of Health Psychology, 4, 507–516.
Hillhouse, J. J., Turrisi, R., & Kastner, M. (2000). Modeling tanning salon behavioral tendencies using appearance motivation, self-monitoring, and the theory of planned behavior. Health Education Review, 15, 405–414.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to underparameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3, 424–453.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Jackson, K. M., & Aiken, L. S. (2000). A psychosocial model of sun protection and sunbathing in young women: The impact of health beliefs, attitudes, norms, and self-efficacy for sun protection. Health Psychology, 19, 469–478.
Jackson, K. M., & Aiken, L. S. (2006). Evaluation of a multi-component appearance-based sun-protective intervention for young women: Uncovering the mechanisms of program efficacy. Health Psychology, 25, 34–46.
Jones, J. L., & Leary, M. R. (1994). Effects of appearance-based admonitions against sun exposure on tanning intentions in young adults. Health Psychology, 13, 86–90.
Keery, H., van den Berg, P., & Thompson, J. K. (2004). An evaluation of the Tripartite Influence Model of body dissatisfaction and eating disturbance with adolescent girls. Body Image, 1, 237–251.
Kim, K. H., & Bentler, P. M. (2002). Tests of homogeneity of means and covariance matrices for multivariate incomplete data. Psychometrika, 67, 609–624.
MacCallum, R. C., Browne, M. W., & Sugawara, H. M. (1996). Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structural modeling. Psychological Methods, 1, 130–149.
Mahler, H. I., Kulik, J. A., Gibbons, F. X., Gerrard, M., & Harrell, J. (2003). Effects of appearance-based interventions on sun protection intentions and self-reported behaviors. Health Psychology, 22, 199–209.
Mahler, H. I. M., Kulik, J. A., Harrell, J., Correa, A., Gibbons, F. X., & Gerrard, M. (2005). Effects of UV photographs, photoaging information, and use of sunless tanning lotion on sun protection behaviors. Archives of Dermatology, 141, 373–380.
Muthen, B., Kaplan, D., & Hollis, M. (1987). On structural equation modeling with data that are not missing completely at random. Psychometrika, 52, 431–462.
Reno, R. R., Cialdini, R. B., & Kallgren, C. A. (1993). The transituational influence of social norms. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64, 104–112.
Rogers, R. W. (1983). A protection motivation theory of fear appeals and attitude change: A revised theory of protection motivation. In J. R. Cacioppo & R. E. Petty (Eds.), Social psychology: A sourcebook (pp. 153–176). New York: Guilford press.
Rosenstock, I. M. (1974). The health belief model and preventive health behavior. Health education monographs, 2, 354–386.
Shroff, H., & Thompson, J. K. (2006). The tripartite influence model of body image and eating disturbance: A replication with adolescent girls. Body Image, 3, 17–23.
Smolak, L., & Thompson, J. K. (2009). Body image, eating disorders and obesity in youth (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. In S. Leinhardt (Ed.), Sociological methodology (pp. 290–312). Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
Stice, E., Trost, A., & Chase, A. (2003). Healthy weight control and dissonance-based eating disorder prevention programs: Results from a controlled trial. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 33, 10–21.
Taylor, A. B., Mackinnon, D. P., Tein, J. (2009). Tests of the three-path mediated effect. Organizational Research Methods (in press).
Thompson, J. K., Heinberg, L., Altabe, M., & Tantleff-Dunn, S. (1999). Exacting beauty. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
US Department of Health and Human Services. (2002). Ultraviolet radiation-related exposures: Broad spectrum ultraviolet (UV) radiation, UVA, UVB, UVC, solar radiation, and exposure to sunlamps and sunbeds. In the Tenth Annual Report on Carcinogens. Retrieved August 27th, 2004, from http://ehis.niehs.nih.gov/roc/tenth/profiles/s183uvrr.pdf.
Weinstock, M. A. (1992). Assessment of sun sensitivity by questionnaire: Validity of items and formulation of a prediction rule. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 45, 547–552.
Wichstrom, L. (1994). Predictors of Norwegian adolescents’ sunbathing and use of sunscreen. Health Psychology, 13, 412–414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cafri, G., Thompson, J.K., Jacobsen, P.B. et al. Investigating the role of appearance-based factors in predicting sunbathing and tanning salon use. J Behav Med 32, 532–544 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-009-9224-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-009-9224-5